Topic VI – Nomenclature and Formulas - Science - Miami
advertisement
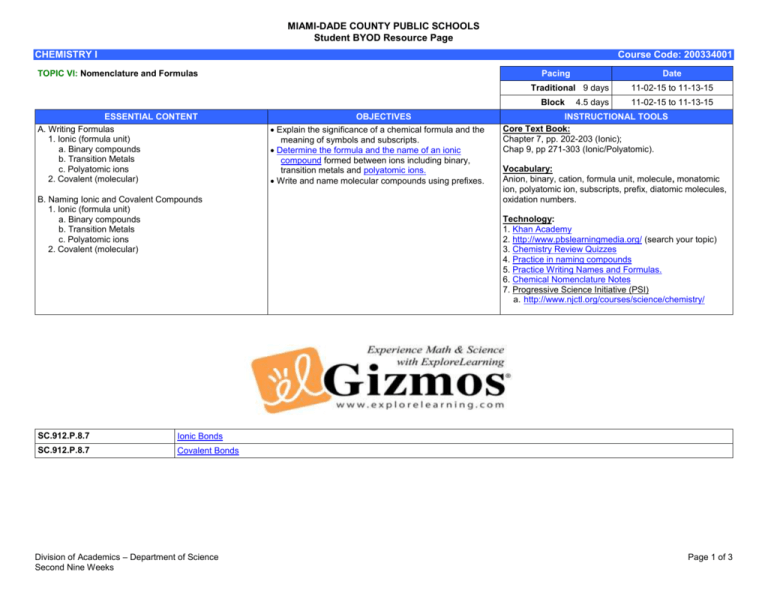
MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page CHEMISTRY I Course Code: 200334001 TOPIC VI: Nomenclature and Formulas Pacing Date Traditional 9 days Block ESSENTIAL CONTENT A. Writing Formulas 1. Ionic (formula unit) a. Binary compounds b. Transition Metals c. Polyatomic ions 2. Covalent (molecular) B. Naming Ionic and Covalent Compounds 1. Ionic (formula unit) a. Binary compounds b. Transition Metals c. Polyatomic ions 2. Covalent (molecular) SC.912.P.8.7 Ionic Bonds SC.912.P.8.7 Covalent Bonds Division of Academics – Department of Science Second Nine Weeks OBJECTIVES Explain the significance of a chemical formula and the meaning of symbols and subscripts. Determine the formula and the name of an ionic compound formed between ions including binary, transition metals and polyatomic ions. Write and name molecular compounds using prefixes. 4.5 days 11-02-15 to 11-13-15 11-02-15 to 11-13-15 INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS Core Text Book: Chapter 7, pp. 202-203 (Ionic); Chap 9, pp 271-303 (Ionic/Polyatomic). Vocabulary: Anion, binary, cation, formula unit, molecule, monatomic ion, polyatomic ion, subscripts, prefix, diatomic molecules, oxidation numbers. Technology: 1. Khan Academy 2. http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/ (search your topic) 3. Chemistry Review Quizzes 4. Practice in naming compounds 5. Practice Writing Names and Formulas. 6. Chemical Nomenclature Notes 7. Progressive Science Initiative (PSI) a. http://www.njctl.org/courses/science/chemistry/ Page 1 of 3 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page CHEMISTRY I Course Code: 200334001 Video Standard: SC.912.P.8.6 Article Standard: SC.912.P.8.7 Video Division of Academics – Department of Science Second Nine Weeks Covalent Bonds and Electronegativity Chemical Bonding: Valence Electrons Electron Transfer and Ionic Bonds Ionic and Molecular Compounds Atomic Structure; Ionic Bonding Atomic Structure; Covalent Bonding Intermolecular Forces Dipole-dipole Bond States of Matter: Intermolecular Forces Hydrogen Bonds in Water Van Der Waal’s Repulsion Hydrogen Bonding and Life Naming Compounds and Balancing Equations Chemical Formulas Polyatomic and Multivalent Ions Defining Ionic Compounds Naming Ionic Compounds Ionic Compounds with Variable Charges Iron Oxides What is a Polyatomic Ion Common Polyatomic Ions Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic Ions: Example Naming Binary Molecular Compounds Naming Carbon Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide Naming Molecules: Example 1 Naming Molecules: Example 2 Naming Molecules: Example 3Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Polarity and Molecular Geometry Studying Molecular Structure Page 2 of 3 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page CHEMISTRY I Course Code: 200334001 Video Glue With Mussels: Purdue Chemist Synthesizes Wet-Set Adhesive Chemistry Professor Researches Metal-Organic Frameworks Fighting to Stop Tuberculosis It's a Wash: The Chemistry of Soap Diamonds, Pencils and Buckyballs: A Look at Buckminsterfullerene Tobacco Plant Lights Up After Scientists Insert Firefly Gene Sustainability: Water - Dead Trees & Dirty Water in the Rockies Sustainability: Water - Baltimore's Urban Streams Chance Discoveries: Kevlar Mars Rover Discovers Complex Chemicals Georgia Tech Chemist Works to Detect "Fake" Medicines Chance Discoveries: Synthetic Dye Image Early--Maybe First--Sketch of a Buckyball (1985) Why Do Flowers Have Scent? Why Spider Webs Glisten With Dew How Can Graphite and Diamond Be So Different If They Are Both Composed of Pure Carbon? Division of Academics – Department of Science Second Nine Weeks Page 3 of 3