Term 1Review - Waukee Community School District Blogs
advertisement

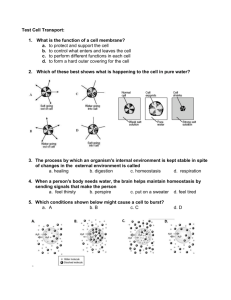
Modern Biology Term 1/3 Review Make sure you go over all of your learning targets. Characteristics of life Scientific Method Hypothesis vs. Theory Microscope techniques What are the characteristics of life? • Characteristics of Life ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Organization Cells Response to Stimuli Homeostasis Metabolism Growth and Development Reproduction Change Through Time Biology The study of life What are the levels of organization? Organization and Cells ATOM BIOLOGICAL MOLECULE ORGANELLE CELL ORGAN TISSUE What is Homeostasis? What is Metabolism? Homeostasis & Metabolism Homeostasis • The maintenance of a stable level of internal conditions even though environmental conditions are constantly changing. Metabolism • The sum of all the chemical reactions that take in and transform energy and materials from the environment. What is the Scientific Method? Steps of the Scientific Method 1. Observation: the act of perceiving a natural occurrence 2. Forming a Hypothesis 1. A statement that explains observations and data and can be tested 3. Test Hypothesis 1. Experimenting -Control group vs Experimental group 2. Independent variable vs dependent variable 4. Record and Study Data 5. Write a conclusion How do I determine the magnification of a microscope? What’s my power? To calculate the power of magnification, multiply the power of the ocular lens by the power of the objective. What are the powers of magnification for each of the objectives we have on our microscopes? Chapter 2 • • • • Atoms Periodic Table of Elements Enzymes and Activation Energy Properties of Water What is an atom and what 3 things make up an atom? ATOMS the simplest particle of an element that retains all of the properties of that element How do I use the Periodic Table? • I can determine the atomic number? ▫ I can determine the number of protons? • I can determine the atomic mass? ▫ I can determine the number of neutrons and electrons? • I can find the chemical symbol? Periodic Table of the Elements ▫ Atomic number: number of protons in the nucleus ▫ Chemical symbol: consists of 1,2, or 3 letters and is usually derived from the name of the element ▫ Atomic mass: the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 2 He Helium 4 What is Activation Energy? • Activation Energy: Amount of energy needed to make a reaction begin. Abbrev = Eact What do cells use to reduce the activation energy? • Enzymes ▫ Made of protein ▫ biological catalysts reduce the Eact to cellular temperatures speeds the reaction to maintain life What is Polarity? What molecule is polar? Why? POLARITY • In covalent bonds where the “sharing” is unequal (like in water). Because of this uneven pattern of charge, water is a polar compound. Chapter 3 • • • • Lipids Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic Acids What are carbohydrates? Carbohydrates Simple sugars What are lipids? Lipids • Are made up of fatty acids and glycerol ▫ Examples: saturated fats, waxes, cholesterol, hormones • Lipids are made up of long CH2 or Carbon chains • This is how we store excess glucose What are proteins? Long chains of amino acids What are nucleic acids? Nucleic Acids • Are made up of nucleotides • Examples are DNA and RNA ▫ DNA is are genetic information and stores all of the instructions the cells needs to do its job ▫ RNA help get the instructions to the cell The Discovery of Cells Organelles of a cell Two basic types of cells – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Relationships between size, shape, function, etc Distinguish between plant and animal cells Makeup of a multicellular organism – cells – tissues – organs – organ systems organism Who had great hair and who didn’t? The History of Cell Robert Hooke Anton von Leeuwenhoek • 1665 • Created the first microscope • Studied cork and saw “little boxes” • 1673 • Dutch trader, considered to be the father on microbiology • Made better lens Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells • What are prokaryotic cells? • What are eukaryotic cells? • How are the same and how are they different? Comparing Cells: Prokaryotes to Eukaryotes SAME FEATURES PROKARYOTES Plasma memb rane DNA Flagel l a Metabo lic functions Ribosomes , All Charac teristics of life, EUKARYOTES DIFFERENT FEATURES No membranebound organelles, Smaller upper limit, Pili, Mesosome, Nucleoid region, Binary fission, circular DNA + plasmids*, Membrane-bound organelles, Nucleus, Larger upper limit, Mitosis/Meiosis*, Linear DNA* Plant and Animals Cells • What type of cell are plant and animals cells? • How are they different? Comparing Cells: Plant to Animal Organelles unique to each PLANTS plastids like chloroplasts cell wall central vacuole ANIMALS centrioles Why do cells stay small? Passive and active transport Diffusion and Osmosis Hypo-, hyper-, and iso- tonic solutions Endocytosis vs Exocytosis What is Passive Transport? Give examples “Passive Transport” • Crossing cell membrane using NO energy. • EXAMPLES ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion through ion channels Explain diffusion Diffusion Explain osmosis Osmosis Solutions • • • • What is an isotonic solution? What is a hypotonic solution? What is a hypertonic solution? What happens to plant and animals cells in each type of solution? What is Active Transport? Give examples Active Transport • Uses energy; against concentration gradient What are endocytosis and exocytosis? Endocytosis Exocytosis The chemical equation The role of chlorophyll & accessory pigments The Light Reaction – roles of reactants and products The Dark Reaction – roles of reactants and products * The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration* Obtaining Energy • What is an autotroph? • What is a hetertroph? Obtaining Energy AUTOTROPHS Gets energy directly HETEROTROPHS Gets energy indirectly Visible Spectrum • Light can be reflected, transmitted or absorbed by the object • Pigments: compounds that absorb light. This subtracts them from the visible spectrum Why are plants green? Why do the leaves of trees change color in the fall? Visible Spectrum • Chlorophyll is a pigment ▫ Reflects green ▫ Absorbs blue and red • Carotenoids are accessory pigments ▫ Absorb green ▫ Enable plants to capture more energy What does this reaction represent? The process of photosynthesis • I can describe what is happening during light reactions • I can describe what is happening during dark reactions The chemical equation The major events of glycolysis Compare the types of fermentation Pathways of aerobic respiration Aerobic vs. anaerobic respiration Fermentation The process which cells release energy (from food molecules) by producing ATP without oxygen Anaerobic Lactic Acid Fermentation Alcoholic Fermentation