Introduction to H.264 / MPEG
advertisement

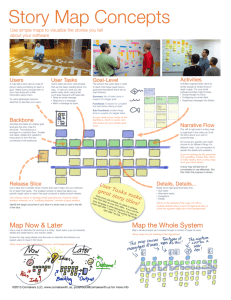
Introduction to H.264 Video Standard Anurag Jain Texas Instruments H.264 Background Jointly developed by ITU-T and MPEG. Upto 50% more efficient at the same virtual quality compared to MPEG-4 ASP Supports wide range of applications. (interlaced, progressive, low bitrate, studio quality digital cinema etc). Multiple profiles (Baseline, Main, Extended, High, FRExt). Good results obtained from interoperability tests making it suitable for wide deployment in short span of time. H.264 Encoder Block Diagram Intra Prediction Modes 9 4x4 & 4 16x16 modes = 13 modes Video Source Intra Prediction +_ Quantization step more resolution for finer control of bit rate Coding Control Intra Transform Quantization Quantized Transform Coefficients Inter Inverse Quantization Predicted Frame Inverse Transform Motion Compensation + + Frame Store Motion Estimation •Seven block sizes and shapes •Multiple reference picture selection •1/4-pel motion estimation accuracy •Referenced B-frames Loop Filter Entropy Coding Bit Stream Out [Single Universal VLC and Context Adaptive VLC] OR [Context-Based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding] Motion Vectors Integer 16-bit fixed point transform with no mismatch Common Elements Common elements with other standards Macroblocks: 16x16 luma + 2 x 8x8 chroma samples Input: association of luma and chroma and conventional block motion displacement Motion vectors over picture boundaries Block Transform Variable block-size motion I, P and B picture coding types High Level Coding Tools Sequence and Picture Parameter Sets (SPS & PPS) Picture Order Count (POC) Decoded Picture Buffer (DPB) Slice group map (FMO) Multiple slices and arbitrary arrangements (ASO) Supplemental Enhancement Information (SEI) Hypothetical Reference Decoder (HRD) Video Usability Information (VUI) High Level Tools: Coding Hierarchy A coded sequence contains one or more access units An access unit is a set of NAL units that contains all necessary information for decoding exactly one (primary) coded picture A coded picture is divided into Slices (VLC NAL units) A slice contains a slice header and a set of macroblocks A macroblock contains a 16x16 luma block and two chroma blocks An I-slice contains a set of INTRA-coded macroblocks A P-slice contains a set of INTRA- and INTER-coded macroblocks An IDR (instantaneous decoding refresh) picture contains only I-slices (SI-slices too in extended profile) Sequence Parameter Set Profile @ Level indicator Profile constraint indicator Sequence parameter set ID (0..31) Picture order count type and infos DPB (Decode Picture Buffer) info Picture size Frame/field coding flag Method for vector derivation of B-direct mode Frame cropping parameters VUI_parameters (Annex E, Video usability information) Picture Parameter Set Picture parameter ID (0..255) Sequence parameter ID (0..31) Entropy coding mode flag (CABAC/CAVLC) Slice POC info presence flag Slice group map parameters Max. number (1..16) of ref. frames used for decoding slices Weighted prediction flags Quantization scales (qp minus 26, range -26 ..+ 25) Chroma QP offset for loop-filter (-12 ..+12) Slice loop-filter control flag (Alpha/Beta table offsets) INTRA predication using pixels of INTER neighboring MBs? Slice redundant pic. parameters presence flag Slice Header Starting macroblock address Slice type (I, P, B, SI, SP ) Temporal reference (frame_num) Picture parameter set ID (0..255) Interlaced frame/field coding, top/bottom field indicators IDR pictire ID (0,… 65536) Slice POC parameters Redundant picture count(0.. 127, 0 for baseline) B-slice temporal or spatial direct mode indicator Max. number (1..32) of ref. pictures for decoding current slice Reference picture reordering parameters (DPB) Weighted prediction parameters DPB marking parameters (e.g. short term, long term pred. Pics) Slice delta QP (-26 ..25) SP switch flag and SP/SI slice QP Loop-filter indicator (0: disabled, 1: enabled, 2: enabled but LP across slice Boundaries disabled) Loop-filter alpha/beta table access offset (-6, +6) Slice group change cycle (derives the No. of MBs in slice group 0) Slice Group Maps For error resilience Ordering of Slices within Slice Groups Low Level Coding Tools Motion compensated prediction Additional intra modes for spatial compensation Transform: 4x4 Integer transform (Baseline, Main Profiles) Transform: 8x8 Integer transform (High Profile) Quantization: Scalar quantization Entropy Coding : CABAC / CAVLC In-loop deblocking filter Enhanced MC (Inter Prediction) Every macroblock can be split in one of 7 ways for improved motion estimation D B A Current Macroblock or Partition or Block C Accuracy of motion compensation = 1/4 pixel Up to 5 reference frames for SDTV size @ L3 Weighted predictions Reference B pictures Trade off between accuracy and side information B Slice - Direct Mode Direct mode Forward / backward pair of bi-directional prediction Prediction signal is calculated by a linear combination of two blocks that are determined by the forward and backward motion vectors pointing to two reference pictures. Current Picture List 0 Reference Spatial Direct mode Temporal Direct mode mvL0 = tb mvCol / td mvL1 = – (td – tb) mvCol / td List 1 Reference ...... mvCol mvL0 co-located partition where mvCol is a MV used in the co-located MB of the subsequent picture direct-mode partition td tb mvL1 B Slice : Multi-picture Reference Mode Generalized Bidirectional prediction Multiple reference pictures mode Two forward references : proper for a region just before scene change Two backward references : proper for a region just after scene change current picture previous pictures ...... next pictures ...... ...... ...... 2 forward MVs traditional Bidirectional 1 forward MV + 1 backward MV 2 backward MVs H.264 Intra Prediction 9 modes for 4x4 blocks 4 modes for 16x16 intra prediction Luma Sub-Pixel Interpolation Chroma Sub-pel Calculation If (vx, vy) is luma vector, then xFracc = vx&0x7, yFracc = vy&0x7 Block Scanning Order in a MB One more extraction of correlation among sub-blocks Transform & Quant Integer 4x4 DCT approximation. 8x8 Cost of transformed differences (i.e. residual coefficients) for 4x4 block using 4 x 4 Hadamard-Transformation for INTRA_16x16 coded macroblocks. Scalar quantization. All integers! 4x4 Luma/Chroma AC 8x8 Luma-Chroma Hadamard Interlaced Coding Deblocking filter Frame / Field Adaptation Picture Adaptive Frame Field (PicAFF). Macroblock Adaptive Frame Field (MBAFF) Field scan and zig-zag scan options Zig-zag Frame Scan Field Scan Entropy Coding Universal Variable Length Coding (UVLC) using Exp-Golomb codes. Context Adaptive VLC (CAVLC) Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) CAVLC Zigzag order: 50 33 27 20 0 5 0 0 1 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 • TotalCoeff = 7 : # of non-zeros • Trailing 1s = 2 : 1, -1 • Sign Trail = 1 0 (reverse order) : minus, plus • Levels = 5 20 27 33 50 (reverse order) : 7 – 2 = 5 • TotalZeros = 3 (# of zeros) • RunsBefore = 0 2 1 : 0 before -1, 2 before 1, and 0’s before 5 Exp Golomb Coding Loop filter Check if the boundary is original to picture or blocking effects 16*16 Macroblock 16*16 Macroblock Horizontal edges (luma) Horizontal edges (chroma) Vertical edges Vertical edges (chroma) (luma) Profiles and Tools H.264 Profiles and Tools: Graphical Representation Main Profile Extended Profile Data partition SI slice SP slice CABAC B slice Weighted prediction I slice P slice CAVLC Arbitrary slice order Flexible macroblock order Redundant slice Baseline Profile FRExt: Fidelity Range Extension Lossless representation Allows more than 8-bits per sample (upto 12-bits) Higher resolution for color representation (4:2:2, 4:4:4) Source editing function like alpha blending Very high bit-rates (often with constant quality) Very high-resolution Color space transformation (YCgCo, YCbCr, RGB) RGB color representation Adaptive block transform sizes Quantization matrices Coding Efficiency Comparision of Standards Feature/Standard MPEG-1 MPEG-2 MPEG-4 part 2 (visual) H.264/MPEG-4 part 10 16x16 16x16 (frame mode) 16x8 (field mode) 16x16 16x16 Block Size 8x8 8x8 16x16, 16x8, 8x8 16x16, 8x16, 16x8, 8x8, 4x8, 8x4, 4x4 Transform 8x8 DCT 8x8 DCT 8x8 DCT/Wavelet 4x4, 8x8 Int DCT 4x4, 2x2 Hadamard Scalar quantization with step size of constant increment Scalar quantization with step size of constant increment Vector quantization Scalar quantization with step size of increase at the rate of 12.5% Entropy coding VLC VLC VLC VLC, CAVLC, CABAC Motion Estimation & Compensation Yes Yes Yes Yes, more flexible Up to 16 MVs per MB Playback & Random Access Yes Yes Yes Yes Macroblock size Quantization Comparision of Standards (cont’d..) Feature/Standard Pel accuracy MPEG-1 MPEG-2 (visual) H.264/MPEG-4 part 10 MPEG-4 part 2 Integer, ½-pel Integer, ½-pel Integer, ½-pel, ¼-pel Integer, ½-pel, ¼-pel Profiles No 5 8 3 Reference picture one one one multiple forward/backward forward/backward forward/backward forward/forward forward/backward backward/backward I, P, B, D I, P, B I, P, B I, P, B, SP, SI Error robustness Synchronization & concealment Data partitioning, FEC for important packet transmission Synchronization, Data partitioning, Header extension, Reversible VLCs Data partitioning, Parameter setting, Flexible macroblock ordering, Redundant slice, Switched slice Transmission rate Up to 1.5Mbps 2-15Mbps Compatibility with previous standards n/a Yes Yes No Encoder complexity Low Medium Medium High Bidirectional prediction mode Picture Types 64kbps - 2Mbps 64kbps -150Mbps References – Related group • MPEG website http://www.mpeg.org • JVT website: ftp://ftp.imtc-files.org/jvt-experts • www.mpegif.org – Test software • H.264/AVC JM Software: http://bs.hhi.de/~suehring/tml/download – Test sequences • • • • • http://ise.stanford.edu/video.html http://kbs.cs.tu-berlin.de/~stewe/vceg/sequences.htm http://www.its.bldrdoc.gov/vqeg ftp.tnt.uni-hannover.de/pub/jvt/sequences/ http://trace.eas.asu.edu/yuv/yuv.html THANKS