Capillaries
advertisement

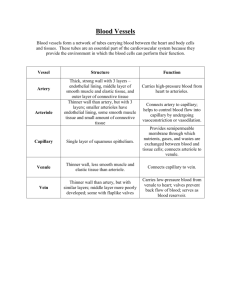
Three main types of blood vessels: 1. Artery (動脈) 2. Vein (靜脈) 3. Capillaries (微血管) Blood Circulation Vein returns blood to the heart Venule Artery Heart Capillary carries blood away from the heart Arteriole Artery Vein Smooth muscles & elastic fibres lumen lining of Fibrous wall Cross section of a blood vessel tissue Cross section of artery Cross section of vein Artery : thicker elastic wall to withstand high blood pressure relatively smaller lumen Cross section of artery Cross section of vein Artery : thicker smooth muscles Not contract to force blood forward Heart drives blood forward Cross section of vein Cross section of artery Blood pressure changes along blood vessels Blood pressure / mm Hg 120 100 90 80 40 Blood flow steadily with no pulse Blood flow with pulse 0 arteries arterioles capillaries venules veins How can blood return to heart through vein under low pressure? Valve open blood can flow Valve closed blood can’t flow back Valves present to prevent backflow of blood Return of blood to heart is aided by contraction of body muscles as they squeeze the blood along the vein valve open contract valve close Demonstration of Venous Flow in the Fore Arm A B X vein elbow joint C D S R Y finger Y squeezing finger X pressing blood down on R towards S finger Y removed finger X still pressing down on R both fingers are removed What is the purpose of tying the arm with a piece of rubber tubing ? Ans: This makes the vein more conspicuous. A B X vein elbow joint C D S R Y finger Y squeezing finger X pressing blood down on R towards S finger Y removed finger X still pressing down on R both fingers are removed With reference to steps B & C, explain why the part of the vein between R and S has disappeared ? Ans: Since In step On thethere other B, finger are hand, valves Y squeezes finger at Xpoint isthe still S,vein blood pressing towards is down point S. Blood on prevented point in R which from this segment flowing prevents back is blood therefore … flowing pushed into R. along … A B X vein elbow joint C D S R Y finger Y squeezing finger X pressing blood down on R towards S finger Y removed finger X still pressing down on R both fingers are removed What structure in the vein is indicated by the appearance of the bulge at S shown in diagram C ? Ans: The valve in the vein. A B X vein elbow joint C D S R Y finger Y squeezing finger X pressing blood down on R towards S finger Y removed finger X still pressing down on R both fingers are removed Why is it necessary to take the rubber tubing away as soon as the demonstration has been completed ? Ans: It is because we need to restore the normal blood flow for the arm as soon as possible. Capillaries • allow exchange of materials between the blood and the body tissues by diffusion. arterioles venules O2 , nutrients capillaries CO2 , waste • the wall is permeable to O2, CO2, glucose, amino acids, salts, water ... etc. cross section of capillary Capillaries Specially adapted for exchange of materials 1 One-cell thick walls – diffusion distance between very small blood and body tissue lumen 2 Very small lumen but large total cross sectional area – blood flow more time for exchange of materials cross section of one cell 3 Greatly branched capillary thick – surface area for efficient diffusion of materials Capillaries v1 A1 Same flow rate (Volume / time) V1 = V2 Total cross sectional area d1 A2 arteriole v2 d2 A1 > A2 d2 > d1 v2 > v1 Exchange of materials between the blood and the body cells white Exchange of materials takes blood place at the capillaries onlycells water Plasma protein plasma O2 tissue fluid Diffuse across the capillary wall capillary nutrients CO2 waste products Squeeze through the wall cell Diffuse across the capillary wall