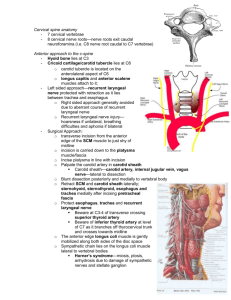
Bones of the Lower Limb
advertisement

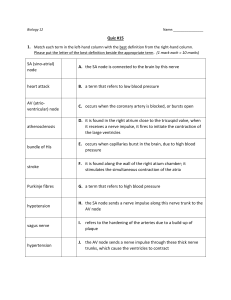
1) Which of the following muscles is NOT a hip flexor? a) Iliacus b) Psoas major c) Gracilis d) Rectus femoris e) Sartorius 2) Which of the following muscles is the longest in the body? a) Iliacus b) Psoas major c) Gracilis d) Rectus femoris e) Sartorius 3) Which of the following adductors of the thigh is innervated by the obturator nerve aswell as the sciatic nerve? a) Adductor longus b) Adductor magnus c) Adductor brevis d) Pectineus e) Gracilis 1 4) Which of the following muscles does NOT attach to the pubic ramus near the pubictubercle? a) Gracilis b) Pectineus c) Adductor brevis/longus d) Adductor magnus e) Sartorius 5) Which of the following is NOT enclosed in the femoral sheath within the subinguinalhiatus? a) Femoral vein b) Femoral artery c) Femoral nerve d) Femoral lymph nodes 6) Which of the following makes up the roof of the femoral triangle? a) Inguinal ligament b) Sartorius c) Adductor longus 2 d) Tensor fascia lata e) Pectineus f) Iliopsoas 7) Which of the following does NOT leave the femoral triangle through the saphenous hiatus? a) Lacuna lymphatica b) Great saphenous vein c) External pudendal artery d) Superficial epigastric artery e) Superficial circumflex iliac artery 8) Femoral hernias are more commonly seen in women. a) True b) False, inguinal canal hernias are more commonly seen 9) What muscle makes up the lateral border of the femoral triangle? a) Inguinal ligament b) Sartorius c) Adductor longus 3 d) Tensor fascia lata e) Pectineus f) Iliopsoas 10) Which of the following is NOT a branch of the external iliac artery? a) Obturator artery b) Popliteal artery c) External pudendal artery d) Deep femoral artery e) Superficial circumflex iliac artery 11) Which of the following arteries forms an anastamotic ring around the femoral neck? a) Artery of ligamentum capitis femoris b) Descending geniculate artery c) Ascending branch of medial circumflex femoral artery d) Ascending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery e) Perforating femoral arteries (I, II, III) 4 12) Which of the following arteries is NOT matched correctly with its origin from thelumbar plexus? a) Iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerve, L1 b) Genitofemoral nerve, L1-2 c) Lateral curaneous femoral nerve, L1-2 d) Femoral nerve, L2-4 e) Obturator nerve, L2-4 13) What nerve innervates the gluteus maximus muscle? a) Superior gluteal nerve b) Inferior gluteal nerve c) Obturator nerve d) Femoral nerve e) Genitofemoral nerve 14) What nerve innervates the gluteus minimus muscle? a) Superior gluteal nerve b) Inferior gluteal nerve c) Obturator nerve 5 d) Femoral nerve e) Genitofemoral nerve 15) Which of the following potentially absent muscles can be found on the posterior abdominal wall? a) Palmaris longus b) Plantaris c) Peroneus tertius d) Pyrimidalis e) Psoas minor 16) Which of the following muscles does NOT attach (insert) onto the greater trochanter? a) Piriformis b) Gluteus maximus c) Gluteus medius d) Gluteus minimus 17) Which muscle (muscle tendon) can be found between the superior and inferior gemellus muscles? a) Quadratus femoris 6 b) Obturator externus c) Obturator internus d) Piriformis e) Gluteus medius 18) Which of the following muscles does NOT attach (originate) onto the ichialtuberosity? a) Gracilis b) Biceps femoris c) Semitendinosus d) Semimembranosus 19) Pes anserinus (“goose’s foot”) is a term for the facial nerve as well as the leg.Regarding the leg, which of the following muscles does NOT attach to the pes anserinus(superficialis)? a) Sartorius b) Gracilis c) Semitendinosus d) Semimembranosus 20) Which of the following describes the root levels of the sciatic nerve? a) L4-S1 b) L4-S3 c) L5-S2 d) S1-S3 7 e) S2-S4 21) Which of the following is most likely to be compressed by the piriformis muscle(piriformis syndrome)? a) Posterior cutaneous femoral nerve b) Superior gluteal nerve c) Inferior gluteal nerve d) Pudendal nerve e) Sciatic nerve Bones of the Lower Limb 1) Which of the following best describes the femoral angle of inclination seen in young children? a) 190 degrees b) 145 degrees c) 126 degrees d) 120 degrees e) 90 degrees 2) Which of the following hip bone (innominate) landmarks is used to determine at what level a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) should be performed? a) Acetabulum 8 b) Greater sciatic notch c) Pubic symphysis d) Posterior superior iliac spine e) Iliac crest 3) Which of the following bones has a surface called sustent aculum tali? a) Talus b) Cuboid c) Calcaneus d) Navicular e) Cuneiform Leg & Foot 1) Which of the following is the strongest pronator of the foot? a) Tibialis anterior b) Extensor digitorum longus c) Extensor hallucis longus d) Peroneus longus e) Peroneus brevis 2) Triceps surae is the strongest plantar flexor of the foot and is comprised of thegastrocnemius and the: 9 a) Plantaris b) Tibialis c) Soleus d) Peroneus e) Popliteus 3) Which of the following muscles originates near the knee, has a small belly, and has along tendon, which may be mistaken for a nerve? a) Plantaris b) Tibialis c) Soleus d) Peroneus e) Popliteus 4) Which of the following fascial compartments is most likely to have minor compartment syndrome seen in athletes or during a workout? a) Posterior compartment of the arm b) Anterior compartment of the arm c) Posterior compartment of the leg 10 d) Lateral compartment of the leg e) Anterior compartment of the leg 5) Which of the following muscles is NOT innervated by the tibial nerve a) Triceps surae b) Tibialis posterior c) Popliteus d) Extensor hallucis brevis e) Flexor hallucis longus 6) Which of the following is NOT a border of the popliteal fossa? a) Biceps femoris b) Semimembranosus c) Semitendinosus d) Gastrocnemius e) Soleus 7) Which geniculate artery supplies most of the cruciate ligaments? a) Medial superior geniculate artery b) Lateral superior geniculate artery c) Median geniculate artery d) Medial inferior geniculate artery 11 e) Lateral inferior geniculate artery 8) What landmark can be used to find the dorsalis pedis artery for palpation? a) Medial to extensor hallucis longus tendon b) Lateral to extensor hallucis longus tendon c) Posterior to medial malleolus d) Posterior to lateral malleolus e) Superior to medial malleolus 9) Which of the following describes the neurovascular structures of the popliteal fossafrom lateral to medial? a) Vein, artery, nerve b) Vein, nerve, artery c) Nerve, artery, vein d) Nerve, vein, artery e) Artery, nerve, vein 10) What nerve accounts for sensation between the first two toes? a) Sural b) Deep peroneal c) Medial plantar d) Superficial peroneal e) Tibial 11) Which of the following is innervated by the lateral plantar nerve? 12 a) Abductor hallucis b) Flexor hallucis longus c) Quadratus planae d) Flexor digitorum brevis e) Lumbricles 12) Which of the following form the plantar arch? a) Lateral plantar artery and deep medial plantar artery b) Lateral plantar artery and superficial medial plantar artery c) Anterior tibial artery and posterior tibial artery d) Dorsalis pedis artery and peroneal artery e) Medial malleolar artery and lateral plantar artery Articulations (Lower Limb) 1) Which of the following joints of the lower limb has a zona orbicularis? a) Sacroiliac b) Hip joint c) Knee joint d) Ankle joint e) Tarsometatarsal joints 2) Which of the following hip ligaments is the strongest ligament in the body? 13 a) Iliofemoral b) Ishiofemoral c) Pubofemoral d) Liagementum teres capitis femoris 3) Which of the following is attached to the medial meniscus? a) Tibial collateral ligament b) Fibular collateral ligament c) Anterior cruciate ligament d) Posterior cruciate ligament e) Ligamentum patellae 4) Which of the following attaches from the lateral surface of the medial femoral condyleto the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia? a) Tibial collateral ligament b) Fibular collateral ligament c) Anterior cruciate ligament d) Posterior cruciate ligament e) Medial meniscus 14 5) Excessive anterior displacement of the tibia on the femur indicates damage to which of the following? a) Tibial collateral ligament b) Fibular collateral ligament c) Anterior cruciate ligament d) Posterior cruciate ligament e) Medial meniscus 6) When the knee is flexed, the ____ are relaxed and the ____ are taut. a) Cruciate ligaments; Collateral ligaments b) Collateral ligaments; Cruciate ligaments c) Cruciate ligaments; Menisci d) Menisci; Collateral ligaments e) Collateral ligaments; Menisci 7) When one’s legs are bent out laterally at the knee (bowlegged) it is described as: a) Genu valgum b) Genu rectum 15 c) Genu varum 8) Which of the following is NOT a component of the deltoid ligament? a) Anterior tibiotalar ligament b) Posterior tibiotalar ligament c) Tibionavicular ligament d) Tibiocalcaneal ligament e) Calcaneofibular ligament 9) Damage at the Lisfranc joint line is seen in automobile accidents, military personnel,runners, and contact sports. What joint line is this? a) Calcaneocuboid joint b) Ligamentum bifurcatum c) Intermetatarsal joint d) Tarsometatarsal joint e) Subtalar joint 10) Laxity in which of the following ligaments would most lead to pes planus (flatfoot)? a) Long plantar calcaneocuboid b) Short plantar calcaneocuboid c) Plantar calcaneonavicular 16 d) Calcaneofibular e) Deltoid Clinical Correlations (Lower Limb) 1) Which of the following scenarios would most likely cause a posterior femoral headdislocation? a) Falling 5 metes and landing on your feet b) Falling 5 meters and landing on your backside c) A head-on car accident with your knees hitting the dashboard d) Being tackled from the side by an American football player e) A forceful kick to the back of the thigh during a soccer game 2) Which of the following ligaments is NOT usually associated with an “unhappy triad”or “terrible triad” knee injury, seen in American football when a lateral force is placed onthe knee while the foot is fixed and externally rotated? a) Anterior cruciate ligament b) Tibial collateral ligament c) Fibular collateral ligament d) Medial meniscus 17 3) A patient presents after being struck with a beer bottle to the lateral portion of theknee. Examination reveals foot drop. What nerve is likely damaged? a) Sciatic nerve b) Tibial nerve c) Femoral nerve d) Obturator nerve e) Peroneal nerve 4) Pott fracture is an archaic term used to describe an injury where an eversion force is applied while the foot is abducted and externally rotated, such as during an American football tackles. Which of the following is/are fractured in this type of injury? a) Tibia b) Fibular c) Medial malleolus d) A & C e) B & C 5) What cutaneous innervation level covers the anterior knee? 18 a) L1 b) L2 c) L3 d) L4 e) L5 6) What cutaneous innervation level covers the back of the thigh and leg? a) S1 b) S2 c) S3 d) S4 e) S5 7) What cutaneous innervation level covers the big toe? a) L1 b) L2 c) L3 d) L4 e) L5 19 8) The superficial vein that is found on the anterior aspect of the medial malleolus is the: a) Small saphenous b) Popliteal c) Great saphenous d) Anterior tibial e) Posterior tibial 9) A patient presents with pain down the lateral side of the left calf, decreased sensationon the skin between the 1st and 2nd toes, and weakness on heel walking. The most likelycord level compromised is: a) L4 b) L5 c) S1 d) S2 e) S3 10) A patient presents with decreased patellar reflex and weakness on hip flexion againstresistance. The most likely compromised nerve is the: a) Obturator 20 b) Femoral c) Tibial d) Sural e) Common fibular 11) During the stance phase of gait, which of the following groups of muscles would beleast active? a) Dorsi flexors b) Flantar flexors c) Hip flexors d) Evertors e) Hip extensors 12) Of the six actions that occur at the hip joint, which muscle group would be leastactive in providing stability to the lower extremity during the stance phase of gait? a) Abductors b) Adductors c) Flexorsd) Extensors 21 e) Medial rotators 13) Which muscle of the medial compartment of the thigh also crosses the knee joint? a) Adductor magnus b) Sartorius c) Gracilis d) Semitendinosus e) Adductor longus 14) Which muscle of the anterior compartment also flexes the hip a) Articularis genu b) Vastus lateralis c) Tensor fascia lata d) Sartorius e) Adductor longus 15) Which muscle functions to unlock (flex) the knee from full extension? a) Vastus medialis 22 b) Vastus lateralis c) Gastrocnemius d) Popliteus e) Semitendinosus 16) Which tendon helps to give support to both the lateral longitudinal and transversearches of the foot? a) Tibialis anterior b) Tibialis posterior c) Flexor hallucis longus d) Flexor digitorum longus e) Fibularis longus 17) The ability to sit down gracefully on the toilet is due in part to paradoxical relaxation of the: a) Gluteus maximus b) Piriformis c) Tibialis anterior d) Biceps femoris 23 e) Iliopsoas 18) The part of the foot and ankle where inversion occurs is the: a) Forefoot b) Midfoot c) Hindfoot d) Medial malleolus e) Lateral malleolus 19) Which muscle helps eversion of the foot but does NOT pass around the lateral malleolus? a) Tibialis anterior b) Extensor hallucis longus c) Fibularis brevis d) Fibularis tertius e) Soleus 20) Stroking the skin on the lateral side of the foot is activating sensory fibers from whichcord level? a) L4 b) L5 24 c) S1 d) S2 e) S3 21) The major blood supply of the deep structures of the foot is the: a) Dorsalis pedis artery b) Medial plantar artery c) Anterior tibial artery d) Lateral plantar artery e) Popliteal artery 22) The hip joint is most easily dislocated if the femur is fully: a) Flexed b) Extended c) Adducted d) Abducted e) Medially rotated 23) A carpenter presents after falling three meters and landing on the balls of his feet. He now complains of a sharp pain in the plantar aspect of his foot, especially on toe-off. He probably has contusion of which structure? a) Tendon of the abductor hallucis longus b) Sesamoid bones in the flexor hallucis brevis c) Common plantar digital nerves from the lateral plantar nerve 25 d) Fibularis longus tendon e) Adductor hallucis tendon 24) Spasm in which muscle is most likely to mimic sciatic pain? a) Quadratus femoris b) Piriformis c) Gastrocnemius d) Gluteus medius e) Iliopsoas Radiology (Lower Limb) 1) What nerve is likely damaged in this x-ray? a) Sciatic nerve b) Tibial nerve c) Femoral nerve d) Obturator nerve e) Common peroneal nerve 2) Which of the following imaging methods would be used for infection or hip pain of unknown etiology? a) X-ray b) CT c) MRI d) SPECT 26 e) Bone scan 3) When looking an AP x-ray of the foot, there appear to be two white structures on the first toe. Which is the most likely? a) Bursitis b) Osteophytes c) Sesamoid bones d) Gouty calcification e) Hammer toe f) Hallux valgus 27