Chemistry of Metals - Miss Jan's Science Wikispace
advertisement

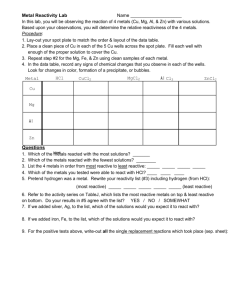
Chemistry of Metals Miss Jan Chemical reactions of metals SLOs • investigate the reactions of metals with oxygen, water, and acids • write word equations and symbol equations for the common reactions of metals • write chemical formulas for metal compounds • understand how the atomic structure of metals can explain their chemical reactivity • relate the uses of metals to their physical properties and reactivity Worksheet • [A] Metals and air (Oxygen gas) –Clean metal if rusted or dirty by rubbing them with sandpaper –Hold in flame using tongs –Record colour of flame and the colour of the product –Record reactivity: react violently, reacts rapidly, reacts, reacts very slowly, do not react DO NOW 1. Name 2 alloys Brass (Cu+Zn), Steel (Fe+C), Amalgam (Hg+ another metal), Bronze (Cu+Sn) 2. State the uses for these alloys Brass – instruments, Steel – pipes, construction, Amalgam – dental fillings, Bronze – statues. 3. Why would we use alloys rather than pure metals? Because they have different properties than the pure metals that makes them suitable for their uses. E.g. Steel and Bronze = stronger and resist rusting. Brass = malleable etc. Many metals react with oxygen Magnesium burns brightly when heated in air. The equations are: magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide Word equation 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO Symbol equation Copper reacts only very slowly when heated in air. It forms black copper oxide. The equations are: copper + oxygen copper oxide 2 Cu + O2 2 CuO Write the word and symbol equation for Al and Fe Aluminium + oxygen Aluminum oxide 4 Al + 3 O2 2 Al2O3 Iron + oxygen iron oxide 2 Fe + O2 2 FeO Colored flame Worksheet Be careful: some reactions may create HEAT!!! • [B] Metals and water –Place small sample of metal in water –Observe and record reactivity –Collect gas and test with flame –Record result of gas test and colour of product –Record reactivity: react violently, reacts rapidly, reacts, reacts very slowly, do not react Some metals react with water Lithium reacts rapidly with cold water to form lithium hydroxide and hydrogen gas (fizzing). The equations are: lithium + water lithium hydroxide + hydrogen 2Li + 2H2O 2LiOH + H2 Write the word and symbol equations for the reaction of Ca with water Calcium + water Calcium hydroxide + hydrogen Ca + H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2 Sodium – stored in mineral oil Calcium in water Worksheet • [C] Metals and acid –1 cm of sulfuric acid in test tube and add a small sample of metal –Observe reaction and record results in table –Collect gas and test with flame –Record reactivity: react violently, reacts rapidly, reacts, reacts very slowly, do not react Be careful: some reactions may create HEAT!!! Many metals react with acids For example, zinc reacts with dilute sulfuric acid to form zinc sulfate and hydrogen gas (fizzing). The equations are: zinc + sulfuric acid zinc sulfate + hydrogen Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 Summary • metal + oxygen metal oxide • metal + water metal hydroxide + hydrogen • metal + acid salt + hydrogen • Pop test – if hydrogen is present, a squeaky pop would be heard if a flame is introduced • Usually metals that react quickly with oxygen also react quickly with water and acids. Activity and uses of metals • Active metals like Na, Li, Ca, Mg aren’t used to make things. • Common metals like Al, Zn, Fe, Pb, Cu are used to make lots of different objects. • Precious metals like Ag, Au are only used in valuable objects.