MSAENV472B Implement and monitor environmentally
advertisement

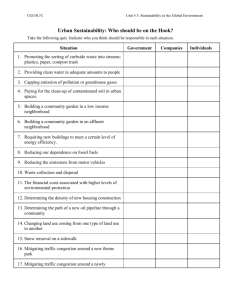
MSAENV472B Implement and Monitor Environmentally Sustainable Work Practices Neale Farmer – Coordinator Major Environmental Initiatives – Hunter TAFE neale.farmer1@tafe.nsw.edu.au Sessions: 1. 2. 3. Wednesday 7 May Wednesday 21 May Wednesday 4 June Overview of Today’s Session - Introductions - Sustainability? - Describe Unit – MSAENV472B - Sustainability at Hunter TAFE - Environmental Compliance - Next Session: Campus Footprint! MSAENV472B Implement and monitor environmentally sustainable work practices Unit descriptor This competency covers the outcomes required to effectively analyse the workplace in relation to environmentally sustainable work practices and to implement improvements and monitor their effectiveness. Application of the Unit Applies to those who have responsibility for a specific area of work or who lead a work group or team. It addresses the knowledge, processes and techniques necessary to implement and monitor environmentally sustainable work practices, including the development of processes and tools. It includes: Identifying areas for improvement Developing plans to make improvements Implementing and monitoring improvements in environmental performance. This competency applies to all sectors of the manufacturing industry and members of its value chain. Applied to all sections of workplace - Contextualised! Visit http://training.gov.au/Training/Details/MSAENV472B for a full description of this Unit and its requirements. Assessment? A typical workplace? The Animals Save the Planet - Energy Efficient Penguin – YouTube (49 secs) Change the way you think! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-nekqKEsbdU Links and Resources to get you started TAFE Student Sustainability Induction: http://ecostudent.tafensw.edu.au/ WWF Footprint Calculator: http://www.wwf.org.au/our_work/peopl e_and_the_environment/human_footpri nt/footprint_calculator/ Global Footprint Network Calculator: http://www.footprintnetwork.org/en/i ndex.php/gfn/page/calculators The Journey to Sustainability Sustainability explained through animation (YouTube: 2mins) The next 10 years will be very unlike the last 10 years (YouTube: 6 mins) Story of Stuff, Full Version; How Things Work, About Stuff (YouTube 21 mins) 1. Sustainability1 – a journey to balance PPP = people, planet, profit EEE = economy, ecology, equity A mechanistic/functionalist approach2 A holistic/interpretive approach2 1. The Brundtland definition of sustainability (1987 cited in Porter and Cordoba 2009) is used here, namely meeting the economic, social, and environmental needs of the present and the future generations 2. Porter and Cordoba, 2009 Copyright of Liz Sidiropoulos Sustainable Work Practices at Hunter TAFE • Google “Hunter TAFE Sustainability” and download the 2013 Hunter TAFE Strategic Plan for the Institute’s objectives, targets and programs related to environmental sustainability • Visit the NSW Department of Environment and Heritage Website for an overview of relevant environmental legislation Learning in Future Environments (LiFE) Framework Copy of Environmental Compliance Training for Kurri Campus Thursday 17 November 2011 neale.farmer1@tafe.nsw.edu.au Ext: 53916 Overview • • • • • • What? Why? Who? How? When? Where? Preventing pollution, Protecting Biodiversity, Conserving Resources. – Protection of the Environment Operations Act 1997 – Pesticides Act 1999 – National Parks and Wildlife Act 1974 – Native Vegetation Act 2003 – Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995 – Radiation Control Act 1990 – Environmental Planning and Assessment Act 1979 – Marine Parks Act 1997 – Environmentally Hazardous Chemicals Act 1985 – Contaminated Land Management Act 1997 – Water Management Act 2000 – Local Government Act 1993 – National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act 2007 – Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 ACTIVITY 1 Environmental Pollution: What is environmental pollution? Why are we talking about it? Who’s liable, Who’s responsible? Protection of the Environment Operations (POEO) Act 1997 • • • • • Air Noise Water Land Waste Enforcement (Appropriate Regulatory Authority) Environment Protection Authority State and local government organisations including contractors + All premises and activities listed on Schedule 1 POEO Act Local Council Everyone else: Including most smallmedium sized businesses and residential premises Offences • Tier 1 – willful or negligent • Tier 2 – strict liability • Tier 3 (on the spot fines issues for minor Tier 2 offences) Tier 1 Offences Maximum penalties Individual Corporation Negligent $500,000 +/or 4 years gaol $2 million Wilful $1million +/or 7 years gaol $5 million Tier 1 Offences • s115 – Disposal of waste to harm the environment • s116 – Leaks, spillages and other escapes • s117 – Emission of ozone depleting substances Willful Negligent Tier 1 Defence • The offence was due to causes over which the person had no control • The person took reasonable precautions and exercised due diligence to prevent the offence. Tier 2 Offences Maximum penalties: Individuals = $250,000 (plus $60,000 a day for continuing offences) Corporations = $1million (plus $120,000 per day for continuing offences) Water Land Air Waste Noise Water Pollution 120 Prohibition of pollution of waters (1) A person who pollutes any waters is guilty of an offence. (2) In this section: pollute waters includes cause or permit any waters to be polluted. Which is water pollution? Duty to notify Notify the appropriate regulatory authority of any pollution incidents causing or threatening material harm to the environment Duty to notify Material harm = 1) actual or potential harm that is not trivial OR 2) Actual or potential loss or property damage amounting to $10,000 Including on your own premises Duty to notify If in doubt call the Office of Environment and Heritage (EPA) 24 hour Pollution Line 131555 2011 Changes to NSW Pollution Legislation • Pollution incidents to be immediately reported, not notified ‘as soon as practicable’; • Establishing the Environmental Protection Authority as an independent, statutory authority headed by a Chief Environmental Regulator. • Double to $2 million the maximum penalty for failing to report an incident immediately; • Clarify the EPA’s powers to conduct mandatory environmental audits. Court decisions • the extent of the harm caused or likely to be caused to the environment • the practical measures that could have been taken to prevent, control, abate or mitigate that harm • the extent to which the person who committed the offence could reasonably have foreseen the harm caused or likely to be caused to the environment Court decisions • the extent to which the person who committed the offence had control over the causes that gave rise to the offence • whether, in committing the offence, the person was complying with orders from an employer or supervising employee. Demonstrate due diligence ACTIVITY 2: What is due diligence? How do WE demonstrate due diligence on this site? How can YOU show due diligence? Environmental improvement plan Site audits Waste disposal receipts Staff training records Due diligence Records of regular inspections and maintenance Environmental Management System Site risk assessment Pollution control equipment and structures – Protection of the Environment Operations Act 1997 – Pesticides Act 1999 – National Parks and Wildlife Act 1974 – Native Vegetation Act 2003 – Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995 – Radiation Control Act 1990 – Environmental Planning and Assessment Act 1979 – Marine Parks Act 1997 – Environmentally Hazardous Chemicals Act 1985 – Contaminated Land Management Act 1997 – Water Management Act 2000 – Local Government Act 1993 – National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act 2007 – Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 Further Information… • NSW Environmental Defenders Office: www.edo.org.au/edonsw • OEH: http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/ E: neale.farmer1@tafe.nsw.edu.au Review of Today’s Session Introductions Sustainability defined Describe Unit – MSAENV472B Sustainability at Hunter TAFE Environmental Compliance at Hunter TAFE Next Session: Campus Footprint! Next Session (21 May) “ knowledge, processes and techniques necessary to implement and monitor environmentally sustainable work practices, including the development of processes and tools” Continuous Improvement Cycle: - Identify and research area/s for improvement, consult, measure baseline. - Set goals, targets, objectives - Implement the improvement - Monitor implementation and results - Revise or adjust plan - etc........... Prepare for Session 2 (21 May) 1. TAFE Sustainability Induction 2. Attempt an online footprint calculator 3. Look at links on legislation (NSW Office of Environment and Heritage and NSW Environmental Defenders Office 4. Google – “Sustainability” and “Sustainable Laboratories” neale.farmer1@tafe.nsw.edu.au