WHATSAPP SOUND CLIPS PROJECT 16.MAY.2014 FRIDAY 1
advertisement

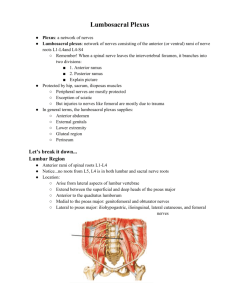
WHATSAPP SOUND CLIPS PROJECT 16.MAY.2014 FRIDAY 1. Lumbar plexus, upper component of lumbosacral plexus @ the posterior abdominal wall anterior to the lumbar transverse processes and around the psoas major muscle 2. Lumbar plexus first 4 lumbar spinal nerves anterior rami + a contribution up (T12-subcostal)+ a contribution down (L5) 3. L4 + L5 anterior rami= Lumbosacral trunk 4. Femoral nerve exists from the lateral side of psoas major, innervates iliacus , then passes under inguinal ligament and innervates anterior thigh muscles 5. Obutator nerve exists from the medial side of psoas major,passes through the obturator canal and innervates muscles in the medial thigh 6. Two main nerves of the lumbar plexus femoral and obturator nerves are formed by the L2-L4 anterior rami 17.MAY.2014 SATURDAY 7. Lumbosacral trunk (L4, L5) is a branch of the lumbar plexus , but passing over the ala of sacrum goes down in the pelvis and contributes to formation of the sacral plexus 8. Both ilio “iliohypogastric” ve “ilioinguinal” from L1, over/anterior to quadratus lumborum , superior to iliac crest, innervated abdominal muscles and also skin over the inguinal ve pubic regions 9. Genitofemoral L1-2 pierces psoas major, lateral to common ve external iliac arteries into femoral and genital branches 10. Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (L2, L3), over iliacus, medial to ASIS passes under the inguinal ligament, skin over the anterolateral thigh 11. L1 upper branch (ilios), lower branch (genitofemoral) L2,3 and 4 ventral and dorsal branches: from here femoral and obturator nerves 12. Femoral nerve iliacus, pectineus and flexors of the hip and extensors of the knee: anterior thigh nerve of quadriceps femoris and sartorius 13. Femoral nerve skin innervastion: anterior and lateral thigh, medial leg and foot 14. Femoral nerve enters the inguinal ligament midpoint @ ASIS and pubic tubercle, fingerbreadth lateral to the femoral pulse (artery)) 15. Saphaneous nerve the biggest cutaneous branch of femoral nerve. Enters the adductor canal. Saphaneous skin nerve of leg and foot medial side 16. Obturator nerve external oblique, thigh adductor muscles, pectineus (some), adductor longus ,magnus, brevis and gracilis and skin over superior medial thigh 17. Sacral plexus S1-S4 anterior rami+ Lumbosacral trunk (L4 and 5). Lumbosacral trunk is shared by the two plexuses 18. Sacral plexus @ pelvis posterolateral wall related to anterior aspect of the piriformis, in the lesser pelvis, main two nerves sciatic and pudendal nerves external to parietal pelvic fascia 19. Most branches of the sacral plexus leave the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. Some not only through here but also through the lesser sciatic foramen. 20. Sacral spinal nerves of the plexus pass out of the anterior sacral foramina and course laterally and inferiorly on the pelvic wall. 21. L4 ant. ramus some and full L5 ant. rami=lumbosacral goes vertically from abdomenden to pelvic cavity passing just anterior to sacroiliac joint 22. Each ramus has ventral and dorsal divisons. Peripheric nerves are formed by the union of ventral or dorsal divisions. S4 ant. ramus has only ventral divison 23. Sacral plexus branches sciatic, gluteal nerves, pudendal nerve: related to perineum. For most greater sciatic foramen is the gateway into pelvis from the gluteal region. Some stay in pelvis and innervate muscles there 24. Two nerves pass through the greater sciatic foramen+ pass also through the lesser sciatic forman medially and enter perineum and lateral pelvic wall: the nerve to obturator internus and pudendal nerve ASIS: Anterior superior iliac spine VAN: Under the inguinal ligament in the femoral triangle from medial to lateral the order: Femoral vein, artery, nerve 1 25. Sup. ve inf. gluetal nerves innervate gluteal region, pudendal nerve perineum, sciatic nerve thigh 26. Sciatic nerve largest peripheral nerve.SCIA=L4-S3 combine anterior to piriformis and its lower border. Passes under piriformis and through the greater sciatic foramenden into the gluteal region; the most lateral structure in this foramen 27. Sciatic nerve passes through the plane between superficial and deep gluteal muscles and innervates posterior thigh, entire leg and foot muscles. Besides the joints of all joints of the lower limb 28. Sciatic nerve passes to the thigh under gluteus maximus midway between ischial tuberosity and greater trochanter. Innervates nothing @ gluteal region .Sensory information: foot and lateral leg 29. Sciatic nerve divides into two branches in the thgih: common fibular (common peroneal) and tibial nerves .L4-S2 dorsal divisions make the common fibular nerve , whereas L4-S3 ventral divisions carried by the tibial part 30. Tibial nerve & common fibular nerve loosely bound together in the same connective tissue sheath. They usually separate in the distal thigh; but sometimes as they leave the pelvis 31. Pudendal nerve S2-S4 main nerve of perineum, chief sensory nerve of external genital region. Most medial nerve @ greater sciatic foramen 32. Other branches of sacral plexus into gluteal region, pelvic wall & pelvic floor: superior and inferior gluteal nerves, nerve to obturator internus and superior gemellus 32. Also belonging to sacral plexus: nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus, nerve to piriformis, nerves to levator ani 33. Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh: branch of sacral plexus getting skin sensory information from the inferior gluteal region, posterior thigh, and upper leg. The nerve that gets the largest area of sensory information in the body 34. Perforating cutaneous nerve of thigh: other branch of sacral plexus. Its feaure: not through sciatic foramina but passes through (by piercing),sacrotuberous ligament. Nerve of the skin over the medial aspect of gluteus maximus 35. And pelvic splanchnic nerves exit from sacral plexus’s S2-S4 spinal nerves. Carry parasympathetic fibers. Other than in the brain, the parasympathetic system @ this level 36. The small coccygeal plexus: a little contribution from S4, mainly S5 & Co (coccyeal nerve) anterior rami. Innervates anal triangle @ lower part of perineum 37. Gluteal bölge gövde ve serbest alt eksremite arası geçiş yeri. Pelvis kemiği posterolateralinde ve femur’un üstteki proximal ucunda yer alır (20 sözcük) 38. Gluteal bölge kasları genellikle femur’a pelvik kemiğe göre abduksiyon, ekstensiyon ve lateral rotasyon yaptırırlar (14 sözcük) 39. Gluteal bölge ön ve içte greater sciatic foramenle pelvik boşlukla, lesser sciatic formanle de perineumla iletişim halinde (17 sözcük) 40. Gluteal bölgede: iki yer belirgin arka kısım buttock, ve lateralde kalça eklemi ve greater trochanter üzerinde yer alan daha az belirgin hip bölgesi (regio coxae) (25 sözcük) 41. Gluteal region is bounded superiorly by the iliac crest, medially by the intergluteal cleft, and inferiorly by the gluteal fold (L. sulcus glutealis), laterally by a line joining anterior superior iliac spine and greater troachanter. 42. Gluteal region:superficial fascia full of fat, deep fascia continuous below with the deep fascia, or fascia lata of the thigh 43. Iliotibial tract: fascia lata thickening on the lateral side of thigh. Iliotibial tract between tubercle of iliac crest and lateral condyle of tibia. Greater part of gluteus maximus attaches on iliotibial tract 44. Iliotibial tract stabilizes the knee both in extension and in partial flexion, used constantly during walking and running. 45. Superficial gluteal group of larger muscles: 3. Starting with gluteus (maximus, medius and minimus). Mainly abduct and extend the hip. Hip and thigh work together just like shoulder and arm 46. Deep gluteal muscles: Lateral rotation of thigh at the hip joint. Piriformis, obturator internus, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, and quadratus femoris (obturator externus @ medial thigh) 2 47. Another gluteal muscle: tensor fasciae latae stabilizes the knee in extension by acting on iliotibial tract 48. Many of the important nerves in the gluteal region are in the plane between the superficial and deep groups of muscles 49. Gluteus maximus: largest muscle in the body, superficial in the gluteal region, poweful extensor of flexed thigh at the hip joint. via iliotibial tract, stabilizes the knee and hip joints. 50. Gluteus maximus laterally rotates and abducts thigh; steadies thigh and assists in rising from sitting position Nerve: Inferior gluteal nerve 51. Gluteus medius & minimus: abduct and medially rotate thigh, keep pelvis level when ipsilateral limb is weight-bearing and advance opposite (unsupported) side during its swing phase. Nerve: Superior gluteal nerve. Also nerve of tensor fascia lataee. 52. Piriformis: most superior of deep gluteal muscles. Lateral rotation and abduction of thigh, L5-S2 nerve to piriformis. A landmark muscle 53. Nerve to quadratus femoris: Unlike others lies anterior to the plane of deep gluteal muscles. Nerve of Quadratus femoris and inf. gemellus muscle up 54. Nerve to obturator internus: Nerve of obturator internus of course and of superior gemellus up. Passes through lesser sciatic foramen. 55. Superior and inferior gluteal arteries branches of internal iliac artery. The gluteal veins are tributaries of the internal iliac veins that drain blood from the gluteal region 19.MAY.2014 MONDAY 56. Femoral region=thigh; region of free lower limb between gluteal, abdominal, and perineal regions proximally and the knee region distally. 57. Femoral region: anteriorly, separated from the abdominal wall by the inguinal ligament; posteriorly, from the gluteal region by gluteal fold superficially, by inferior margins of the gluteus maximus and quadratus femoris on deeper planes. 58. Posteriorly thigh continous with gluteal region; major structure passing through= sciatic nerve. Medially between thigh and pelvic cavity through the obturator canal: structures passing through this canal: obturator nerve and associated vessels 59. Anteriorly thigh communicates with abdominal cavity through aperture between inguinal ligament and pelvic bone. Major structures passing through here: iliopsoas, pectineus, VAN (femoral vein, artery, nerve), lymphatic vessels 60. Vessels and nerves passing between the thigh and leg pass through the popliteal fossa posterior to the knee joint. 61. Deep fascia of thigh (fascia lata) attached to the pelvis and the inguinal ligament. Saphenous hiatus(opening) in the fascia lata just below the inguinal ligament. Great saphenous vein through hiatus saphenus to drain into femoral vein. 62. Anterior compartment of thigh muscles: mainly extend the leg at the knee joint (Femoral nerve);Medial compartment: adduct the thigh at the hip joint (obturator nerve); posterior: extend the thigh at the hip joint and flex the leg at the knee joint (sciatic nerve) FOS 63. Femoral triangle: Major artery, vein and lymphatic channels enter thigh anterior to pelvic bone here inferior to inguinal ligament. Inguinal ligament between ASIS & pubic tubercle 64. Inguinal ligament formed by the most inferior part of the aponeourosis of the external oblique muscle 65. Anterior thigh muscles: sartorius and the four large quadriceps femoris muscles (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius) + iliopsoas: chief flexor of thigh 66. Sartorius: Longest muscle of the body. Act both on hip and knee joints. Flexes hip and participates in flexion of knee. weakly abducts thigh and laterally rotates it. Cross-legged sitting position. 67. Quadriceps femoris: great extensor of the leg. rectus femoris assists flexion of the thigh. vastus muscles stabilize the position of the patella during knee joint movement. 68. Medial compartment of thigh contains six muscles (gracilis, pectineus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus), obturator externus. All innervated by obturator nerve :except pectineus by femoral nerve (partly obturator), hamstring part of adductor magnus by sciatic nerve, 3 69. Adductor longus/magnus adduction of the thigh, its medial rotation.Pectineus addition to these two fxns; flexion of the thigh, adductor brevis adduction of the thigh 70. Gracilis an exception: only adductor/medial thigh muscle crossing knee: Adducts thigh; flexes leg; helps rotate leg medially 20.MAY.2014 TUESDAY 71. Hamstring muscles: All posterior thigh muscles except short head of biceps femoris. Biceps femoris long head, semitendinosus, semimembranosus: Tibial nerve, origin: ischial tuberosity, extensors of hip, flexors of knee/leg 72.Gracilis, sartorius, semitendinosus tendons attach on medial surface of superior tibia and form pes anserinus. GS TS . Stabilizes medial part of knee, iliotibial band lateral part of knee. 73. External iliac artery after passing under inguinal ligament becomes femoral artery. Branches: Superficial circumflex iliac artery, superficial epigastric artery, superficial & deep external pudendal arter, a. profunda femoris, descending genicular artery 74. Superficial veins of the thigh and leg: dorsal venous arch on dorsum of the foot: medially originating from here great saphenous vein:drains into femoral vein, originating from lateral side of the arch: small saphaneous vein drains into popliteal vein 75. Thigh sensory innervation: lateral sides of the thigh and the knee (lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh), anterior: intermediate ;medial medial cutaneous nerve of thigh; these two of the femoral nerve; posterior (post. cutaneous nerve of thigh 76. Femoral triangle: superiorly inguinal ligament, medially adductor longus medial margin, laterally sartorius. @ the triangle: femoral vein, artery, nerve, femoral sheath ve deep inguinal lymph nodes 77. Femoral sheath encloses femoral artery and vein, also femoral canal most medially. Medial to the canal lacunar ligament, superiorly inguinal ligament, posteriorly pelvic bone. Here is where the femoral hernia ocur. Weak 78. Adductor canal: Hunter canal: @ mid 1/3 of thigh, under sartorius. Through the canal saphaneous nerve, nerve to vastus medialis, obturator nerve terminal branches, femoral artery and vein , deep lymph vessels pass 79. Adductor canal bordered anteriorly and medially vastus medialis, posteriorly adductor longus/magnus and anterior wall sartorius. Finishes as adductor hiatus formed by tendons of adductor magnus 80. Popliteal fossa: biceps femoris superolateral border, semimembranosus superomedial border, inferomedial and inferolateral borders gastrocnemius medial and lateral heads. Femoral artery leaves the adductor canal and becomes popliteal artery 81. In the Popliteal fossa: small saphaneous vein, popliteal artery/vein, tibial/common fibular nerves, post. cutaneous nerve of thigh, popliteal lymph nodes and vessels 82. Sciatic nerve over the popliteal fossa (1/3 lower thigh) divides into tibial and common fibular nerves. Tibial nerve goes vertically down in the popliteal fossa and exits from margin of plantaris and runs in the posterior leg compartment 83. Common fibular nerve by the medial border of biceps femoris tendon, @ lateral part of popliteal fossa, swings around the fibular neck and enters the lateral leg compartment 84. Popliteal artery branches: 4 arteries; superior and inferior (med./lat.) genicular arteries. Lateral to midline of the leg divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. ======================================================================================= 21.MAY.2014 WEDNESDAY 91. 92. 4 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 112. 113. 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 5