Child Development Theories: Freud, Erikson, Mead, Piaget
advertisement

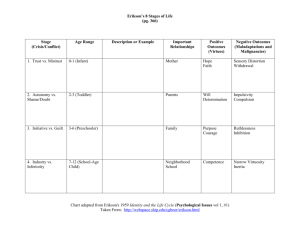
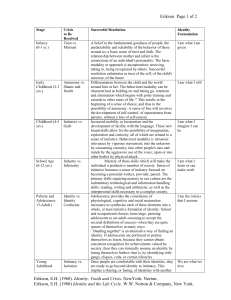
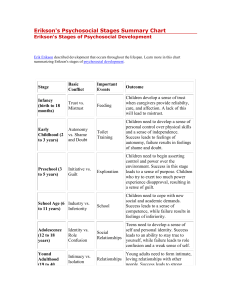
Theories on Child Development Types and Categories ● ● Psychoanalytic – Freud – Erikson – Mead Cognitive – Piaget Class Challenge Formulate your own theory after hearing about the others. Consider: 1. What category would you place it under. 2. How many, if any stages would you include. 3. How would you demonstrate your theory in action? Erik Erikson's Psychosocial Theory ● ● ● ● He explains the impact of social experiences across the lifespan. Each stage is concerned with becoming competent in an area at a certain stage in life At each stage a task or conflict must be met. If it is growth and development has occured. If not, failure. In the “Young Adult” Unit we covered the last 4 stages (Identity vs Role Confusion, Intimacy vs Isolation, Generativity vs Isolation, Integrity vs Despair) Erikson and Child Development ● ● ● ● Trust vs Mistrust (Birth to One Year) – security and fear Autonomy vs Shame/Doubt (1 – 3 years) – learn to control your surroundings. Failure results in inadequacy Initiative vs Guilt (Preschool) – assert power and control over the world. Failure of this task brings about lack of initiative. Industry vs Inferiority (5 – 11 years) – children begin to develop pride in their work and accomplishments. Parents and teachers affirm a child's success through encouragement. Erikson's Stages George Mead (Symbolic Interactionalist Theory) ● ● ● An individual is a product of their society Children learn through social experience, interactions and gestures Child Development depends on two things – symbols (language) and roles Mead's Stages of Development ● ● 1. Preparatory Stage – Children copy behaviour without understanding – Repetition because we encourage it through language 2. Play Stage – Children begin to imagine and understand actions of others – Role models teach children how to play 3. Game Stage – Become involved in groups with others – Learn appropriate behaviour or is sanctioned – Conformity