File
advertisement

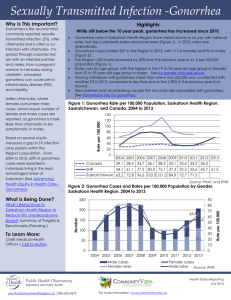
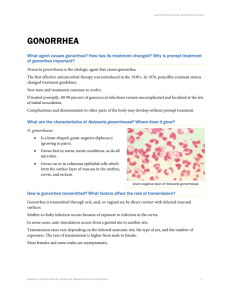
Sexually transmitted disease caused by a bacterium Grows in warm, moist body cavities of both men and women. Attacks the mucous membranes Curable (Crosta, 2009) Dates back to medieval times Known as the “clap” or “drip” The earliest treatment of gonorrhea was with the use of mercury 1879-Albert Neisser discovered gonococcus 1890’s-First Vaccine prepared from killed gonoccoci, taken from Neisser’s laboratory 1909- Vaccine introduced. 1940’s- Antibiotics came in to use (penicillin) (Mandal, n.d.) Anyone that engages in sexually activity ( anal, vaginal, or oral sex). Passed via sexual fluids (but does not require ejaculation to become infected or pass infection) Untreated mother to baby transmission In the United States, the highest reported rates of infection are among sexually active teenagers, young adults, and African Americans. (CDC,2014) Swab Samplesample from part of the body that is most likely infected. Gram StainSampled from the urethra or a cervix is placed on a slide and stained with dye. (Women’s Health, 2011) Urine testGonorrhea in the cervix or urethra can be diagnosed with a urine sample. Incubation period: 1 to 14 days More frequent urination than usual Pus-like discharge from the penis Pain or burning feeling while urinating Painful or swollen testicles Rectal infectionanal itching, bleeding, soreness, painful bowel movements, and discharge Oral infection: rarely shows symptoms, but can cause a sore throat One out of 10 men with gonorrhea has no gonorrhea (Planned Parenthood, 2012) symptoms Incubation period: 1 to 14 days Fever Abdominal pain Throwing up Bleeding between menstrual periods Menstrual irregularities Rectal infectionanal itching, bleeding, soreness, painful bowel movements, and discharge Painful intercourse Painful urination Vulva tenderness Urge to urinate Yellowish or yellow –green discharge Oral infection: rarely shows symptoms, but can cause a sore throat Four out of five women with gonorrhea have no gonorrhea symptoms. (Planned Parenthood, 2012) Untreated gonorrhea -Bacteria can spread to blood and joints -Inflammation of joints -Increased risk of HIV infection In women can cause pelvic inflammatory disease -Causes scar tissue in the fallopian tubes - Can cause an ectopic pregnancy - Can cause infertility In pregnant women the infection can be transmitted to the baby as it passes through the birth canal. These infections can lead to blood, joint, and eye infections. In men can cause epididymitis -painful condition of the testicles -swollen testicles -can cause infertility (NIAID,2011) Simple and Effective, when detected early. antibiotics -Cipro® XR 500 mg a single dose -Levaquin® 500 mg a single dose, -Tequin® 400 mg a single dose Consult with health care provider to decide which treatment is the best (STD,2011) Take full prescribed dosage of medicine. Do not share medication Consult doctor if symptoms persist Make sure partner(s) is/are tested/treated. -Get tested after three weeks to make sure the infection is gone. -No sexual activity until doctor confirmation that infection is gone (Planned Parenthood, 2012) Gonorrhea has progressively developed resistance to the antibiotic drugs Cephalosporin antibiotics have been the foundation of recommended treatment for gonorrhea. -Cephalosporin-resistant gonorrhea would significantly complicate the ability of providers to treat gonorrhea successfully. Increasing need to research and develop new treatments -decreasing antibiotic options Each year in the United States, at least 2 million people become infected with bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics and at least 23,000 people die each year as a direct result of these infections. (CDC,2014) (CDC,2014) CDC estimates that, annually, 820,000 people in the United States get new gonorrhea infections and less than half of these infections are detected and reported to CDC. CDC estimates that 570,000 of them were among young people 15-24 years of age. In 2012, 334,826 cases of gonorrhea were reported to the CDC (CDC,2014) Number of reported cases underestimates incidence Incidence remains high in some groups defined by geography, age, race/ethnicity, or sexual risk behavior Increasing proportion of gonococcal infections caused by resistant organisms (CDC,2014) (CDC,2014) (CDC,2014) Gonorrhea — Rates by Year, United States, 1941 – 2012 (CDC,2014) Gonorrhea — Rates by Sex, United States, 1992 – 2012 (CDC,2014) Gonorrhea — Rates by State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012 (CDC,2014) Gonorrhea — Rates by Age and Sex, United States, 2012 (CDC,2014) Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Gram-negative, intracellular, aerobic diplococcus. The bacteria adhere to columnar epithelial cells, penetrate them, and multiply on the basement membrane. Mainly affects the host’s columnar or cuboidal (Todar,2013) epithelium Humans are the only natural host, mainly sexual contact. (Mayo Clinic, 2014) Possible mother to child transmission. Females/ Male can contract gonorrhea during vaginal, oral, or anal sex with an infected partner. Gonorrhea most often affects the urethra, rectum or throat. In females, gonorrhea can also infect the cervix. (Mayo Clinic, 2014) (ASHA,2014) Organism is fragile and cannot survive outside of human host. -Affected by temperature changes, drying, UV light, and other environmental stresses. Organism cannot be transmitted from clothing, toilet seats, or household utensils to healthy person. Organism can affect any sexual active person, even if they are healthy. (Todar,2013) Engaging in risky sexual activity Lack of condoms use/ Lack of access to condoms. Lack of sexual education Lack of communication between partner(s) Lack of routine STI screenings Lack of access to medical care (CDC,2014) (Planned Parenthood, 2012) Abstaining from sexual activity Increase condom use Increase sexual education Increase routine STI screening Reduce infection rates Increase new effective treatments Reduce contact between infected and uninfected. Seek and receive treatment Take full treatment and do not engage in any sexual activity until cleared of infection. Development of Vaccination 1. 2. 3. 4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014, January 07).Gonorrhea - CDC fact sheet. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/stdfact-gonorrhea.htm Crosta, P (2009 , June ,29). What Is Gonorrhea? What Causes Gonorrhea?. retrieved February 05 2014, from Medical News Today Web Site: http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/155653.php Todar, K (2008-2012). Gonorrhea. retrieved February 06 2014, from Online Textbook of Bacteriology Web Site: http://textbookofbacteriology.net/neisseria.html Mandal, A Gonorrhea History. (n.d) retrieved February 08 2014, from News Medical Web Site: http://www.newsmedical.net/health/Gonorrhea-History.aspx 5.Planned Parenthood (2012). Gonorrhea. retrieved February 09 2014, from Planned Parenthood Web Site: http://www.plannedparenthood.org/health-topics/stds-hivsafer-sex/gonorrhea-4269.htm 6.Women's Health (2011). Gonorrhea Fact Sheet. retrieved February 09 2014, from Women's Health Web Site: http://womenshealth.gov/publications/ourpublications/fact-sheet/gonorrhea.html#e 7. NIAID (2011). Gonorrhea . retrieved February 07 2014, from National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Web Site: http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/gonorrhea/understanding/4.Pages/complications .aspx 8.STD (2011). Gonorrhea . retrieved February 07 2014, from Sexually Transmitted Diseases Guide Web Site: http://www.std-gov.org/stds/gonorrhea.htm 9. Mayo Clinic (2014). Gonorrhea. retrieved February 09 2014, from Mayo Clinic Web Site: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseasesconditions/gonorrhea/basics/causes/con-20020917 10. ASHA (2014). Gonorrhea. retrieved February 07 2014, from American Sexual Health Association Web Site: http://www.ashasexualhealth.org/std-sti/gonorrhea.html