File - Ms. vargas course website
advertisement

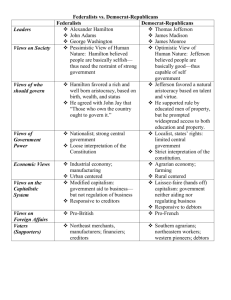
Washington, Adams, and Jefferson Presidencies Washington: Development of Two National Parties Federalists and Republicans o Federalists: saw America as becoming a nation-state with a strong central government and complex commercial economy – Alexander Hamilton o Republicans: America should have a modest national government and remain predominantly a rural and agrarian nation – Jefferson and Madison Hamilton’s Funded Debt Proposal The federal government should assume state debt from the Revolutionary war, so that the wealthy who had helped out the states and the nation would look to the federal government for repayment; by always having a debt, he would give the wealthy a stake in the survival of the federal government (otherwise their money goes bye-bye) Hamilton’s National Bank Hamilton created a National Bank to provide loans and provide a sound place for the government to deposit its money; the eventual question would arise…was this Constitutional? Hamilton’s Taxes: Tax on Whiskey led to the Whiskey Rebellion o Whiskey Rebellion 1794 Penn backcountry farmers (it’s always farmers) refuse to pay tax on Whiskey and attach tax collectors (sounds a lot like Shay’s Rebellion, so let’s see how the new government will deal with the problem); at Hamilton’s urging, Washington called out the militia of three states and personally marched 15,000 militia to take on the farmers, who quickly ran away. “Report on Manufactures” outlined a plan for stimulating economic growth and developing manufacturing Foreign Affairs o Jay’s Treaty 1794, Treaty preventing war with Great Britain during G.B.’s war with revolutionary France; created reasonable commercial ties and confirmed America sovereignty over the Northwest territory o Pinckney’s Treaty 1795, Between US and Spain confirming the American right to the Mississippi river (essential for shipping goods down to the port of New Orleans) Adams Won the 1796 election by just 3 electoral votes over Jefferson who became VP. XYZ Affair: American officials arrive in Revolutionary France in 1797 and the French Minister demands a bribe and is met with the cry, “No, no, not a sixpence!”; when the attempted bribe becomes known to the American public they are outraged and support Adam’s call to prepare for war The “Quasi War” with France 1798-1799 American and France engage in an undeclared war; capturing French armed ships and even beginning to work with Great Britain, which leads France to want to conciliate with America, ending the undeclared war. o Alien and Sedition Acts Alien Act: made it harder for foreigners to become citizens Sedition Act: allowed the federal government to prosecute those who were engaged in “sedition” against the government but what is a libelous or treasonous activity? Republicans saw these laws as an effort to use the federal government to destroy them and any opposition o Virginia and Kentucky Resolves Presented the idea that states had only delegated powers to the central government and could nullify laws where the state felt that the government had exceeded its power Election of 1800 o A dirty campaign o Judiciary Act of 1801 – since the only branch that would stay in Federalist hands was the Judicial, Adams expanded the number of federal justices (not S.C. justices) so he could make last minute appointments (known as the “midnight appointments”) Jefferson Reversing Federalist Programs: o 1802, Jefferson gets Congress to get rid of all taxes – so only sale of western land and customs duties are the sources of revenue for the federal government o reduced government spending o Cuts the national debt in half o Scales down the armed forces And Yet… o He founds West Point – military academy for training officers o Increases the Navy to fight Barbary Pirates o Louisiana Purchase 1803, Jefferson buys France’s territory in N. America (Lousiana) from Napoleon for $15 million Sent Lewis and Clarke to explore the new territory Marbury v. Madison, 1803 o Says Marbury has a right to his office but that the court has no authority to compel Madison to deliver it in the Judiciary Act of 1789 Congress gave the S.C. the power to compel executive officials to deliver commissions, but the S.C. argued that this law itself was invalid and had exceeded the Constitutional powers given to Congress while seeming to limit their power (can’t compel executive officials) they instead enlarged it (they are the final rulers on the Constitutionality of laws) Thank you Chief Justice John Marshall – so smart Jefferson and Aaron Burr o Essex Junto Radical Federalists who believed that their only way to come back into power was to have New England secede from the Union Wow, the first idea of secession came from the North! Aaron Burr agreed to run for governor of NY and the plan for secession – Hamilton called him a traitor, etc, etc, they fought a duel and Hamilton was mortally wounded Yes, an American VP killed someone, so Dick Cheney shooting his friend while hunting is not really that bad compared to Aaron Burr Burr began corresponding with the governor of the Louisiana Territory and plotting to take the Southwest and make his own empire he was put on trial for treason (though he was later acquitted) Impressment and Embargo o France and G.B. are still fighting and are trying to blockade each other from receiving goods America feels that they are neutral and should be able to sell goods to both countries freely The British began impressing (forcibly putting them into the army) American sailors into the British army Chesapeake-Leopard Incident British ship fired and then boarded an American ship o In response Jefferson declared an Embargo in 1807 that no American ships could leave for foreign ports The most hurt by this were merchants in the Northeast, most of whom were federalists o Non-Intercourse Act passed just before Jefferson left office, it reopened trade with G.B. and France Madison also announced that in 1811 an embargo on G.B. would go into effect unless they stopped harassing American ships Jefferson and Indians o Harrison Land Law – 1800, allowed easier settlement of western land o Jefferson’s Choice: 1) Indians could convert themselves into settled farmers and become part of white society or 2) they could move to the west of the Mississippi Assimilation Policy o Tecumseh Tenskwatawa is the “prophet” who wants to get rid of the evil effects of white culture and his brother, Tecumseh, helped created unified military efforts to resist white settlement of their territories 1809 began to try to unite tribes into the Tecumseh Confederacy argued that Harrison and the American government did not have title to any land because their treaties with each tribe did not count – land belonged to all tribes Battle of Tippecanoe – Harrison provokes a fight which leaves the confederacy in disarray Tecumseh uses the summer of 1812 to raid and fight along the frontier – with the aid and encouragement of the British in Canada – which leads Harrison and others to push for Canada’s annexation and removal of all British presence in North America