UTI
advertisement

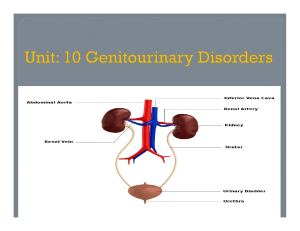
Urinary Tract Infections Tory Davis, PA-C UNE PA Program UTI Can involve any part of urinary tract – – – – Urethra Bladder Ureter(s) Kidney(s) Bladder and urethra most commonly involved How, who and why MC pathogen E.coli from GI tract (70-80%) Also Enterococcus faecalis In women: – Close proximity of urethra to anus – Short distance from urethral opening to bladder In men: – more often due to obstruction, incl Structural abnormalities Catheterization Neurogenic bladder Enlarged prostate Symptoms Can Indicate Location Urethritis causes dysuria Cystitis causes: – Urinary urgency & frequency, hematuria, suprapubic pain, malodorous urine Pyelonephritis: – flank pain, fevers/chills, nausea/vomiting Risk Factors Female Sexually active Use of contraceptive diaphragm and/or spermicidal agents Aging – Post meno estrogen causes thinner tissue in vag, urethra, bladder base More risk factors For both males and females: Urinary tract obstruction Immunocompromise Urinary catheter Work up History – past UTI, blood present, flank pain, recent intercourse (new bacteria), PE – + CVAT (costoverterbral angle tenderness – bang on kidneys) – make you think pyelo. Diagnosis Clean-catch (midstream urine) – Dip for nitrites (b/c bac-t produce enzyme that converts urine nitrates to nitrites) and leukoesterases (protein produced by WBCs) – Microscopy for WBCs – Urine culture and sensitivity Antibiotics In an uncomplicated outpt, no catheter Bactrim (TMP/SMX) DS (double strength) bid for 3 days Fluoroquinolone (ie Ciprofloxacin) BID x3d Amoxicillin+clavanulate (Augmentin) Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid) And have a heart.. Urinary analgesic phenazopyridine (Pyridium) 200 mg TID prn dysuria NB - Makes urine orange or blue Tx other Fluids- lots of water Avoid bladder irritants- coffee, soda, alcohol Cranberry- decreases ability of bac-t to adhere to bladder wall UTI Prevention Cranberry Wipe front-to-back Urinate after intercourse Avoid irritants, incl feminine hygiene products and smoking Shower rather than bath Prophylactic abx for recurrent UTIs – Dosing: daily low dose vs post-sex dose vs prn symptomatic dosing Special populations require special considerations Like who? What’s special about them? Pyelonephritis Ascending infection from lower urinary tract travels up ureters to the pyelum (pelvis) of the kidney (nephros) and causes an “–itis” Or hematogenous spread Not good Sick people Pyelo Fevers Rigors Flank pain Nausea/vomiting + CVAT +/- lower UTI sx + blood cultures – But good hx and PE, plus urine may be enough Pyelo Tx Admission if fevers and leukocytosis IV fluids IV abx (Cipro, ampicillin if preg) – Continue abx until fever-free x 24h, but can switch to oral dosing when pt improves