organic chemistry
advertisement

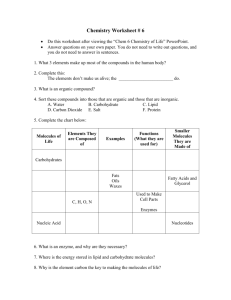
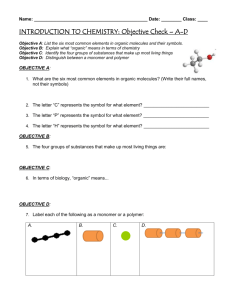
INDEPENDENT READING/CORNELL Marking your TextNOTES -Use COLOR and DRAWINGS (including arrows/circles) to HIGHLIGHT and MARK your TEXT and NOTES!! Marking your Text Marking your Text Marking your Text 6.4 BUILDING BLOCK of LIFE WHAT YOU’LL LEARN: -4 major groups of biological macromolecules -functions of each group of biological macromolecules ORGANIC CHEMISTRY MAIN IDEA: Organisms are made up of carbon-based molecules ORGANIC -study of organic compounds CHEMISTRY -the compounds that contain carbon = organic PROBLEM/Q: _PROBLEM/Q: _____________________________________________________ ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4 ORGANIC IDENTIFY # valence electrons in carbon atom.____ CHEMISTRY 4 DETERMINE: # covalent bonds carbon can form ____ CALCULATE: What % of the outer energy level is full? 50% __________________ EXPLAIN: 4/8 = 1/2 = 50% outer energy level holds up to 8 electrons—4 of 8 is 50% ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -Diversity of life due to many different carbon structures -in the form of: straight chain molecules branched molecules ring molecules MACROMOLECULES MACROMOLECULES -large molecules formed by… joining smaller organic molecules polymers -repeating units of nearly or identical monomers monomers -linked by series of covalent bonds BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES CARBOHYDRATES -general formula: CH2O monosaccharides -simple sugars disaccharides -2 ______________________ -monosaccharides linked together polysaccharides -carbohydrate molecules -longer chains of _____________________________ CALCULATE: If a monosaccharide has 4 carbon atoms, 8 how many hydrogen atoms does it have? ________ BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES LIPIDS -fats/oils/waxes saturated fats -single bonds between carbons -no more bonds can form unsaturated fats -at least 1 double bond between carbons -can form at least 1 other bond w/hydrogen steroids -cholesterol—starting pt for vitamin D -hormones— important for gender/reproductive functions IDENTIFY the key characteristics of lipids that enables them to keep unwanted substances from penetrating cell membranes. ________________ Non-polar -do not dissolve in water BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES PROTEIN -made of small compounds called amino acids STRUCTURES amino acids -made of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen and sometimes sulfur -20 different amino acids DRAW CONCLUSIONS: What protein function suggests most enzymes are proteins? -speed up chemical reactions BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES NUCLEIC ACIDS nucleotides -macromolecules store/transmit genetic info -small units make up nucleic acids -made up of 3 subunits: -nitrogen base -phosphate -ribose sugar DRAW CONCLUSIONS: What group of macromolecules do you think DNA belongs? -nucleic acids BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES carbohydrates nucleic acids lipids amino acids DNA CH2O -fatty acid tails nucleotides BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES CIRCLE each nucleotide grouping DATA ANALYSIS/REVIEW TRUE/FALSE 1-Carbon atoms can bond together in straight chains, TRUE branched chains or rings. 2-Large molecules containing carbon atoms are called FALSE-macromolecules micromolecules. 3-Polymers are molecules made from repeating units of identical organic compounds that are linked together by hydrogen bonds. FALSE- covalent TRUE 4-Carbon is a component of almost all biological substances. 5-Macromolecules can be organized into vitamins, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. FALSE- carbohydrates COOPERATIVE LEARNING LAB GROUP(3-5 students) -working TOGETHER as a cooperative group to COMPLETE TASK -EVERY TEAM MEMBER has a job and participates EQUALLY 1-READ THROUGH EACH TASK (silently or together) 2-DISCUSS (use POSITIVE communication) 3-ANSWER 4-MOVE ON (only when ALL team members understand) QUESTIONS ?’s -each other CLARIFICATION -Asking Mrs. Schlatter for clarification NOT answers. FYI -discussion within COLORED group ONLY 6.4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY EVALUATE: the number of molecules of each element in the carbohydrate described by the formula: (CH2O)6 6 carbon _____ hydrogen _____ 12 oxygen _____ 6 -ratio of C/H/O: _________________ 1:2:1 -type of carbohydrates -monosaccharide BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES LABEL the diagrams: saturated unsaturated BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES LABEL the diagrams: DATA ANALYSIS/REVIEW LABEL the diagrams: DATA ANALYSIS/REVIEW DATA ANALYSIS 1-IDENTIFY the INDEPENDENT VARIABLE diet 2-IDENTIFY the DEPENDENT VARIABLE cholesterol levels 3-DESCRIBE the effects soluble fiber appears to have on cholesterol levels in the blood. -lowers cholesterol levels -lowers male levels more than females 6.4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LAB SUPPLIES: -hot plate -test tube tongs -beakers 50mL 250mL 600mL -3 test tubes -2 plastic cups TEST INDICATORS -biuret solution--protein -benedicts solution--sugar -*iodine--starch -paper sack--lipids -*place iodine on petri dish outside of tray—will stain skin/clothes/plastic 6.4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LAB LAB: MURDER and a MEAL Pre-LAB TESTS: 1-LIPID: 1 drop of oil on paper sack paper towel 2-CARB/SUGAR: corn starch in benedict solution/heat test tube 3-CARB/STARCH: iodine on cracker plastic cup 4-PROTEIN: biuret solution on egg white small 50 mL beaker 6.4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LAB LAB: MURDER and a MEAL LAB TESTS: unknown stomach contents 1-LIPID: paper sack paper towel 2-CARB/SUGAR: benedict solution/heat test tube 3-CARB/STARCH: iodine plastic cup 4-PROTEIN: biuret solution small 50 mL beaker 6.4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LAB CLEAN UP: -turn off hot plates -dump all food in trash -wash all equipment/return to lab trays -use test tube brush to clean test tubes -leave iodine on petri dish outside of tray -lids on TEST INDICATORS/return to lab trays SUPPLIES: -hot plate -biuret solution--protein -test tube tongs -benedicts solution--sugar -beakers -*iodine--starch 50mL -paper sack--lipids 250mL 600mL -*place iodine on petri dish outside of -3 test tubes tray—will stain skin/clothes/plastic -2 plastic cups