Anatomy of the Chest in Computed Tomography
advertisement

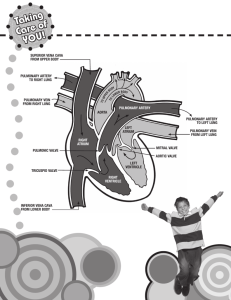
Anatomy of the Chest in Computed Tomography Michael C. Ficorelli, RT Lesson Description To explain the various exams pertaining to the chest and thorax using computed tomography, incorporating cross sectional anatomy from images Lesson Description • To be able to identify anatomy of the thoracic cavity. Understand the clinical indications for exams of the chest. To understand the methods of patient scanning, positioning, and protocols. To understand indications for contrast. • Chapter 16 CT of the Chest Bony Thorax / Visceral Thorax Bony Thorax • Protects and aids in the organs of respiration – Thoracic vertebrae – ( 12 ) - Posterior boundary – Sternum – Anterior boundary with 3 components • Manubrium – superior articulates with clavicles and first pair of ribs, contains jugular notch (level T2 – T3) – Sternal Angle – where manubrium and body come together ( T4 – T5 ) • Body – articulates with the cartilage of the 3rd through 7th ribs • Xiphoid – muscle attachments – Ribs – ( 12 pair ) – head, neck, tubercle and body • First 7 pair = True ribs • Lower 5 pair = False ribs – Costal Cartilage Thoracic Apertures • 2 openings • Superior – Thoracic Inlet – Formed by first thoracic vertebrae, First pair of ribs w/ costal cartilage, and Manubrium – Allows passage of nerves, vessels and viscera from the neck • Inferior – Thoracic Outlet – Much Larger than the Inlet, made up of 12th thoracic vertebrae, 12th pair of ribs and xiphoid sternal junction Pleural Cavities • Pleura – serous membrane in which each lung lies which secrete fluid to provide lubrication for the lungs while breathing – Parietal Pleura – outer layer; continuous with thoracic wall and diaphragm; moves with inspiration – Visceral pleura – inner layer; closely covers outer surface of lung and falls into the fissures Lungs Lungs • Conical shaped organs of respiration composed of spongy like material called parenchyma – Apex – above level of first rib – Bases – aka diaphragmatic surfaces – dome of the diaphragm – 3 borders • Inferior • Anterior • Posterior – 2 Angles • Cardiophrenic sulcus – medial • Costophrenic sulcus - lateral Lungs – Divided into lobes by fissures lined by pleura • Right – 3 lobes – Inferior lobe separated from middle by oblique fissure – Middle lobe separated from superior by horizontal fissure • Left – 2 lobes – Lobes separated by oblique fissure – Cardiac Notch – located on medial surface – Lingula – tongue-like projection on infero-anterior surface • Hilum – opening on the medial surface of each lung which acts as a passage for main bronchi, blood vessels, lymph and nerves entering and exiting Bronchi • Trachea bifurcates into right and left mainstem bronchus at carina ( T-5 ) – Right mainstem is wider, shorter and more vertical than the left • Enter the lungs and divide into secondary bronchi • Secondary divides into tertiary or segmental bronchi which extend into each of the approximately 10 segments within the lung • Continues to divide into smaller bronchi then into bronchioles which continue to divide into alevoli ( functional units of the respiratory system ) Secondary Pulmonary Lobule • Basic unit of pulmonary structure and function • Surrounded by connective tissue and consists of 3 – 5 acini ( which contain alveoli ) for gas exchange • Visualized with High-Resolution Chest CT – ILD (Interstitial Lung Disease) Mediastinum • Midline region of the thoracic cavity between the two pleural cavities of the lungs which is further divided into 2 compartments – Contains the thymus gland, trachea, esophagus, lymph nodes, thoracic duct, heart, great vessels and various nerves – Bounded by the sternum anteriorly and posteriorly by the thoracic vertebrae – Superior compartment – contains thymus gland and acts as a conduit for entrance and exits of structures – Inferior compartment – subdivides • Anterior - anterior to pericardial sac and posterior to sternum • Middle – contains pericardial sac, heart and root of great vessels • Posterior – posterior to pericardium and anterior to the inferior 8 thoracic vertebrae Mediastinum Thymus Gland and Lymph Nodes of Chest • Thymus = Triangular shaped bilobed gland located in superior mediastinum – Responsible for immunity, produces thymosin (maturation of lymphocites) • Lymph nodes in mediastinum are clustered around the great vessels – Difficult to see in scan unless abnormal • Thoracic Duct – main vessel of lymph system – Begins inferior to diaphragm Lymph Chain of Chest Heart • Four chambered muscular organ lying obliquely in the chest with 2/3 of its mass situated on the left – Base – Posterior aspect – Apex – formed by left ventricle – Sternocostal – Anterior surface formed by right atrium and ventricle with small portion of left ventricle – Diaphragmatic – rests on diaphragm and formed by both ventricles and right atrium – Pulmonary – left surface; left ventricle and rests in the cardiac notch of the lung Pericardium Pericardium • Sac which encloses the heart and proximal portions of the great vessels • Fibrous pericardium – attached to central tendon of diaphragm through which the IVC emerges – Serous pericardium – double layered inner surface of the fibrous pericardium • Parietal layer – Inner surface of fibrous pericardium • Visceral layer – covers outer surface of the heart and roots of the great vessels • Pericardial cavity – between the two layers and contains serous fluid for lubrication Heart Wall • 3 layers – Epicardium – thin outer layer – Myocardium – thick middle layer made of cardiac muscle – Endocardium – thin inner lining which also lines the heart valves and inner lining of the vessels Heart Chambers • 4 chambers – Right / Left Atrium and Right / Left Ventricles – Atrium – Superior chambers • Right Atrium – receives de-oxygenated blood from the Vena Cava (Inf. and Sup.), coronary sinus and cardiac veins • Left Atrium – Posterior to right, receives oxygenated blood from lungs from the pulmonary veins (4 total) – Ventricles – Inferior chambers • Right Ventricle – Lies on diaphragm, receives de-oxygenated blood from the atrium and displaces it to the pulmonary architecture in the lungs • Left Ventricle – Receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps it into the Aorta Cardiac Valves • 4 valves of the heart – Atrioventricular (2) • Entrances to ventricles – Tricuspid – right – Bicuspid (Mitral) – left – Semilunar (2) • Ventricles to Great Vessels – Pulmonary semilunar – right – Aortic semilunar - left Blood Path in Heart 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. SVC Rt. Atria Tricuspid Valve Rt. Ventricle Pulmonary Valve Pulmonary Artery Lungs Pulmonary Veins Lt. Atrium Mitral Valve Left Ventricle Aortic Valve Ascending Aorta Great Vessels • Aorta – Largest artery of the body divided into ascending, aortic arch and descending – Ascending - begins at base of left ventricle • Aortic root divides into 3 sinuses for coronary flow – Aortic Arch – ( T-3 ) superior, posterior curve of the ascending aorta located over the right pulmonary artery and the left mainstem bronchus – Descending – passes slightly anterior and to the left of the vertebrae and continues through both the thoracic and abdominal cavities Aorta Great Vessels • Branches of Aortic Arch – 3 main branches – Brachiocephalic (Innominate) Artery – First major vessel arising from arch which divides into the right common carotid and right subclavian arteries • Right Common Carotid – extends superiorly until C-4 where it divides into right external and internal carotids • Right subclavian – becomes right axillary artery – Left Common Carotid – Second vessel on arch extends superiorly until C-4 where it divides into left external and internal carotids – Left Subclavian Artery - becomes left axillary artery Aorta / Arterial Network of Neck Great Vessels • Pulmonary Trunk (Artery) – main pulmonary artery lying within the pericardial sac – Arises from the right ventricle and ascends in front of the aorta until T-4 where it bifurcates into the right and left pulmonary arteries • Right pulmonary artery – enters hilum of right lung and divides into 2 branches; upper feeds superior lobe, lower feeds middle and inferior lobes • Left pulmonary artery – shorter and most superior pulmonary vessel; enters hilum of left lung – Both arteries descend and divide into lobar and segmental arteries and continue to branch out into smaller divisions of the pulmonary tree Great Vessels • Pulmonary Veins – (4) – 2 superior and 2 inferior – Start as capillary network along alveoli and continue to merge until they form a single trunk for each lobe eventually combining until both pairs extend into the left atrium from the lungs Great Vessels • Vena Cava – Largest Vein in the body – Superior Vena Cava – formed by junction of brachiocephalic veins and carries blood from thorax, upper limbs, head and neck • Found posterior and lateral to ascending aorta before entering the right atrium – Inferior Vena Cava – formed by junction of common iliac veins in pelvis, ascends through the abdomen to the right of the abdominal aorta Vena Cava Chest Imaging • May be performed to assess the chest and its organs for tumors and other lesions, injuries, intra-thoracic bleeding, infections, unexplained chest pain, obstructions, or other conditions, particularly when another type of examination, such as X-rays or physical examination, is not conclusive – – – – Lung Infiltrates Surveys for metastatic disease Parenchyma disease Pleural disease Preparation • • • • • Patient is in the supine position and either feet or head first Arms over the head Scout from the thoracic inlet to adrenal glands on inspiration Assess patient to see if they and hold breath for need time Contrast indications – Pumonary emboli – Mediastinal and hilar masses – Lung infiltrates ( differentiating infiltrate from lung cancer ) – Lung nodules • High resolution scans can be done supine and prone Chest Protocol Parameters Single Slice 4 SLICE • Lung nodules APEX TO ADRENAL GLANDS SAME SCANNING AREA • Cancer 100ML AT 2ML/SEC @ 45 SAME CONTRAST • Vascular disease SECOND DELAY NA 4X1MM OR 1.25MM DETECTOR COLLI • Effusion and infiltration DEPENDS ON PATIENT SAME DFOV • Trauma 5 MM SAME SLICE THICKNESS • Pulmonary Parenchymal diseases NONE SAME ANGLE • Hilar Masses 6MM VARIES TABLE FEED/ROT PATIENT HEAD or FEET FIRST. SUPINE SAME 16 SLICE SAME SAME SAME 16X0.75 OR 16X1.25 SAME SAME SAME VARIES PITCH 1 OR 1.5 VARIES VARIES ROT TIME 1 SEC 0.5 SEC 0.5 SEC RECON STANDARD/LUNG SAME SAME WINDOW 450W/30L—1600W/600L SAME SAME Chest CT (Lower Neck) 1 2 1 – Trachea 2 – Jugular Vein 3 – Common Carotid 4 – Esophagus 3 4 Apex of Chest 1 2 3 4 1 – Right Subclavian 2 – Right Common Carotid 3 – Left Common Carotid 4 – Clavicle 5 - Scapula 5 Main Takeoffs of Heart 2 1 3 4 1 – SVC 2 – Rt. Innominate 3 – Lt. Common Carotid 4 – Lt. Subclavian 5 – Lt. Brachiocephalic Vein 5 Mag View of Takeoffs and Cava 7 2 1 1- SVC 3 2- Brachiolcephalic Artery 3- Lt. Common Carotid Artery 4 4- Lt. Subclavian Artery 5- Esophagus 5 6 6- Trachea 7- Lt.Brachiolcephaic Vein Aortic Arch 2 1 1 – SVC 2 – Aortic Arch 3 – Trachea 4 - Espohagus 3 4 Chest Pulmonary Trunk 1 1 – SVC 3 2 2 – Ascending Aorta 3 – Main Pulmonary Trunk 4 – Right Pulmonary Artery 5 – Carina 6 – Descending Aorta 6 4 5 7 7 – Left Pulmonary Artery Chest MidHeart 1-Rt.Ventricle 3 1 2- Rt.Atrium 2 3- Aortic Root 6 4-Lt. Atrium 5- Pulmonary Vein 6-Lt.Ventricle 4 5 Chest Heart 1 2 3 1 – Rt. Atrium / SVC 2 – Aortic Root 3 – Lt. Ventricle 4 – Rt. Pulmonary Vein 5 – Lt. Atrium 4 5 Chest Heart 2 3 1 4 1 – Right Atrium 2 – Aortic Root 3 –Right Ventricle 4 – Left Ventricle 5 – Right Pulmonary Vein 6 – Left Atrium 5 6 Chest Heart 1 2 3 1 – Right Ventricle 2 – Septum 3 – Left Ventricle 4 – Left Atrium Chest Inferior 2 1 1 – Liver 2 – Stomach 3 – Descending Aorta 4 – Spleen 5 5 – Splenic Flexure 4 4 3 Lung Windows 1 – Posterior segmental bronchus of right upper lobe 2 – Anterior segmental bronchus of right upper lobe 3 – Rt. Mainstem bronchus 4 – Lt. Main Bronchus 5 – Superior lobe Lt. Lung 6 – Inferior Lobe Lt. Lung From Google… Lung Windows Nodule Pulmonary Embolism Protocols • Pulmonary Embolism (PE) – sudden blockage in a lung artery, normally from a blood clot traveling to the lungs from the legs (DVT) – Can be fatal as low oxygen levels in the blood could be a byproduct of a large clot Pulmonary Embolism Protocols • Considered CTA of Chest (Pulmonary Arteries) – Results are best when MDCT is utilized for exam – Approximately 50 – 150 cc of contrast injected through a large bore IV cannula (generally 18 gauge however 20 gauge can be used) at a rate up to 8 cc per second…(practically 3.5 – 5) – When utilizing bolus tracking, scan is started when intensity of contrast is optimized in a region of interest taken in the main pulmonary artery** • **Localized at level of carina – Generally slices between 0.5 mm to 3 mm are utilized with thinner slices being preferred • Reformats especially in coronal plane Pulmonary Embolism Protocols High Resolution Chest CT • HRCT is utilized for the diagnosis and assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) – Ex. Asbestosis, Sarcoidosis, Lupus, Pulmonary Fibrosis • Utilizes narrow slice widths (1 – 2 mm) in sections approximately 10 – 40 mm apart in a axial (conventional) acquisition in a high pass algorithm (Bone/Detail) – Soft tissues generally present a great amount of noise due to the algorithm so it is not utilized for routine diagnosis Parameters PATIENT Single Slice HEAD or FEET FIRST. SUPINE PRONE FOR ASBESTOSIS 4SLICE SAME • Lung nodules APEX TO ADRENAL GLANDS SAME SCANNING AREA • Cancer NONE SAME CONTRAST • Vascular disease NA 2X0.5MM OR .625MM DETECTOR COLLI SKINinfiltration TO SKIN SAME DFOV • Effusion and 1 MM SAME SLICE THICKNESS • Trauma NONE SAME ANGLE • Pulmonary10Parenchymal diseases MM SAME TABLE FEED/ROT 1NA VARIES • Hilar Masses PITCH 16 SLICE SAME SAME SAME 1MM SAME SAME SAME SAME VARIES ROT TIME 1 SEC 0.5 SEC 0.5 SEC RECON HIGH RESOLUTION/LUNG SAME SAME WINDOW 1600W/600L SAME SAME High Resolution Chest CT Chest Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Chest (cont’d) Case Presentation 1. Pulmonary Embolus Protocol 2. Hi-Resolution Chest 3. “Low Dose” Chest