Product Ideation 1 Module Specification - University of Brighton
advertisement

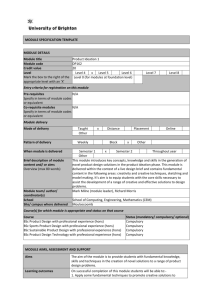
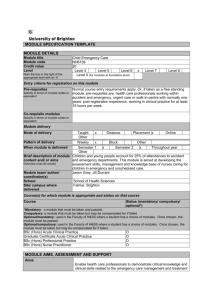
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Product Ideation 1 Module code DP162 Credit value 20 Level Level 4 x Level 5 Level 6 Mark the box to the right of the Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) appropriate level with an ‘X’ Level 7 Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites N/A Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules N/A Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught Other Pattern of delivery Weekly When module is delivered Brief description of module content and/ or aims Overview (max 80 words) Module team/ author/ coordinator(s) School Site/ campus where delivered x Distance Block Placement x Online Other Semester 1 Semester 2 Throughout year x Other This module introduces key concepts, knowledge and skills in the generation of novel product design solutions in the product ideation phase. This module is delivered within the context of a live design brief and contains fundamental content in the following areas: creativity and creative techniques, sketching and model making. It’s aim is to equip students with the core skills necessary to assist the development of a range of creative and effective solutions to design problems. Mark Milne (module leader), Richard Morris School of Computing, Engineering, Mathematics (CEM) Moulsecoomb Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course BSc Product Design with professional experience (hons) BSc Sports Product Design with professional experience (hons) BSc Sustainable Product Design with professional experience (hons) BSc Product Design Technology with professional experience (hons) Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims The aim of the module is to provide students with fundamental knowledge, skills and techniques in the creation of novel solutions to a range of product design problems. Learning outcomes On successful completion of this module students will be able to:1. Apply some fundamental techniques to promote creative solutions to defined product design problems. 2. Demonstrate and apply fundamental skills in product sketching. 3. Apply fundamental skills in the creation and manufacture of basic models to support product ideation. Content The content of the module will include:Creativity • Introduction to creativity and creative techniques • Brainstorming etc. Sketching • Different sketching types • Perspective • Viewpoint • Shading and shadow • Using markers and colour • Basic elements – cylinders, spheres…. Modelling – Creating space models • Foam models • Working with wood • Fabrication with plastics Learning support The details of the entire set of product design courses have been mapped out in project management software to enable students to see with complete transparency the structure of the courses and the development of content throughout the years. Most importantly this facility will support a rich planning and project management experience for students throughout their degree programme. The module will make extensive use of studentcentral to facilitate a blended learning environment. Lectures will where possible be recorded and made available through studentcentral, as will links to all taught, tutorial and reference material. The module will aim to make use of a technology oriented blended learning format (e.g. use of flip lectures) to provide students with as much supporting material as possible prior to lessons to maximise the effectiveness of the contact time with staff. The module will be linked where appropriate to products that students have designed in previous modules. Where possible industrial and exhibition visits, guest lectures and additional support sessions will be arranged in rotation to provide a rich and cutting edge learning environment for students. Reading lists:Creativity • Silverstein, D. 2012, The Innovator’s Toolkit: 50+ Techniques for Predictable and Sustainable Organic Growth. ISBN 978-1118298107 Sketching • Eissen, K and Steur, R. 2012, Sketching – The Basics. ISBN 978 90 6369 253 7 • Pipes, A. 2007, Drawing for Designers. ISBN 978-1-85669-533-6 Modelling • Hallgrimsson, B. 2012. Prototyping and Modelmaking for Product Design. ISBN 978-1-85669-876-4 General:Financial Times Design Week, New Design, ICON and WIRED magazines Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities The module consists of Lectures, Seminars, Tutorials, Demonstrations, Practical classes and workshops, Supervised time in studio/workshops, Guided independent study, Allocation of study hours (indicative) Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours Study hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, external visits, and work-based learning. 24 (12%) GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 176 (88%) PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University that is not workbased learning or a year abroad. N/A TOTAL STUDY HOURS 200 hours Assessment tasks Details of assessment for this module The portfolio of work (LOs 1,2,3) required for this module will include evidence of product ideation consistent with the content delivered throughout. This may be a combination of written, graphical, electronic, web based formats as well as physical prototypes and models applied to their specialist area of product design. Types of assessment task1 Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. % weighting (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN Select the single most appropriate assessment task per weighted CAMS component 0% COURSEWORK Select the single most appropriate assessment task per weighted CAMS component PRACTICAL Select the single most appropriate activity type per weighted CAMS component Portfolio 100% 0% 1 Set exercises, which assess the application of knowledge or analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills, are included under the type of assessment most appropriate to the particular task. EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board Engineering and Product Design Refer to Faculty Office for guidance in completing the following sections External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Date tenure ends Professor Peter Ford Professor of Design and group coordinator, De Montfort University 2013 2016 QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision Only complete where this is not the first version Date of approval for this version Version number 1 Modules replaced DP131, DP133, DP135 Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Yes x No