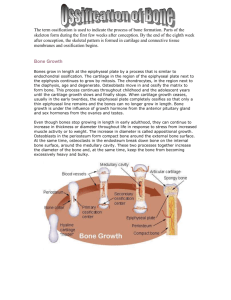
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone
advertisement

Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone 1. Cartilage: organ=Cartilage tissue+perichondrium 1) structure of cartilage tissue ---cell: chondrocyte ---cartilage matrix ① chondrocyte: ---Structure: LM embedded in cartilage lacuna peripheral cells: --small and immature --single and flattened central cell: --large and mature, --round and in group of 2-8 cells --small and round nucleus --basophilic cytoplasm --EM: rich in RER and Golgi complex *isogenous group: several cells locates in one lacuna, which are derived from a single(same) parent cell ② Cartilage matrix ---ground substance: proteoglycan: --same to loose CT --there are more chondroitin sulfate distributed at the periphery of cartilage lacuna---called as cartilage capsule(basophilic) chondronectin water ---fiber: type and number of fiber depends on the type of cartilage 2) Classification: according to the fiber a. Hyaline cartilage: less collagenous fibril←type II collagen articular surface, rib cartilage, trachea and bronchi b. Fibrous cartilage: large amount of collagenous fiber bundles cells are small and less intervertebral disc, symphysis pubis c. Elastic cartilage: large amount of elastic fiber external ear, epiglottis 3) perichondrium two layers: ---out layer: contain more fiber-protection ---inner layer: more cells-osteoprogenitor cell(fusiform in shape) 4) growth of cartilage ---interstitial growth: inner chondrocyte proliferation→ produce fiber and matrix. immature cartilage ---appositional growth: osteoprogenitor cell→cartilage cell (chondrocyte) → produce fiber and matrix. growing and mature cartilage 2.Bone ---consists of bone tissue, periosteum and endosteum, bone marrow 1) Bone tissue ① Cells: a. osteoprogenitor cell: stem cell ---structure: fusiform, small ovoid nucleus slight basophilic cytoplasm exist in periosteum and endosteum ---function: differentiated into osteoblast and chondrocyte b. osteoblast: ---structure: LM: single layer of cuboidal or low columnar cell round nucleus basophilic cytoplasm located on the surface of bone tissue EM: fine processes rich in RER, Golgi complex ---function: ⅰ.synthesize bone collagen fiber and ground substance-osteoid ⅱ.release matrix vesicle: 0.1um in diameter membrane-coated ALPase(Alkaline phosphatase), ATPase and pyrophosphatase and phosphoester (phospholipid) calcium, crystal of bone salt and calbindin function: promote calcification c.osteocyte ---structure: flattened cell with multiple long thin processes located in bone lacuna and bone canaliculus basophilic cytoplasm adjacent cells connect in bone canaliculus by gap junctions ---function: Maintain bone matrix regulate the balance of calcium phosphonium and d. osteoclast ---structure: LM: multinuclear large cell, 30-100um 6-50 nuclei acidophilic cytoplasm located at peripheral part of bone EM: ruffled border-processes light zone: --under the ruffled border --microfilament primary lysosome, pinosome and secondary lysosome RER, mito. and Golgi ---function: dissolve and absorb bone matrix ②Bone matrix ---organic matter: bone collagen fiber -collagenous fiber (type I collagen) ground substance: glycosaminoglycan glycoproteins: osteocalcin: involve in calcification of bone and regulate absorption of bone osteonectin: related to adherence between cell and bone matrix, regulate calcification of bone osteopontin ---inorganic matter: bone salts Hydroxyapatite crystal: Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 pin-shaped 10-20 nm longitudinal arranged *bone lamella: bone matrix arranged in layers at different direction 2) Architacture of long bone Long bone is an organ, made up of bone tissue(shaft and epiphyses), periosteum and endosteum, bone marrow ① shaft: consists of compact bone a. circumferential lamella: /outer concentrically-arranged /inner around inner surface of bone b. Haversian system (osteon): /cylindric structure, 3-5mm /central canal: N, BV, CT /Haversian lamella: 4-20 layers c. interstitial lamella: /irregular lamella /remnant of Haversian or circumferential lamella *perforating canal: /transverse canal /connect with Haversian canal ② epiphyses: composed of spongy bone ---trabeculae: formed by parallelly-arranged lamella form a spongy-liked network ---Bone marrow: hemopoietic tissue ③ periosteum and endosteum: CT membrane ---periosteum: DCT outer layer:more fiber bundles form perforating fiber inner layer: rich in BV, N and osteoprogenitor cells ---endosteum: thin, a layer of osteoprogenitor cell and CT ---function: provide nutrition and osteoblast for bone growth and repairing 3) osteogenesis ①basal processes ---formation: osteoprogenitor cell→ osteoblast → osteoid ↓ ↓calcification osteocyte + bone matrix bone tissue ---absorption: osteoclast →dissolve bone tissue→reconstruction ②basal manner a. intramembranous ossification: ---CT membrane →osteoprogenitor cell → osteoblast→ossification center→bone trabeculae →thicker and longer ---flattened bone and irregular bone formed in these manner b. endochondral ossification: e.g. long bone ⅰ.formation of cartilage model Mesenchymal cell→osteoprogenitor cell →chondroblast→chondrocyte→cartilage model( consists of hyaline cartilage and perichondrium) ⅱ.formation of bone collar osteoprogenitor cell (perichondrium) → osteoblast →bone tissue * These bone tissue surround the central segment of cartilage model as collar-shaped, so called bone collar ⅲ.formation of primary ossification center and bone marrow cavity chondrocytes of model center stop differentiation, enlarge in size, calcification, dead →CT, BV in periosteum enter degenerating zone→osteoblast, osteoclast, osteoprogenitor cell and mesenchymal cell enter at same time→ossification→primary ossification center primary bone marrow cavity(space between trabeculae) →bone marrow cavity ⅳ.Formation of secondary ossification center and epiphyses secondary ossification center appears at the two end of long bone(epiphyses) epiphyseal plate: cartilage layer between epiphysis and bone shaft, growing zone ③ Further growth of bone ---Become longer: by growth of epiphyseal plate from epiphyses to shaft, four zones can be seen: i. reserve cartilage zone: cell is small, round and basophilic ii. proliferating cartilage zone: cell is flattened, isogenous group cell arrange in single line iii. calcified cartilage zone: cell become large, mature, round and degenerated, strong basophilic iv. ossification zone: ---become thicker: periosteum cell → osteoprogenitor cell→osteoblast