Aryan Civilization
advertisement

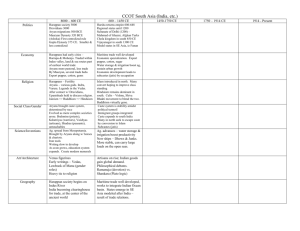
Harappan Writing Undecipherable to date. Decline of Harappans • Harappans used up their natural resources • Cut down too many trees • Indus River Valley was invaded Aryan Migration pastoral depended on their cattle. warriors horse-drawn chariots. The Aryans • Semi nomadic group of warriors –Used chariots –Immigrated into India over a period of hundreds of years –Each tribe headed by chieftain and priest –Cow was the standard of trade • The Vedas (“Wisdom”) were collections of prayers and hymns of the Indo-European Aryans who migrated into India around 1500 B.C. The Vedas – Reflect the knowledge that priests needed to carry out their functions Fanciful depiction of the IndoAryans entering India The Vedas 1200 BCE-600 BCE. written in SANSKRIT. Hindu core of beliefs: Rig Veda oldest work. hymns and poems. religious prayers. magical spells. lists of the gods and goddesses. Sanskrit writing • The Aryans developed a social structure with sharp distinctions between individuals and groups according to the occupations and roles in society – These distinctions became the basis of the caste system – Brahmins (priests) were at the top of the caste system • The term caste comes from the Aryan Social Order Portuguese word casta meaning a social class of hereditary and usually unchangeable status –Coined by Portuguese merchants and mariners who visited India during the 16th Century Varna (Social Hierarchy) Brahmins Kshatriyas Vaishyas Shudras Pariahs [Harijan] Untouchables • After about 1000 B.C., Aryans increasingly recognized four main castes. Varnas –Brahmins (priests) –Kshatriyas (warriors and aristocrats) –Vaishyas (cultivators, artisans, and merchants) –Shudras (landless peasants and serfs) • Some centuries later, category of untouchables was added Untouchables • The untouchables performed dirty or unpleasant tasks such as butchering animals or handling dead bodies Members of the untouchable class • Such work made them become so dispose of corpses after the 2004 tsunamicould polluted that their very touch defile individuals of higher status Social Order • Individuals came to identify themselves more closely with their jati than with their cities or states • The caste system served as the principal foundation of social stability in India, doing what states and empires did to maintain public order elsewhere Geographic Expansion • At first the caste system was confined to northern India where the Aryans had first entered • As commercial relationships pushed south, the caste system took hold there as well • By the 11th Century the caste system was the principal basis of social organization in southern India Caste in India Today • The preamble of India's constitution forbids negative public discrimination on the basis of caste. • In reality, caste ranking and castebased interaction continue –More prominent in the countryside than in urban settings and more in the realms of kinship and marriage than in less personal interactions The Vedic Age The foundations for Hinduism were established! Mauryan Civilization • Had huge army and secret police • Government owned all of the land • Peasants had to pay taxes Mauryan Civilization • Commerce and industry flourished • Artisans manufactured jewelry, perfumes, fine fabrics, leather work, pottery, and clothing. • Swords and arrowhead were made • Traded increased Chandragupta Maurya • As he grew older, he became interested in a religion called Jainism • In Jainism, the true being was the jiva or eternal soul that lived inside the physical body • They believed that every living thing has a soul and that killing any living thing is the greatest evil The Caste System WHO IS… Brahmins Kshatriyas The mouth? The arms? The legs? The feet? What is a JATI? Vaishyas Shudras