Social Development
advertisement

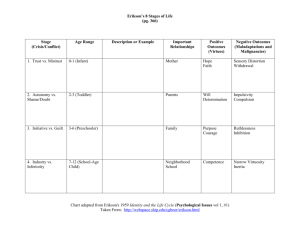
Social Development Issues facing the Discriminated Self- conscious Bad sense of self-image Don’t fit in Gangs and other criminal activity Hate yourself AND others Quiet Inferiority-complex No hope for success Fight back! Erik Erikson Erik Erikson’s Theory of Social Development **Focuses on experiences and social interactions in developing our sense of self, of who we are. Essential Question for Today: Which of Erikson’s eight stages seems most important? Why? Erikson’s Social Development Stages Please, please, PLEASE do NOT lose any of the pieces from your envelope (8 cut outs) Using your unfinished Erikson model, place your 8 cut out pieces in the order you believe that you went through the crisis.** Listen to the song and make any corrections necessary to your order. Exit Slip Which of Erikson’s eight stages seems most important? Why? ERIK ERIKSON (not Leif Erickson) AND PSYCHOSOCIAL DEVELOPMENT Erikson’s Social Development Stages Essential Questions How did Erik Erickson view social development from prenatal development to death? Which stage of Erikson’s social development model is most important for teachers to understand? Why? Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 1: Trust VS Mistrust (age 0-1) sensorimotoronly trust mom Main question- Is my environment trustworthy or not? In the first year of life, infants depend on others for food, warmth, and affection, and therefore must be able to blindly trust the parents (or caregivers) for providing those. Stage 1 Trust V Mistrust If an infant is well cared for= they will develop faith in the future. If an infant is NOT well cared for= look at the world with fear and suspicion https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HEHW 8oTj0BA Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 2: Autonomy VS Doubt (ages 2-3) Beginning preoperational Main question- Do I need help from others or not? Toddlers learn to walk, talk, use toilets, and do things for themselves. Their self-control and selfconfidence begin to develop at this stage. Stage 2 Autonomy VS Doubt If the child receives praise and reassurance for their attempts= the child will develop the confidence needed to cope with future situations that require choice, control, and independence. If the child receives too much criticism for their attempts or parents are overprotective=she may begin to feel ashamed of her behavior, or have too much doubt of his/her abilities. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ru74VlqC8MU Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 3: Initiative VS Guilt (3 - 6 years). preoperational Main question- Am I good or am I bad? Children have newfound power at this stage as they have developed motor skills and become more engaged in social interaction with people. They now must learn to achieve a balance between eagerness for more adventure and more responsibility, and learning to control impulses and childish fantasies. Stage 3 Initiative VS Guilt If parents are encouraging, but consistent in discipline= children will learn to accept that certain things are not allowed, but at the same time will not feel shame when using their imagination and engaging in make-believe role plays. If the child is constantly discouraged or punished= child will feel shamed/guilty, take the easy way out, depend on adults for instruction. Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 4: Competence VS Inferiority (6 - 12 years). concrete Main question-Am I good at something or am I worthless? School is the important event at this stage. Children learn to make things, use tools, and acquire the skills to be a worker and a potential provider. And they do all these while making the transition from the world of home into the world of peers. Stage 4 Competence VS Inferiority If the child receives praise for their work and have success= confident in abilities to cope with life(industry), feels successful. If the child receives too much criticism of their work or too much failure= lead to long-term feelings of inferiority Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 5: Identity vs. Role Confusion (Teenagers). Formal. YOU Main question- Who am I and where am I going? This is the time when we ask the question "Who am I?" To successfully answer this question, Erikson suggests, the adolescent must integrate the healthy resolution of all earlier conflicts. Did we develop the basic sense of trust? Do we have a strong sense of independence, competence, and feel in control of our lives? Adolescents who have successfully dealt with earlier conflicts are ready for the "Identity Crisis", which is considered by Erikson as the single most significant conflict a person must face. Stage 5 Identity VS Role Confusion If the child fails in this stage= they will feel confused on who they are, and who they’re “suppose” to be. If the child succeeds in this stage= they will feel confident in their own personality, love who they are now and what they will be in the future. Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 6: Intimacy vs. Isolation (Early Adulthood) ME “Main question- Shall I share my life with another or live alone? In this stage, the most important events are love relationships. No matter how successful you are with your work, said Erikson, you are not developmentally complete until you are capable of intimacy. An individual who has not developed a sense of identity usually will fear a committed relationship and may retreat into isolation. Stage 6 Intimacy VS Isolation A person who is secure in their identity=can have an intimate partnership and compromise for another. A person who is not secure in their identify= feel isolated and unable to depend on anyone in the world, might be in long-term relationship but avoids true closeness Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 7: Generativity vs. Self-Absorption (Middle adulthood 40-60) Main question- Will I make life better for the next generation? By "generativity" Erikson refers to the adult's ability to look outside oneself and care for others, through parenting, for instance. Erikson suggested that adults need children as much as children need adults, and that this stage reflects the need to create a living legend. Stage 7 Generativity VS Selfabsorbed Positive outcome: People can solve this crisis by having and nurturing children, or helping the next generation in other ways. Negative outcome: If this crisis is not successfully resolved, the person will remain self-centered and experience stagnation later in life. Erickson’s Social Crisis Theory Stage 8: Integrity vs. Despair (Late Adulthood 65-death) Main question- Have I lived a full life? Old age is a time for reflecting upon one's own life and its role in the big scheme of things, and seeing it filled with pleasure and satisfaction or disappointments and failures. Stage 8 Integrity VS Despair Positive outcome: If the adult has achieved a sense of fulfillment about life and a sense of unity within himself and with others, he will accept death with a sense of integrity. Just as the healthy child will not fear life, said Erikson, the healthy adult will not fear death. Negative outcome: If not, the individual will despair and fear death A Quick Review Erikson’s Social Development review. Question: “Which stage/crisis do you believe is most important for teachers to understand?” Evaluating Erickson’s Theory Strengths: Explains how our personality stays the same over time and how/why it changes Criticisms: Relies too heavily on case studies Does not explain the enormous differences in personality among various people Skit- Stage Identification With a partner read each skit and identify which stage of Erickson’s theory the child is at.