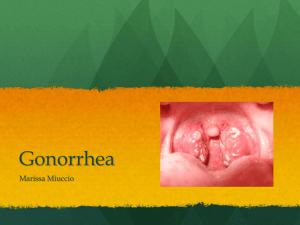
Gonorrhea
advertisement

Sexually Transmitted Infection -Gonorrhea Why Is This Important? Health Equity in Health Care Gonorrhea). Gonorrhea rates in Saskatoon Health Region have varied above or on par with national rates, but are consistently below provincial rates (Figure 1). In 2013, rates rose dramatically. Gonorrhea cases totaled 207 in the Region in 2013, with 111 in females and 96 in males (Figure 2). The Region’s 2013 rate increased by 35% from the previous year to 61.5 per 100,000 population (Figure 1). Rates vary by age group, with the highest in the 19 to 24 year-old age group in females and 20 to 29 year-old age group in males. See by gender and age group. Among individuals with gonorrhea, more than one in four (26.5%) was co-infected with another STI in 2013, compared to less than one in five (18%) in the previous year (not shown). New partners and alcohol/drug use are the two main risks associated with gonorrhea. See transmission risks for gonorrhea. Figure 1: Gonorrhea Rate per 100,000 Population, Saskatoon Health Region, Saskatchewan, and Canada, 2004 to 2013 Chief Medical Health Officer’s Call to Action 6 5.7 4 2 120 100 7.8 80 60 40 4.3 5.3 5.9 20 Saskatoon 0 Canada Rural2005 SHR 2006 2007 SHR 2008 2009 SK Canada 2004 2010 2011 2012 2013 29.1 28.5 34.7Geography 36.1 38.2 33.1 33.4 33.2 36.2 SHR 34.1 61.1 77.3 80.0 75.1 37.3 32.3 33.6 45.7 61.5 lth Region, Saskatchewan and Canada, 2011 Saskatchewan 63.2 72.8 96.6 103.3 131.3 84.9 72.7 71.5 Source: PHAC and iPHIS Figure 2: Gonorrhea Cases and Rates per 100,000 Population by Gender, Saskatoon Health Region, 2004 to 2013 10 250 Percent (%) Number To Learn More: 8 0 What Is Being Done? What’s Being Done In Saskatoon Health Region to Reduce STIs and Bloodborne Illness?; Summary of Targets & Benchmarks (Pending ) 140 10 90 80 8 200 6 150 4 5.7 4.3 5.3 5.9 96 7.8 70 65.9 60 57.2 50 40 30 0 20 111Canada Rural SHR SHR SK 50 Saskatoon 10 Geography 0 0 lth Region, Saskatchewan Canada, 2011 2010 2011 2012 2013 2004 2005 2006and 2007 2008 2009 2 100 Male cases Female rates Rate per 100,000 Based on several equity measures a gap in STI infection rates persists within the Region’s population. From 2004 to 2010, 62% of gonorrhea cases were reported in individuals living in the least advantaged areas of Saskatoon (See Advancing While still below the 10 year peak, gonorrhea has increased since 2010. Rate per 100,000 Unlike chlamydia, where females outnumber male cases, almost equal number of female and males cases are reported, as gonorrhea is more likely than chlamydia to be symptomatic in males. Highlights Percent (%) Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported sexually transmitted infection (STI), after chlamydia and is often a coinfection with chlamydia. It is spread through unprotected sex with an infected partner, and, rarely, from a pregnant woman to her baby during childbirth. Untreated gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility. Female cases Male rates Source: iPHIS Health Status Reporting July 2014 pho@saskatoonhealthregion.ca │306.655.4679 For more information: www.communityview.ca