What is an Air Source Heat Pump?
advertisement

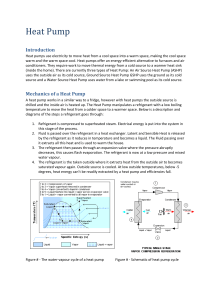
Air Source Heat Pumps Presentation Heading Jordan Jeewood Heating Technical Executive What is an Air Source Heat Pump? What is an Air Source Heat Pump? Refrigeration circuit used to heat water – fridge in reverse Sealed refrigerant unit outputs hot water – outdoor unit Plate heat exchanger transfers energy from hot refrigerant to water What is an Air Source Heat Pump? Produces hot water 25-58ºC – heating only 5kW, 8.5kW, 14kW Mitsubishi Electric Ecodan – domestic market No need for refrigeration qualification to install Approved Ecodan Installers – plumbers and heating engineers Air @ -5ºC Water @ 58ºC What is an Air Source Heat Pump? R410A refrigerant Very efficient way to heat water ~ 300-400% For every 1 unit of energy put in, 3 useful units of energy out – high COP 450 400 400 350 350 % Efficiency 300 250 200 150 99 93 91 86 Direct Electric Gas LPG Oil 100 50 0 Ground Source Air Source Heat pump technology Inverter driven compressor and fan Weather compensation These technologies lead to greater efficiencies Inverter Compressor Inverter control PCB Inverter Drive Technology Duty (kW) Heat load Fixed speed Inverter 10 5 0 Time Weather Compensation Heat load of property reduces as ambient temperature increases Weather Compensation Reducing flow temperature matches output of boiler to heat load Weather Compensation Heat pump has to draw less power to output lower flow temperatures COP increases Weather Compensation UK Market Size – Domestic Heating 60 million people 26 million homes 1.6 million heating systems replaced / yr 85% gas boilers 4.5 million homes – off gas grid 4.7 million social housing Why now? Cost effective Reliable and maintainable as existing systems “Scalable” solution that can be easily “adapted” for the whole country Future proof Has to be absolutely acceptable to homeowners in terms of space, noise and usability Cost effective Payback period typically 5-10 years compared to oil, LPG, electricity Payback period will decrease as: Fossil fuels increase in price The Technology becomes more commoditized Manufacturing costs are decreased through economies of scale Introduction of Renewable Heat Incentive (2012) Reliability & Maintainability Proven technology – air conditioning units used for years Minimal servicing needed – like a fridge Essentially a visual inspection, heat exchanger to be kept clean Hot water to clean the coil and brush to remove debris e.g. leaves Scalability Potentially over 16 million homes are suitable – new build and retrofit 14kW 8.5kW 5kW 2 Bed Flat 3 Bed Semi 4 Bed Detached Scalability Geographically and seasonally independent Manufactured in Scotland National distribution network – already in place through aircon Supporting Approved Ecodan Installers all over UK Grid Future proof Hot Water Turbine Radiators mCHP PV Under floor Heating Acceptable to homeowners No change in lifestyle or comfort level Capable of providing both heating and hot water requirements for a property all year round – tank can be heated to 55ºC Radiators and underfloor heating Use of standard domestic heating controls Quiet unit operation – typically 48dBA Applying Air Source Heat Pumps Applying Air Source Heat Pumps Radiators or underfloor heating can be used Heating and hot water separate – S Plan plumbing Integrated like conventional boiler system DHW cylinder supplying shower etc. Heat pump positioned externally Supplies space heating via underfloor or rads Applying Air Source Heat Pumps S Plan System All fitting on cylinder package Zone valves Pump Flow setter Boiler buddy Pump Principals of Heat Pump Sizing Heat Loss from Dwellings: Fabric Heat Loss Ventilation Heat Loss Heat pump should be sized on peak heat loss of dwelling Heat Loss of a Dwelling Victorian House 1970’s House 2006 House Minimum boiler output = 10.8kW Minimum boiler output = 6.6kW Minimum boiler output = 3.9kW All 80m2 floor space, similar shape and -3oC outside, 22oC inside Emitter Selection 3 Points to consider: Desired Room Temperature = 20oC 1. Water flow temperature through emitter 2. Peak heat loss of room 3. Space to locate emitter Mean Water Flow Temperature = 40oC Applying Air Source Heat Pumps Site survey is required for accurate heat loss calculation Thank you Discussion