Spinal Cord Injuries
advertisement
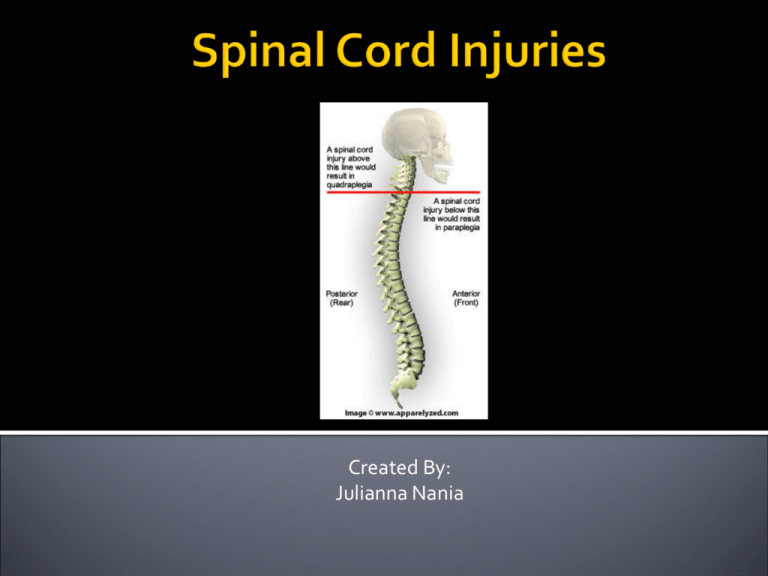
Created By: Julianna Nania SCI – Spinal Cord Injuries Spinal cord is, “The major bundle of nerves carrying impulses to and from the brain to the rest of the body. Rings of bone, called vertebrae, surround the spinal cord. These bones constitute the spinal column or back bones.” Causes: Can be congenital: ▪ Polio or Spina Bifida Can be acquired: ▪ Car accidents, sports injuries, sometimes arthritis SCI statistics Anatomy of the Spine: The spine consists of 33 vertebrae, including the following: 7 cervical (neck) 12 thoracic (upper back) 5 lumbar (lower back) 5 sacral* (sacrum-located within the pelvis) 4 coccygeal* (coccyx-located within the pelvis) Complete Total lack of sensory and motor function below the level of injury ▪ Quadriplegic Incomplete Spinal cord still has the ability to convey messages to and from the brain is not completely lost Some movement and sensation is still possible below the level of injury Classifications: Quadriplegia- all four limbs are affected ▪ Loss of movement and sensation ▪ Occurs at T1 or above ▪ Also affect breathing and chest muscles Paraplegia- 2 limbs are effected (legs) ▪ Loss of movement and sensation ▪ Occurs at T1 and below Triplegia- 3 limbs are affected (one arm and two legs) ▪ Loss of movement and sensation ▪ Results from incomplete SCI Muscle weakness Loss of feeling in the trunk, arms, or legs Muscle spasticity Breathing problems respiratory infections Problems with heart rate and blood pressure Digestive problems ulcers Pressure Soars If an accident happens and SCI occurs: “25% to 57% of persons with SCI might have a concomitant traumatic brain injury” “Difficulties with attention, concentration, memory, problem solving, abstract reasoning, new learning, and high-level cognitive skills” Will have to go through rehabilitation for memory if traumatic brain injury occurs with SCI. Learn basic skills such as eating, talking, processing, along with physical movement If born with SCI cognitive functions are usually normal unless born with a cognitive disability as well Can be very social still with SCI SCI students can educate friends or family SCI students can ask for help or inform their friends/family if they can do things independently Paraplegic can be independent and social in a wheelchair Play sports such as wheelchair basketball, sit volleyball, modified skiing, etc. Quadriplegic will be dependent on many people due to the lack of movement in their body Quadriplegic will not be able to physically exercise on their own Respiratory fitness ▪ Beat-boxing Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) Exercise Paraplegic Lower body is affected with physical exercise Can still use upper body Lifting Weights Wheelchair pushing Wheelchair aerobics Swimming Hand cycling Area’s of fitness Affected Cardiovascular conditioning Muscle strength Muscle endurance is Stretching for flexibility Arm bicycles Rowing Machines (Wheelchair accessible) Weight lifting Free weights Stretching Reduces spasticity in the muscles Sports Wheelchair Tennis Wheelchair Basketball Power chair Soccer Find these activities through a local gym (weight lifting), yoga programs Special Olympics Respect SCI student’s personal space- teacher and other students Only touch wheelchair if student asks for help Lower nets for students in wheelchairs Students without SCI can play on their knees Larger Ball Volleyball – Omnikin ball Softball Use a tee, put bases closer together No activities that will cause further damage to the spine Protective wheelchairs for certain sports ▪ Wheelchair basketball ▪ Powerchair Soccer Only do what is comfortable Know what their body can handle ▪ Ex: when lifting National Spinal Cord Injury Association Support groups Part of their Mission: “We provide active-lifestyle information, peer support and advocacy that empower individuals to achieve their highest potential in all facets of life.” http://www.spinalcord.org/ American Spinal Cord Association Provides a professional Journal about spinal cord injuries Provides research all about spinal cord injuries Holds annual meetings http://www.asia-spinalinjury.org/index.php Chair Volleyball Adapted Volleyball for students with Spinal Cord Injuries ▪ Quadriplegic (upper body) ▪ Students in wheelchairs can stay in wheelchair Rules: Buttocks remains in chair at all times Net is the same height as normal or can be brought down 3 touches per side Goal is the same as normal volleyball Rally scoring 6 folding chairs per side Beach ball http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IMZj7cv8xeI Ann, M. Warren, J., Pullins, & T., Elliott (2008). Concomitant Cognitive Impairment in Persons with Spinal Cord Injuries in Rehabilitation Settings. Retrieved from http://people.cehd.tamu.edu/~telliott/documents/Warren-PullinsElliott%20chapter%20edited%202008.pdf http://www.cnn.com/HEALTH/library/spinal-cord-injury/DS00460.html - CNN Health http://www.christopherreeve.org/site/c.mtKZKgMWKwG/b.4514603/- Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/pain-management-spinal-cord-injurymedref - WebMD http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/conditions/physical_medicine_and_re habilitation/spinal_cord_injury_85,P01180/- John Hopkins Medicine http://sci.washington.edu/info/forums/reports/universal_fitness.asp#cardio – Northwest Regional Spinal Cord Injury System http://www.ncpad.org/111/860/Spinal~Cord~Injury~and~Exercise -NCHPAD http://dsp.berkeley.edu/TeachStudentsWithDisab.html - Berkeley University of California, Disabled Students’ Program http://www.auburn.edu/~brocksj/4360hastietext/brock02_final.pdf -Auburn University http://webpages.shepherd.edu/TDARNL01/volleyball.htm - Chair Volleyball







