Lecture_7-Introduction to Simulink
advertisement

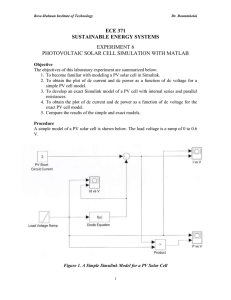
Simulink by Dr. Amin Danial Asham References MATLAB Help Telemark University College - Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics – Tutorial Simulink - Getting Started Guide UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE UPON TYNE - School of Electrical, Electronic and Computer Engineering Matlab/Simulink Tutorial What is Simulink? It is a simulation tools developed by MathWorks. This tool is used for modeling, simulating and analyzing dynamic systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool. This tool is tightly integrated with rest of the Matlab environment. Key Features Graphical editor for building and managing hierarchical block diagrams Libraries of predefined blocks for modeling continuous-time and discrete-time systems Simulation engine with fixed-step and variable-step ODE solvers Scopes and data displays for viewing simulation results Project and data management tools for managing model files and data Model analysis tools for refining model architecture and increasing simulation speed MATLAB Function block for importing MATLAB algorithms into models Legacy Code Tool for importing C and C++ code into models. System Modeling Continuous Dynamic systems are described by differential equations. Discrete Dynamic systems are described by difference equations. Solving differential equations or difference equations gives the behavior of the corresponding dynamic systems. Differential equations and difference equations describe the rate of change and difference for variables, respectively. Equations without rates or differences are algebraic equations. Ex. 𝐼𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 = 𝐼1 + 𝐼2 What is Purpose? To give the basics for simulating different models using Simulink. Consequently, common and many default settings for blocks will be used. For more detailed features students must refer to Matlab for the considered blocks. Starting Simulink Start here Starting Simulink Start here Simulink Library Browser Simulink Continous Blocks Simulink Math Operations Simulink Sinks Simulink Sources Scope window — If a Scope window is closed at the start of a simulation, scope data is still written to the connected Scope. As a result, if you open a Scope after a simulation, the Scope window displays the input signal or signals. Examples Source Sink Examples Sine Vector that defines two sine signals Cosine Examples On the Scope window toolbar, click the Parameters button The values you entered or selected apply to the next simulation. Examples To add signals to a Floating Scope, click the Signal Selector button , and then select signals from your model. For more information, see Signal Selector. Examples Displaying X-Y plot of signals using MATLAB figure window Thanks







![[Sample Course Title Slide Insert Presentation Title]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010147253_1-30e478bdeabf2400e526b54ddedf7a37-300x300.png)