20130821144372
advertisement
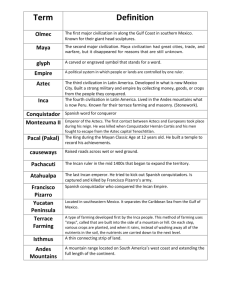
Roots of the American People Section 1: Earliest People 1st Americans • Who were they? – Asians • Where did they come from? • How did they reach the Americas? • 2 Theories – Land bridge • Bering Strait bridge (Siberia—Alaska) – Coastal-Route LANDBRIDGE COASTAL ROUTE THEORY Who were these people? Why did they come to the Americas? • Hunters – Followed large animals (wooly mammoth) – Supplied all needs from animals • What happened when the large animals began to die out? – Environment Adaptation • Gatherers – Traveled across lands – Searched for wild plants/small animals Neolithic Revolution • Environment adaptation does not stop – Neolithic Revolution occurs • Technique of farming is developed – How does that affect society? Affect of Farming on Society FARMING STOP TRAVELLING ESTABLISH COMMUNITIES GROW SURPLUS CIVILIZATIONS DEVELOPED 3 Early/Major Civilizations of Ancient America • 1. Mayas – Where? • Mexico and Central America – When? • A.D. 250—A.D. 900 – What did the civilization look like? • Pyramids, plazas, temples, ball courts, palaces – What advancements did they make? • Arts, government, written language, astronomy – What happened to them? • No one truly knows • Cities abandoned 3 Early/Major Civilizations of Ancient America • 2. Aztecs – Where? • Mexico • Capital city Tenochtitlan (Mexico City) built on a lake – What did the civilization look like? • Very religious—many temples built for Aztec Gods • Human Sacrifice • Conquered/controlled large parts of Mexico • Obtained wealth from their conquered subjects 3 Early/Major Civilizations of Ancient America • 3. Incas – Where? • South America—Andes Mountains • Capital City Cuzco: linked to other cities by network of roads – What was the civilization like? • • • • Buildings made of immaculate carved stone Intelligent engineers Skilled in metalwork/weavings Vast amount of gold and silver Section 2: Cultures of North America Early peoples of North America • Civilizations in North America – Mound Builders • Where? – Lived in the vast region from Appalachian Mts. and Mississippi Valley – Multitude of different tribes • Purpose of Mounds – Burial grounds or public buildings • Who were these people? – Largest group: Mississippians http://youtu.be/vTrVZr-DLHQ Early peoples of North America • Anasazi – Where? • Southern Utah, Colorado, Northern Arizona, New Mexico – What was civilization like? • Large cliff dwellings • Made pottery, jewelry, baskets • Heavy traders – What happened to them? • Homes were eventually abandoned Early peoples of North America • Hohokam – Where? • Arizona – When? • Reigned from B.C. 300—A.D. 1450 – What was the civilization like? • Skilled farmers, mastered irrigation • Heavy traders Living as a Native in North America • Lived in areas called culture areas – Populations grew larger in farming areas • Basic needs – Women were collectors – Men were hunters • Tools – Developed from sticks, animal bones, rocks, and shells • Beliefs – Focused on a relationship with nature – Established own creation stories Culture Areas of North America • Far North – 2 Regions: • Arctic: – cold, ice covered ground all year – No cities – Hunted whale, seal, walruses in winter, caribou in summer • Subarctic – Dense forests – Too cold for farming – Hunted to survive Culture Areas of North America • Northwest – Alaska down into northern California – Land filled with plentiful amount of food – Large cities developed despite no farming Culture Areas of North America • Far West: Consists of 3 regions – 1. California – 2. Great Basin – 3. Plateau • Northern region – Harsh winters, forest and grassland • Southern region – Desert like lifestyle • California region – Warm summers, mild winters, abundant food • Housing – Pit houses – Coned bark – Wooden plank Culture Areas of North America • Southwest – Arizona, New Mexico, southern Utah, and Colorado – Mostly dry: few rainy seasons – Farming took place with irrigation, some hunting/gathering – Pueblos were successful homes Culture Areas of North America • Great Plains – Large region located between Mississippi River and Rocky Mts. • Eastern part – farmers, women were the planters – Earth homes • Western part – No farming, treeless region – Tepees, pits – Hunted buffalo Culture Areas of North America • Eastern Woodlands – Northeastern part of North America – Full dense forests – 2 large groups • Algonquian—Southern Canada, Great Lakes, Atlantic coast • Iroquois—New York – Women were important, owned all property, chose leaders – Formed a Union to keep peace. LEAGUE OF IROQUOIS Culture Areas of North America • Southeast – Mild climate with hot summers – Idealistic for farming – Large native tribes • Cherokee, Creek, Natchez – Mud plastered homes