Fact Sheet on Alcohol
advertisement

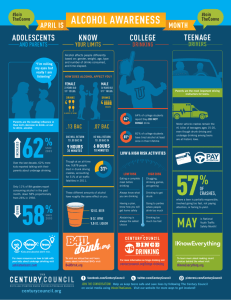
Fact Sheet on Alcohol By: Susan Eck April 1, 2011 What is alcohol? Alcohol is a beverage that contains ethanol. It is a colorless volatile flammable liquid, C2H5OH, synthesized or obtained by fermentation of sugars and starches and widely used either pure or denatured, as a solvent and in drugs, cleaning solutions, explosives, and intoxicating beverages. Also called ethanol, ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol. (Yahoo education). Alcohol can also be made from corn, barley, grain, rye or a beverage containing ethyl. There are three classes of alcohol, beer, wines, and spirits. Alcohol is a psychoactive drug that has a depressant effect. The amount of alcohol in a beverage is stated as the percentage of alcohol by volume (ABV) or as proof. Alcohol is created from grains, fruits or vegetables that are fermented. The consumption and social impact of alcohol consumption in Wisconsin: Wisconsin has led every state in its percentage of drinkers since 1995 Wisconsin has led the nation in binge drinking every year since 1995 Wisconsin is the only state in the country that treats first-offense drunken driving as a traffic ticket. More than one-third of the people convicted of drunken driving in Wisconsin last year were repeat offenders. In 2007 alone, Wisconsin’s drunken driving excess claimed more than 70 lives above the norm What is the “Standard measure of alcohol”? The difference between potency measures based upon “percent of alcohol by volume” and measures based upon “percent of alcohol by weight”. Blood alcohol content (BAC), the medical term used for measurement of alcohol concentration in blood. It can also be denoted as a percentage by mass per volume our by mass or a combination or both. Example, blood alcohol content (BAC), of 0.10% means 1 gram of alcohol per 100 grams of blood. Or 0.1 gram of alcohol per 100 milliliters of blood. What are the physiological effects from the abuse of alcohol? Alcohol affects the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) which control all body functions. The effects determine on how much alcohol is in the blood (blood alcohol concentration - BAC). When a person drinks alcohol, about 20 percent is absorbed in the stomach and 80 percent is absorbed in the small intestine. Once the 1. Alcohol is absorbed into the tissues it affects your mind and body. Alcohol leaves the body in three ways: the kidneys, lungs and liver. Drinking alcohol damages the kidneys, the lungs and the liver. The effects of alcohol at different levels of BAC o Euphoria; is the initial stage, BAC levels at 0.03 to 0.12%, this phase the person is more relaxed, confident and has no worries o Lethargy; has BAC levels of 0.09 to 0.23%, this phase the person starts to loose balance, his vision becomes blurred and appears sleepy o Confusion; BAC level increases to 0.17 to 0.28%, this phase the person becomes intense with his emotions and feelings, they become dizzy and nausea with weird feelings o Stupor; this stage is marked by a BAC count ranging from 0.25 to 0.39%, the person becomes impaired and starts loosing and again regaining consciousness at frequent intervals. This stage has a high risk of a coma. o Coma; BAC ranges from 0.35 to 0.50%, patients become unconscious, body reflexes become very poor, there is a drop in heart beats and breathing. o Death; BAC exceeds the mark of 0.50%, this is a very fatal stage marked by central nervous system failure, which ultimately leads to death. The signs and symptoms of alcohol dependence: The alcohol problem is based on the effects drinking has on your life and how you use alcohol. Alcohol related illnesses Memory lapses (blackouts) after heavy drinking Craving-a strong need, or urge, to drink Drinking alone Hostility when confronted about drinking Loss of control – not being able to stop drinking once drinking has begun Making excuses to drink Missing work or school Neglecting to eat Physical dependence – withdrawal symptoms, such as nausea, sweating, shakiness and anxiety after stopping drinking Tolerance – the need to drink greater amounts of alcohol to get “high” Shaking in the morning What are the withdrawal effects from alcohol? Alcohol is a depressant on the CNS (central nervous system), it also has a depressant effect on the PNS (peripheral nervous system). Long term drinking, lead to physical dependence. Goals for treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome are to relieve discomfort and to prevent medical complications. An alcohol will have to undergo intensive treatment for their addiction. 2. Levels of alcohol withdrawal are: Level 1) minor withdrawal; Insomnia Nausea Sweating Shakiness Headache Anxiety after stopping drinking; these symptoms accor within 6 to 12 hours after drinking. Level 2) mid-level withdrawal; Minor withdrawal intensified Visual, auditory, or tactile hallucinations (patients are not usually aware of hallucinations) Possible seizures Racing pulse Irregular heartbeat; these symptoms appear within 12 to 48 hours after quitting drinking Level 3) major withdrawal; Delirium Alcohol-induced hallucinations Profuse sweating Seizures Sever blood pressure spikes, racing and irregular heartbeat Sever tremors; these symptoms appear within 48 to 72 hours after quitting drinking and peak in five days. What are the short term health risks? Alcohol depresses the CNS activity at all doses producing definable results. Upset stomach Diarrhea Lack of coordination and judgment Headaches: and Insomnia 3. What are the long term health risks? The whole body is affected and these problems can lead to death. Heart disease: high blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, heart damage, heart failure Cancer (more from cigarette smoke) Liver problems: liver damage, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cancer Problems of the stomach, lungs, kidneys, skin, muscle, and bones; Infections )alcohol suppresses the immune system) Mental disorders: problems with attention, learning, and memory; depression; mood swings; anxiety disorders; Insomnia Malnutrition Impotence and infertility in men. Fetal alcohol syndrome and effects: Babies whose mothers drink during pregnancy may be born with low birth weight and with physical, mental and behavioral problems. The principal symptoms of a child born with fetal alcohol syndrome are retarded growth both before and after birth. Various abnormalities of the central nervous system and certain characteristic abnormalities of the face and head. Microcephaly (small head), short palpebral fissures (small eye openings), ptosis (eyelid droop), epicanthic folds (skin folds over the inside eye corner); and short unturned nose; long smooth philtrum (are between nose and mouth), thin upper lip. Other effects; o poor growth while in the womb, and after birth o Decreased muscle tone and poor coordination o Delayed development with significant functional problems, with thinking, speech, movement, or social skills o Heart defects such as (VSD) ventricular septal defect, or (ASD) atrial septal defect o Structural problems with the face, narrow, small eyes with large epicanthal folds, small heads, small upper jaw, smooth groove in upper lip and smooth and thin upper lip. 4. References: Buzzle.com; Blood Alcohol Content; http://www.buzzle.com/articles/blood-alcohol-content.html Drugs and Society; Tenth Edition; Chapter 7-8. E Health MD; http://ehealthmd.com/library/alcohol-use/alcoholuse-alcoholic.html “Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS).” Britannica Encyclopedia; Encyclopedia Britannica online. Encyclopedia Britannica, 2011, web.28 march 2011 http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/205469/fetal-alcohol-sydrome HAMS: Harm Reduction for Alcohol; What is alcohol withdrawal? http://hamsnetwork.org/withdrawal Yahoo Education; http://education.yahoo.com/reference/dictionary/entry/alcohol Wasted in Wisconsin; http://www.jsonline.com/news/wisconsin/31237904.html Wikipedia, The free Encyclopedia: Alcohol beverages. 5.