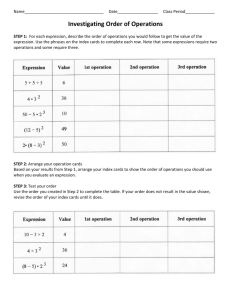
Unit 2:Music
advertisement

上海金融学院外语系 教案 一.课程名称:英语泛读(二) 二、课程类型:专业必修课 三|、授课专业和年级: 外语系 2011 级(秋) 四.授课时间: 2012 年 2 月-----2012 年 7 月 五、授课教师:蒋晓红 六、授课学时:34 学时 七、使用教材: 泛读教程(二)主编:王守仁 上海外语教育出版社 八、教学方法:课堂讲授,启发式教学,课堂讨论,研究性教学,当堂测试,提问式教学,师生互动。 九、教学手段:教师讲解、课堂讨论、阅读训练相结合,使用大屏幕投影仪 PowerPoint 教学课件来辅助课堂讲解。 十、考核方式:集中闭卷考试 Unit 1:Reading I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 1 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information The Importance of Reading Extensively Reading is important in English learning. Students should try to develop their reading skills: Educational researchers have found that there is a strong correlation between reading and academic success. In other words, a student who is a good reader is more likely to do well in school and pass exams than a student who is a weak reader. Good readers can understand the individual sentences and the organizational structure of a piece of writing. They can comprehend ideas, follow arguments, and detect implications. They know most of the words in the text already, but they can also determine the meaning of many of the unfamiliar words from the context. They can extract from the writing what is important for the particular task they are employed in. And they can do it quickly! Educational researchers have also found a strong correlation between reading and vocabulary knowledge. In other words, students who have a large vocabulary are usually good readers. This is not very surprising, since the best way to acquire a large vocabulary is to read extensively, and if you read extensively you are likely to be or become a good reader! Reading extensively will help students develop the reading competence that is essential for academic achievement. narcotic reading This is done by a person who wants to get rid of his everyday troubles, depressions, frustrations, problems, through reading magazines, stories, novels, essays and others. Seemingly, he considers the reading materials as having narcotic effect like a drug or opium that dulls the senses and makes one unconscious or unaware of realities in life. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 How to benefit from a developmental reading course Four areas of the reading process: A. The visual process: to move our eyes scientifically in reading B. Word knowledge and experience: have a good vocabulary C. Establishing a purpose for reading: To have a purpose or goal for reaing D. Comprehension fundamentals : a. Literal understanding b. Critical understanding c. Aesthetic understanding Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference literal meaning/narcotic reading/narcosis adjust/adaptability/irony diagnosis(diagnose ) consistent/reverse/regression vocalize/vocalization adolescence 2 Use of English: Take Take on/ take in/ take up/ take back/ take turns/ take st. for granted Stem cent/centi, claim/clam, firm Synonyms flexibility→ adaptability goal→ purpose tense→ strained retain→ hold conquer→ defeat Step 4. Reading skills 1. Develop Reading Skill –Finding the Main Idea In Book I ,we have already learned to distinguish between the topic and the main idea in a reading passage. The topic is the subject of a passage .The main idea is the writer’s opinion ,judgment, or idea about the topic. It is the controlling idea that the writer wishes to prove or explain .The details are the poof or explanation that supports this general concept. The maid idea is a generalization, whereas the supporting detail are more specific. Being able to tell the main idea from the specific details is another essential skill to aid comprehension. 2. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1) About the relationship between reading comprehension and reading speed 2).How to improve guessing ability(predictive ability ) in reading 3). How to read silently without moving lips. 4). How to adapt ourselves to do normally, thoroughly and rapidly. Step 5. Reading in Depth About reading tastes and habits Four kinds of reading: A. Reading for information B. Literary reading C. Intellectual reading D. Narcotic reading Step 6. Assignment 1. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 2. Cloze 3. Preview : Unit 2 :Music 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Newspapers and Headlines The major newspapers in Britain: Dailies: The Times The Guardian Financial Times 3 The Daily Telegraph Daily Express Daily Mail Daily Mirror Sundays: News of the World The Observer The Sunday People Sunday Mirror The Sunday Telegraph The Sunday Times The major newspapers in the United States: New York Times USA Today Washington Post Chicago Daily Tribune Los Angeles Times Detroit News Wall Street Journal New York Daily News Christian Science Monitor 上海金融学院外语系 教案 一.课程名称:英语泛读(二) 二、课程类型:专业必修课 三|、授课专业和年级: 外语系 2011 级(秋) 四.授课时间: 2012 年 2 月-----2012 年 7 月 五、授课教师:蒋晓红 六、授课学时:34 学时 七、使用教材: 泛读教程(二)主编:王守仁 上海外语教育出版社 八、教学方法:课堂讲授,启发式教学,课堂讨论,研究性教学,当堂测试,提问式教学,师生互动。 九、教学手段:教师讲解、课堂讨论、阅读训练相结合,使用大屏幕投影仪 PowerPoint 教学课件来辅助课堂讲解。 十、考核方式:集中闭卷考试 Unit 2:Music I: Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 4 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Music Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Common elements of music are pitch (which governs melody and harmony), rhythm (and its associated concepts tempo, meter, and articulation), dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture. The word derives from Greek. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Music can help solve world problems. Music brings the people of the world together, and perhaps with music we can also change the world and make it a better pace. Different types of music A. Country and folk music B. Rock ‘in’ roll(rock and roll music) C. Punk or New Wave (a new kind of rock music) D. Soul ,disco and rap E. MTV Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference teenager/adolescent /sensuous/sensual 5 folk/capacity/abuse/clarity/strive Semantic variations Stem pos(e), tract, Synonyms subtle→ discriminating general→ widespread harmony→ compatibility clarity→ clearness connection→ association Step 4. Reading skills 3. Develop Reading Skill –Finding the Main Idea In Book I ,we have already learned to distinguish between the topic and the main idea in a reading passage. The topic is the subject of a passage .The main idea is the writer’s opinion ,judgment, or idea about the topic. It is the controlling idea that the writer wishes to prove or explain .The details are the poof or explanation that supports this general concept. The maid idea is a generalization, whereas the supporting detail are more specific. Being able to tell the main idea from the specific details is another essential skill to aid comprehension. 4. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1). About the famous German composer Ludwig Van Beethoven 2).Spiritual and blues are two different types of music developed from the African rhythms that had formed the basis for the Negroes’ work songs. 3).About one of the world’s oldest instruments----trumpet 4).How does a composer make a piece of music 5). A traditional Chinese musical instrument----Erhu Step 5. Reading in Depth How to listen to music?( How to become a real music listener?) When we are listening to the music. We should listen in three ways ,that is the sensuous level, the expressive level and the musical level ,at the same time instinctively. Then we may become more active and more conscious to the music .When we are listening to the music ,not just listening, but listening for something. Step 6. Assignment 1. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 2. Cloze 3. Preview : Unit 3 :Generation 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others 6 Unit 3:Generation I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Generation Gap The generational gap refers to differences between people of a younger generation and their elders, especially between a child and their parent's generation. Although some generational differences have existed throughout history, because of more rapid cultural change during the modern era differences between the two generations increased in comparison to previous times, particularly with respect to such matters as musical tastes, fashion, culture and politics. This may have been magnified by the unprecedented size of the young generation during modern times, which gave it unprecedented power and willingness to rebel against social norms. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 About the conflict between a father and his daughter Question : How to bridge the generation gap and resolve differences ? 7 Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference obedient / disobedient/ docile/ conformist / excel certificate/ colleague/ veteran/well-meaning mobile / mobility extend/ compliment/ irritate/dominant/underestimate emotional/ sentimental obsolete/sloppy a repressive society/ a squalid environment Semantic variations Stem duce/duct, ject, mit, miss, peo Antonyms promising→ hopeless obedient → disobedient trivial → weighty oppose→ agree confused → clear Step 4. Reading skills 4. Develop Reading Skill –Finding the Main Idea In Book I ,we have already learned to distinguish between the topic and the main idea in a reading passage. The topic is the subject of a passage .The main idea is the writer’s opinion ,judgment, or idea about the topic. It is the controlling idea that the writer wishes to prove or explain .The details are the poof or explanation that supports this general concept. The maid idea is a generalization, whereas the supporting detail are more specific. Being able to tell the main idea from the specific details is another essential skill to aid comprehension. 5. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1).The old and the young can also find some common interests(have a lot in common ). 2). What are the causes of the generation gap in the u.S.? 3). To teenager’s disobedient (rebellious (behavior ),parents should adapt to their children 4).Young people often complain and irritate their parents to get enjoyment 5). It is impossible for children to be both excel and docile at the same time. (How to train children to be creative and imaginative ?) Step 5. Reading in Depth Generation gap between father and son a blue-collar father--------→ a white-collar son work to live --------→ live to work Step 6. Assignment 6. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 8 7. Cloze 8. Preview : Unit 4 :Weather and climate 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 4:Weather and Climate I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Climate and Weather Climate includes the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods. Climate can be contrasted to weather, which is the present condition of these elements and their variations over shorter periods. A region's climate is generated by the climate system, which has five components: Atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, land surface, and biosphere. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, terrain, and altitude, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and 9 the typical ranges of different variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 What make the weather ?(The factors which makes the weather ) A. The mountain and valleys B. The sun C. Clouds D. Wind Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference Weather forecast/ weather forecaster constant temperature/air pressure/atmosphere/vapor/humidity monsoon /rainfall/moist/moisture equator/ latitude/ altitude North Pole / South Pole / Northern Hemisphere/ Southern Hemisphere fluctuate/ fluctuation/ saturate/ saturation prevail/vertical/ expand/ bizarre/approximately Semantic variations Stem vid/vis, tain/tent Synonyms combination→ mixture permanent→ eternal influence→ impact moisture→ humidity distant→ remote Step 4. Reading skills Develop Reading Skill –Finding the Main Idea In Book I ,we have already learned to distinguish between the topic and the main idea in a reading passage. The topic is the subject of a passage .The main idea is the writer’s opinion ,judgment, or idea about the topic. It is the controlling idea that the writer wishes to prove or explain .The details are the poof or explanation that supports this general concept. The maid idea is a generalization, whereas the supporting detail are more specific. Being able to tell the main idea from the specific details is another essential skill to aid comprehension. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1).About Beijing’s bizarre weather (choking particles everywhere) 2). About the climate change in some American states 3). About Indian Summer 4). About global warming caused by ‘greenhouse effect’ 5) The difference between climate and weather Step 5. Reading in Depth 10 Types of Climate Climate is the combination of temperature, moisture, wind, and sunshine at a place over a period of many years . Different types of climate and their influence on people’s way of life and the factors which affect climate Elements of climate : temperature and the amount of rainfall Types of climate A. tropical climate B. subtropical climate C. mid-latitude climate D. high-latitude climate Causes of different climate A. Latitude B. Altitude C. Land D. Ocean currents E. Wind Step 6. Assignment 9. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 10. Cloze 11. Preview : Unit 5 : Work 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 5:Work I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 11 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Why do people work ? Work is the focus of our lives ,the source of people’s identity and creativity. Work not only provides happiness ad contentment for our physical life ,but also provide psychological well-being (pride and fulfillment ) for our spiritual life. Work is the opportunity to realize one’s potential. Work is a significant source of human satisfaction. Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference contentment/intangible/psychological well-being/ psychiatrist/sin accumulate/accumulation/contemplation/compulsion self-confidence/ ego/ corny/ambulance/acute/forfeit exert/ derive/ substitute/ flextime Use of English: Go go down/ go off/ go over/ go back on/ go round go out of business/ go bad to worse Stem press, cede, ceed, sist Synonyms elegant→ graceful impulsively→ spontaneously object→ oppose normal→ usual customer → client Step 4. Reading skills 12. Develop Reading Skill –Finding the Main Idea In Book I ,we have already learned to distinguish between the topic and the main idea in a reading passage. The topic is the subject of a passage .The main idea is the writer’s opinion ,judgment, or idea about the topic. It is the controlling idea that the writer wishes to prove or explain .The details are the poof or explanation that supports this general concept. The maid idea is a generalization, whereas the supporting detail are more specific. Being able to tell the main idea from the specific details is another essential skill to aid comprehension. 13. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea 12 B. Scanning: details 1).Women hold up half the sky(play an important role ) in the modern society. 2). About flextime (flexible working hours ) 3). About workaholic (people who are addicted to work ) 4) How to write a functional resume (to help job hunters to be employed ) 5). About office layout .(It is very important for the company to have a good layout, because the company needs good communication, smooth exchange of ideas and paper work, and flexibility demand a different planning. Its aim is to provide a pleasing working environment for all employees ) Step 5. Reading in Depth How to succeed in business ? A. To work hard and have a clean living B. To be a flexible person C. To conduct self-analysis on a regular basis D. To judge people correctly E. To have the ability of top management cohesiveness F. To have technical, managerial and professional skills G. To expand one’s knowledge H. To meet changes and challenges Step 6. Assignment 14. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 15. Cloze 16. Preview : Unit 6 : The African-Americans 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 6:The African-Americans I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 13 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Martin Luther King Martin Luther King, Jr. (January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American clergyman, activist, and prominent leader in the African-American Civil Rights Movement. He is best known for being an iconic figure in the advancement of civil rights in the United States and around the world, using nonviolent methods following the teachings of Mahatma Gandhi.[King is often presented as a heroic leader in the history of modern American liberalism. A Baptist minister, King became a civil rights activist early in his career. He led the 1955 Montgomery Bus Boycott and helped found the Southern Christian Leadership Conference in 1957, serving as its first president. King's efforts led to the 1963 March on Washington, where King delivered his "I Have a Dream" speech. There, he expanded American values to include the vision of a color blind society, and established his reputation as one of the greatest orators in American history. In 1964, King became the youngest person to receive the Nobel Peace Prize for his work to end racial segregation and racial discrimination through civil disobedience and other nonviolent means. By the time of his death in 1968, he had refocused his efforts on ending poverty and stopping the Vietnam War. King was assassinated on April 4, 1968, in Memphis, Tennessee. He was posthumously awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1977 and Congressional Gold Medal in 2004; Martin Luther King, Jr. Day was established as a U.S. federal holiday in 1986. Great Depression The Great Depression was an economic slump in North America, Europe, and other industrialized areas of the world that began in 1929 and lasted until about 1939. It was the longest and most severe depression ever experienced by the industrialized Western world. Rose Park Rosa Louise McCauley Parks (February 4, 1913 – October 24, 2005) was an 14 African-American civil rights activist, whom the U.S. Congress called "the first lady of civil rights", and "the mother of the freedom movement". On December 1, 1955 in Montgomery, Alabama, Parks, age 42, refused to obey bus driver James Blake's order that she give up her seat to make room for a white passenger. Parks' action was not the first of its kind to impact the civil rights issue, and there had been others, including Lizzie Jennings in 1854, Irene Morgan in 1946, Sarah Louise Keys in 1955 and Claudette Colvin, on the same bus system nine months before Parks, who had taken similar steps. But Parks' civil disobedience had the effect of sparking the Montgomery Bus Boycott. Parks' act of defiance became an important symbol of the modern Civil Rights Movement and Parks became an international icon of resistance to racial segregation. She organized and collaborated with civil rights leaders, including boycott leader Martin Luther King, Jr., helping to launch him to national prominence in the civil rights movement. At the time of her action, Parks was secretary of the Montgomery chapter of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) and had recently attended the Highlander Folk School, a Tennessee center for workers' rights and racial equality. Nonetheless, she took her action as a private citizen "tired of giving in". Although widely honored in later years for her action, she suffered for it, losing her job as a seamstress in a local department store. Eventually, she moved to Detroit, Michigan, where she found similar work. From 1965 to 1988 she served as secretary and receptionist to African-American U.S. Representative John Conyers. After retirement from this position, she wrote an autobiography and lived a largely private life in Detroit. In her final years she suffered from dementia, and became involved in a lawsuit filed on her behalf against American hip-hop duo OutKast. Parks eventually received many honors ranging from the 1979 Spingarn Medal to the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the Congressional Gold Medal and a posthumous statue in the United States Capitol's National Statuary Hall. Her death in 2005 was a major story in the United States' leading newspapers. She was granted the posthumous honor of lying in honor at the Capitol Rotunda. African-American Civil Rights Movement (1955–1968) The African-American Civil Rights Movement (1955–1968) refers to the movements in the United States aimed at outlawing racial discrimination against African Americans and restoring voting rights in Southern states. This article covers the phase of the movement between 1954 and 1968, particularly in the South. By 1966, the emergence of the Black Power Movement, which lasted roughly from 1966 to 1975, enlarged the aims of the Civil Rights Movement to include racial dignity, economic and political self-sufficiency, and freedom from oppression by white Americans. The movement was characterized by major campaigns of civil resistance. During the period 1955–1968, acts of nonviolent protest and civil disobedience produced crisis situations between activists and government authorities. Federal, state, and local governments, businesses, and communities often had to respond immediately to crisis situations that highlighted the inequities faced by African Americans. Forms of protest and/or civil disobedience included boycotts such as the successful Montgomery Bus Boycott (1955–1956) in Alabama; "sit-ins" such as the influential Greensboro sit-ins (1960) in North 15 Carolina; marches, such as the Selma to Montgomery marches (1965) in Alabama; and a wide range of other nonviolent activities. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Martin Luther King: He was an American civil rights leader who worked to bring about social, political and economic equality for African-Americans by peaceful means. During the 1950s and 1960s ,his struggle for racial justice won the support of millions of persons ,both black and white. A Baptist minister ,he preached ‘nonviolent resistance’ .he won the 194 Nobel peace prize for leading the black struggle for equality through nonviolent means. Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference civil rights movement /nonviolent resistance/racial segregation/ legacy boycott/ unprecedented/ desegregate/menace preach /enroll/assault/ tax evasion Semantic variations Stem migr, port, scent, volv Antonyms violate→ observe bar →admit appoint→ dismiss denounce→ eulogize withdraw→ advance Step 4. Reading skills---------Recognizing the Pattern of Details Details are the proof or explanation of the main idea of a reading passage. There are many ways of organizing details. A. Space relationship B. Time Sequence C. Example or Illustration D. Comparison and Contrast E. Cause and Effect F. Addition Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1). About W.E.B.DuBois 2). The effect of World War I on the black urbanization and institutional development 3).About Affirmative action 4).About a famous American actor: Denzel Washington 5).About a famous figure in America :Jesse Jackson Step 5. Reading in Depth The first black woman receives Nobel Prize in Literature 16 Toni Morrison Toni Morrison (born on February 18, 1931) is a Nobel Prize and Pulitzer Prize-winning American novelist, editor, and professor. Her novels are known for their epic themes, vivid dialogue, and richly detailed characters. Among her best known novels are The Bluest Eye, Song of Solomon and Beloved. She also was commissioned to write the libretto for a new opera, Margaret Garner, first performed in 2005. Step 6. Assignment 17. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 18. Cloze 19. Preview : Unit 7 : Greek Stories 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 7: Greek Stories I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information 17 Greek stories (Ancient Greek Myths and Legends - The Stories of the Ancient Greeks) Greek myths and legends. Stories about the Greek gods and goddesses and the fantastic adventures of the heroes of Greek mythology, as well as glossary entries on many of the famous names from Greek mythology. Apollo is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities in Greek and Roman mythology. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun, truth and prophecy, medicine, healing, plague, music, poetry, arts and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, and in the modern Greco–Roman Neopaganism. Pandora In Greek mythology, Pandora (ancient Greek, "gift", thus "all-gifted", "all-endowed") was the first woman As Hesiod related it, each god helped create her by giving her unique gifts. Zeus ordered Hephaestus to mold her out of earth as part of the punishment of mankind for Prometheus' theft of the secret of fire, and all the gods joined in offering her "seductive gifts". Her other name, inscribed against her figure on a white-ground kylix in the British Museum, is Anesidora, "she who sends up gifts,"[3] up implying "from below" within the earth. According to the myth, Pandora opened a jar (pithos), in modern accounts sometimes mistranslated as "Pandora's box" (see below), releasing all the evils of mankind — although the particular evils, aside from plagues and diseases, are not specified in detail by Hesiod — leaving only Hope inside once she had closed it again.She opened the jar out of simple curiosity and not as a malicious act. Echo and Narcissus Echo and Narcissus is an episode from Ovid's Metamorphoses, a Latin mythological epic from the Augustan period. The introduction of the myth of the mountain nymph Echo into the story of Narcissus, the beautiful youth who rejected sexuality and falls in love with his own reflection, appears to have been Ovid's invention. Ovid's version influenced the presentation of the myth in later Western art and literature. Dionysus Dionysus was the god of the grape harvest, winemaking and wine, of ritual madness and ecstasy in Greek mythology. His name in Linear B tablets shows he was worshipped from c. 1500—1100 BC by Mycenean Greeks: other traces of Dionysian-type cult have been found in ancient Minoan Crete. His origins are uncertain, and his cults took many forms; some are described by ancient sources as Thracian, others as Greek. In some cults, he arrives from the east, as an Asiatic foreigner; and in others, from Ethiopia in the South. He is a god of epiphany, "the god that comes", and his "foreignness" as an arriving outsider-god may be inherent and essential to his cults. He is a major, popular figure of Greek mythology and religion, and is included in some lists of the twelve Olympians. His festivals were the driving force behind the development of Greek theater. 18 Poseidon Poseidon was the god of the sea, and, as "Earth-Shaker," of earthquakes in Greek mythology. The name of the sea-god Nethuns in Etruscan was adopted in Latin for Neptune in Roman mythology: both were sea gods analogous to Poseidon. Linear B tablets show that Poseidon was venerated at Pylos and Thebes in pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, but he was integrated into the Olympian gods as the brother of Zeus and Hades.[1] Poseidon has many children. There is a Homeric hymn to Poseidon, who was the protector of many Hellenic cities, although he lost the contest for Athens to Athena. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Orpheus and Eurydice Orpheus was a legendary musician, poet, and prophet in ancient Greek religion and myth. The major stories about him are centered on his ability to charm all living things and even stones with his music; his attempt to retrieve his wife from the underworld; and his death at the hands of those who could not hear his divine music. As an archetype of the inspired singer, Orpheus is one of the most significant figures in the reception of classical mythology in Western culture, portrayed or alluded to in countless forms of art and popular culture including poetry, opera, and painting. Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference Semantic variations Stem val/ vail, serv, tend/tens Antonyms allow→ forbid baffle→ clarity wander→ remain reveal→ conceal joy→ sorrow Step 4. Reading skills---------Recognizing the Pattern of Details Details are the proof or explanation of the main idea of a reading passage. There are many ways of organizing details. G. Space relationship H. Time Sequence I. Example or Illustration J. Comparison and Contrast K. Cause and Effect L. Addition Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1)Apollo 2).Pandora 3).Echo and Narcissus 4).Dionysus 19 5). Poseidon Step 5. Reading in Depth A Greek Story --------The Return of Odysseus Odysseus was a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the Odyssey. Odysseus also plays a key role in Homer's Iliad and other works in the Epic Cycle. King of Ithaca, husband of Penelope, father of Telemachus, and son of Laërtes and Anticlea, Odysseus is renowned for his guile and resourcefulness, and is hence known by the epithet Odysseus the Cunning (or "cunning intelligence"). He is most famous for the ten eventful years he took to return home after the ten-year Trojan War and his famous Trojan Horse trick. After reading you should: Know the stories Odysseus relates at the court of the Phaeacians. Know how he returned to Ithaca after leaving Phaeacia and killing the suitors. Recognize how the Odyssey can been seen to follow the pattern of a Mesopotamian cosmogonic myth. Step 6. Assignment 20. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 21. Cloze 22. Preview : Unit 8 : Attitude Towards Life 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 8: Attitude towards Life I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. 20 III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Theodore Roosevelt Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt (January 6, 1919) was the 26th President of the United States (1901–1909). He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity. He was a leader of the Republican Party and founder of the short-lived Progressive ("Bull Moose") Party of 1912. Before becoming President, he held offices at the city, state, and federal levels. Roosevelt's achievements as a naturalist, explorer, hunter, author, and soldier are as much a part of his fame as any office he held as a politician. Roosevelt was the first American to win the Nobel Prize in any field. Robert H. Schuller Robert Harold Schuller (born September 16, 1926 in Alton, Iowa) is an American televangelist, pastor, speaker, motivator and author. He is principally known for the weekly Hour of Power television program which he began in 1970. He is also the founder of the Crystal Cathedral in Garden Grove, California, where the Hour of Power program originates.[1] On January 22, 2006, Schuller announced his retirement. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 What is the good attitude towards life ? Three basic types of attitudes A. Attitude about ourselves B. Attitude towards others and things around us C. Attitude towards life itself Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference positive/negative optimist/optimistic/optimism pessimist/pessimistic/pessimism realist/realistic/consistent emerge/hectic/cultivate strength/weakness/weightless/treasure strenuous/tough/toughness/adversity/winner/loser 21 considerate/cooperative/ expansive/ open-minded/mature/persistent respectful/caring/sincere/truthful/ motivate/motivation/perceive/perception perseverance/determination/well-being inter-personal relationship/ emotional need/ psychological adjustment self-esteem/self-respect/ self-centered/ be doomed to do st. a flourishing business/a silver spoon in one’s spoon fortify/elicit/elevate/reverse/penetrate/preach/batter Semantic variations Stem Terr, scrib/scrip Antonyms vanish→ appear reluctant→ ready expose→ hide clumsy→ skillful deliberate→ careless Step 4. Reading skills---------Recognizing the Pattern of Details Details are the proof or explanation of the main idea of a reading passage. There are many ways of organizing details. M. Space relationship N. Time Sequence O. Example or Illustration P. Comparison and Contrast Q. Cause and Effect R. Addition Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1). The proper attitudes life is not to go to extremes, never to be too optimistic ,nor too pessimistic. It is better to be realistic towards life ,seeing the world as it really is. 2). Happiness depends on one’s attitude towards life. 3).a good attitude can be acquired from young and will produce good results. 4). Teenagers should be encouraged to develop an optimistic and progressive philosophy towards life. 5). Life is a journey to be tasted each step of the way, so we should have a right direction of the course of our life. Step 5. Reading in Depth To have a willing attitude towards life Attitude is an intangible thing ,but we can see the effects of attitude ,both positive and negative, in the results it creates in our lives. We should have the ability to have the will to win ,(develop a winning attitude ),which is the most important determining factor in success. “Will to win “ in action means an attitude of perseverance, determination to succeed. 22 “Tough times don’t last, tough people do ” . The ‘winners’ are those who are going strong in tough times and who can make the most miserable circumstances a challenge to survive and defeat adversity. Step 6. Assignment 23. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 24. Cloze 25. Preview : Unit 9 : First Aid 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 9: First Aid I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information First Aid First aid is the provision of initial care for an illness or injury. It is usually performed by non-expert, but trained personnel to a sick or injured person until definitive medical 23 treatment can be accessed. Certain self-limiting illnesses or minor injuries may not require further medical care past the first aid intervention. It generally consists of a series of simple and in some cases, potentially life-saving techniques that an individual can be trained to perform with minimal equipment. CPR(Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation心肺复苏术) Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure which is performed in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person in cardiac arrest. It is indicated in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example agonal respirations. It may be performed both in and outside of a hospital. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 First Aid Rules and methods (techniques ) 1. Basic rules 2. CPR and life support: Procedure A. Airway clearance B. Breathing/ Artificial respiration(mouth-to-mouth respiration) C. External hear massage( chesty compression) Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference victim/medical personnel/ drug/ antidote ambulance/emergency/urgent/foreign object/sterile dressing massage/yell/faint/thrust/trivial/dilute contaminate/poison/poisonous/ vomit/exhale/slap/compress/crack/smother vein/artery/abdomen/windpipe/navel/rib/lung fracture/blister/tetanus/rabies/wound infection/skin graft artificial respiration/heart arrest allergy/allergic reaction pedestrian/ fatality/ impair Use of English :Come come in for/ come to terms with/ come back/come to the boil come into effect/ come out Stem sol/sul, ser(t ), pet/peat Synonyms reader→ give halt → stop sterile→ antiseptic prevent→ block pierce→ penetrate Step 4. Reading skills---------Recognizing the Pattern of Details Details are the proof or explanation of the main idea of a reading passage. There are many ways of organizing details. S. Space relationship 24 T. Time Sequence U. Example or Illustration V. Comparison and Contrast W. Cause and Effect X. Addition Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1).About home accidents 2).The most difficult to learn about first aid is what not to do. 3).How to protect our home against fire and how to escape in case of fire 4).About eye irritation 5). About nosebleed Step 5. Reading in Depth How to deal with common emergencies ? A. Animal bites (Be bitten by an animal ) B. Bleeding (severe) C. Burns D. Choking on food (food stuck in one’s throat ) E. Drowning F. Electric shock G. Fainting and dizziness H. Heatstroke, sunstroke and heat exhaustion I. Insect sting allergy J. Poisoning Step 6. Assignment 26. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 27. Cloze 28. Preview : Unit 10 : Marriage 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 10: Marriage I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 25 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Protestant Protestantism is one of the three major groupings (Catholicism, Orthodoxy, and Protestantism) within Christianity. It is a movement that began in central Europe in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices. Roman Catholic Church The Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ,[2] administering the sacraments and exercising charity.[4] The Catholic Church is among the oldest institutions in the world and has played a prominent role in the history of Western civilisation.[5] It teaches that it is the church founded by Jesus Christ, that its bishops are the successors of Christ's apostles and that the Pope is the successor to Saint Peter. Catholic doctrine maintains that the Church is infallible when it dogmatically teaches a doctrine of faith or morals. Catholic worship is centered on the Eucharist in which the Church teaches bread and wine are supernaturally transubstantiated into the body and blood of Christ. The Church holds the Blessed Virgin Mary in special regard. Catholic beliefs concerning Mary include her Immaculate Conception and bodily Assumption at the end of her earthly life. Judaism Judaism is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people. Originating in the Hebrew Bible (also known as the Tanakh) and explored in later texts such as the Talmud, it is considered by Jews to be the expression of the covenantal relationship God developed with the Children of Israel. According to traditional Rabbinic Judaism, God revealed his laws and commandments to Moses on Mount Sinai in the form of both the Written and Oral Torah. This was historically challenged by the Karaites, a movement that flourished in the medieval 26 period, retains several thousand followers today and maintains that only the Written Torah was revealed. Eastern Orthodox The Orthodox Church, also officially called the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church, is the dominant Christian denomination in Greece, Romania, Moldova, Cyprus, Georgia, parts of Sicily and the Slavic countries of Russia, Belarus, Serbia, Bulgaria and Ukraine. It considers itself to be the One, Holy, Catholic and Apostolic Church established by Jesus Christ and his Apostles almost 2,000 years ago. Orthodoxy is the second largest Christian communion in the world, with an estimated 300 million adherents. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 A Happy Marriage—An old woman recalls her happy marriage life with her past husband. They had a peaceful, happy marriage throughout their lives..They make each day count. That is what the marriage really means. Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference Use of English: Keep keep company/keep a straight face/ keep sb .in the dark keep an open mind/ keep away from /keep one’s head Stem aster/astr, brief/brev/bridg/ fus(e ) Synonyms mischievous→ naughty heavenly→ divine shatter→ break deliver→ give capture→ seize Step 4. Reading skills---------Recognizing the Pattern of Details Details are the proof or explanation of the main idea of a reading passage. There are many ways of organizing details. Y. Space relationship Z. Time Sequence AA. Example or Illustration BB. Comparison and Contrast CC. Cause and Effect DD. Addition Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1). In the past, marriage contributed to the stability of society.(was a device to ensure the safety and security of women).In modern society, women no longer need marriage as a guaranteed security. 2).About the Muslim marriage 3). About Japanese Shinto wedding and Hindu marriage 27 4).About Greek wedding ceremony 5). About the Filipino wedding ceremony Step 5. Reading in Depth Wedding Ceremonies in the West A. Good luck to the Bride and Groom B. Legal Procedures C. Marriage Rites: a. protestant b. Roman catholic c. Jewish d. Eastern Orthodox Step 6. Assignment 29. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 30. Cloze 31. Preview : Unit 11 : Creativity 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 11: Creativity I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 28 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Encyclopedia Britiannia The Encyclopædia Britannica (Latin for "British Encyclopaedia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., a privately held corporation. Articles are aimed at educated adults, and written by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 expert contributors. It is regarded as one of the most scholarly of encyclopaedias. The Britannica is the oldest English-language encyclopaedia still in print. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, and grew in popularity and size, its third edition (1797) and supplement (1801) reaching 20 volumes together.[ UCLA ---- University of California, Los Angeles The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public research university located in the Westwood neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, USA. It was founded in 1919 as the "Southern Branch" of the University of California and is the second oldest of the ten campuses. UCLA, considered to be one of the flagship institutions of the University of California system, offers over 300 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in a wide range of disciplines and enrolls about 26,000 undergraduate and about 11,000 graduate students from the United States and around the world. Strengths in liberal arts and sciences and research strengths earned it membership in the Association of American Universities. MIT----Massachusetts Institute of Technology The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. MIT has five schools and one college, containing a total of 32 academic departments, with a strong emphasis on scientific and technological education and research. Benjamin Franklin Benjamin Franklin (January 17, 1706 – April 17, 1790) was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. A noted polymath, Franklin was a leading author, printer, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, musician, inventor, satirist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his discoveries and theories regarding electricity. He invented the lightning rod, bifocals, the Franklin stove, a carriage odometer, and the glass 'armonica'. He formed both the first public lending library in America and the first fire department in Pennsylvania. Franklin earned the title of "The First American" for his early and indefatigable campaigning for colonial unity; as an author and spokesman in London for several colonies, then as the first United States Ambassador to France, he exemplified the emerging American nation. Franklin was foundational in defining the American ethos as a marriage of the practical and democratic values of thrift, hard work, education, community spirit, self-governing institutions, and opposition to authoritarianism both political 29 and religious, with the scientific and tolerant values of the Enlightenment. In the words of historian Henry Steele Commager, "In a Franklin could be merged the virtues of Puritanism without its defects, the illumination of the Enlightenment without its heat." To Walter Isaacson, this makes Franklin "the most accomplished American of his age and the most influential in inventing the type of society America would become."[4] Franklin, always proud of his working class roots, became a successful newspaper editor and printer in Philadelphia, the leading city in the colonies. He was also partners with William Goddard and Joseph Galloway the three of whom published the Pennsylvania Chronicle, a newspaper that was known for its revolutionary sentiments and criticisms of the British monarchy in the American colonies.[5] He became wealthy publishing Poor Richard's Almanack and The Pennsylvania Gazette. Franklin gained international renown as a scientist for his famous experiments in electricity and for his many inventions, especially the lightning rod. He played a major role in establishing the University of Pennsylvania and was elected the first president of the American Philosophical Society. Franklin became a national hero in America when he spearheaded the effort to have Parliament repeal the unpopular Stamp Act. An accomplished diplomat, he was widely admired among the French as American minister to Paris and was a major figure in the development of positive Franco-American relations. For many years he was the British postmaster for the colonies, which enabled him to set up the first national communications network. He was active in community affairs, colonial and state politics, as well as national and international affairs. From 1785 to 1788, he served as governor of Pennsylvania. Toward the end of his life, he freed his slaves and became one of the most prominent abolitionists. His colorful life and legacy of scientific and political achievement, and status as one of America's most influential Founding Fathers, have seen Franklin honored on coinage and money; warships; the names of many towns, counties, educational institutions, namesakes, and companies; and more than two centuries after his death, countless cultural references. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 How are bright ideas formed ? To have creative thought means to let unknown become known. In creative thought the unconscious is responsible for the production of new organized forms from relatively disorganized elements. Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference creative/ creativity/ memoir/ perceptive/ mighty/stable conscious/unconscious/exemplified instinctive/prelude/applaud/impulse doze/ evaluate/ resurgence/sketch MIT----Massachusetts Institute of Technology IQ--- Intelligence quotient Use of English: Make make peace/ make out/ make hair stand on end make things worse/ make most of st./ make no secret Stem clos/clud/clus, cor/ cord/cour Antonyms 30 retrieve→ lose prolific→ sterile vertical→ horizontal novel→ old diverse→ identical Step 4. Reading skills---------Outlining In reading a passage ,outlines are helpful if the reader wants to see how the details explain or develop the main idea, and to put these part into a whole, which makes it easier for readers to understand and remember the important ideas. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1)About a genius(with an IQ above 206)---Eugene Volokh 2). About Benjamin Franklin 3). The peak (time )for creative people varies with different professions. 4).We think with our mind, which is a function ,an activity. Step 5. Reading in Depth How to get a great idea ? A. To have creative thought and act upon them. B. To achieve our creative potential. C. Some best techniques to increase a person’s creativity a. Capture the fleeting b. Daydream c. Seek challenges d. Expand our world Step 6. Assignment 32. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 33. Cloze 34. Preview : Unit 12 : Travel 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 12: Travel I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills 31 II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Tourism Tourism is travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people who "travel to and stay in places outside their usual environment for more than twenty-four (24) hours and not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes not related to the exercise of an activity remunerated from within the place visited." Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Travel around U.S.A When we travel abroad, we should know what to take and how to take it. A. take as little as possible. B. Means of transportation: 1) For long distance travel : a. Bus b. Car c. Air 2) For inter-city (Urban )Travel : a. City buses b. Subway c. Taxis Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference tourism/tourist/tourist attraction/sightseeing /resort/natural scenery check in/check out/motel/budget/fare/consulate metropolis/metropolitan/cosmopolitan customs duty/souvenir/handcraft/boutique purchasing power/carnival/amusement park/a cruise ship/ Use of English: Put Put on/put off/put one’s finger on/ put behind/put forward/put pressure on Stem 32 Dic(t), frag/fract Synonyms major→ chief investigate→ examine reputation→ fame regional→ local unique→sole Step 4. Reading skills---------Outlining In reading a passage ,outlines are helpful if the reader wants to see how the details explain or develop the main idea, and to put these part into a whole, which makes it easier for readers to understand and remember the important ideas. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1).How to understand the implication of a question? 2). How do Gordon and Walter plan their travel ? 3).About travel in London 4).About in Germany 5).About travel in Greece Step 5. Reading in Depth Tourism Major tourist attractions are located in all around the world. Actually Almost any place can become a tourist attraction as long as it is different from the place where the traveler usually lives. People travel for any number of reasons, and there are numerous attractions that appeal to a wide variety of tastes. Step 6. Assignment 35. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 36. Cloze 37. Preview : Unit 13 : Examination 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 13: Examinations I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills 33 II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Test (/examination/ Assessment ) A test or an examination (or "exam") is an assessment intended to measure a test-taker's knowledge, skill, aptitude, physical fitness, or classification in many other topics (e.g., beliefs). A test may be administered orally, on paper, on a computer, or in a confined area that requires a test taker to physically perform a set of skills. Tests vary in style, rigor and requirements. For example, in a closed book test, a test taker is often required to rely upon memory to respond to specific items whereas in an open book test, a test taker may use one or more supplementary tools such as a reference book or calculator when responding to an item. A test may be administered formally or informally. An example of an informal test would be a reading test administered by a parent to a child. An example of a formal test would be a final examination administered by a teacher in a classroom or an I.Q. test administered by a psychologist in a clinic. Formal testing often results in a grade or a test score.[1] A test score may be interpreted with regards to a norm or criterion, or occasionally both. The norm may be established independently, or by statistical analysis of a large number of participants. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Types of examinations A. Objective Examinations: (including Standard Examinations) B. Subjective (or Essay-type )Examinations Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference Semantic Variations Stem broad, cap/cei(v)/ cup Synonyms frustrate→ thwart tremendous→ huge 34 breach→ break apparent→ obvious attain→ accomplish Step 4. Reading skills---------Outlining In reading a passage ,outlines are helpful if the reader wants to see how the details explain or develop the main idea, and to put these part into a whole, which makes it easier for readers to understand and remember the important ideas. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1)What should a student after failed in an exam ? 2).’’My’ attitude and expectations towards students 3).How to deal with ten-minute quiz 4).How to make reviewing plans 5). How to review before exams Step 5. Reading in Depth Cheating :Alive and Flourishing Step 6. Assignment 38. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 39. Cloze 40. Preview : Unit 14 : Intellectual Property 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 14: Intellectual Property I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 35 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Intellectual Property Intellectual property (IP) is a term referring to a number of distinct types of creations of the mind for which a set of exclusive rights are recognized—and the corresponding fields of law. Under intellectual property law, owners are granted certain exclusive rights to a variety of intangible assets, such as musical, literary, and artistic works; discoveries and inventions; and words, phrases, symbols, and designs. Common types of intellectual property rights include copyrights, trademarks, patents, industrial design rights and trade secrets in some jurisdictions. Copyright A copyright is a set of exclusive rights granted by a state to the creator of an original work or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for public disclosure of the work. This includes the right to copy, distribute and adapt the work. In most jurisdictions copyright arises upon fixation and does not need to be registered. Copyright owners have the exclusive statutory right to exercise control over copying and other exploitation of the works for a specific period of time, after which the work is said to enter the public domain. Uses covered under limitations and exceptions to copyright, such as fair use, do not require permission from the copyright owner. All other uses require permission. Copyright owners can license or permanently transfer or assign their exclusive rights to others. World Intellectual Property organization(世界知识产权组织) The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is one of the 16 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world". WIPO currently has 184 member states, administers 24 international treaties, and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Copyright Introduction about copyright The social purpose of the copyright system is to encourage creativity and the advancement of knowledge by giving those who make intellectual contributions an ‘exclusive right to their 36 writings and discoveries’ for limited times. Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference patent/ patentability /patentee/ patentable preeminent/ exclusive right/ contemporary/prevail/recruitment renewable/ provision/register/ enforce/ substantial/signatory procedure/variety/multiple/ application/ promote/ diligent/ novelty Use of English: Get get down/ get over with/ get through/ get on nerves/ get along/ get round Stem cred, dens, fend/ fenc(s) Synonyms competitive→ rival ultimate→ final diversity→ variety private→ personal exclude→ bar Step 4. Reading skills---------Outlining In reading a passage ,outlines are helpful if the reader wants to see how the details explain or develop the main idea, and to put these part into a whole, which makes it easier for readers to understand and remember the important ideas. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1).About U.S. patient 2).About U.S. plant patent 3).About trademark 4).About China’s intellectual property system 5)Because of digital piracy, CD sales has sharply fallen ,movie DVD sales have been depressed Step 5. Reading in Depth Patents The fundamental goal of the Patent system of the world is to provides a reward to each inventor to disclose his or her findings of the long-term benefit of society. Competition and cooperation Early Patent System The U.S. Patent System Nature and Purpose of Patent System Step 6. Assignment 41. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 42. Cloze 43. Preview : Unit 15 : Law 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others 37 Unit 15:Law I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Law is a system of rules and guidelines, usually enforced through a set of institutions. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus ticket to trading on derivatives markets. Property law defines rights and obligations related to the transfer and title of personal and real property. Trust law applies to assets held for investment and financial security, while tort law allows claims for compensation if a person's rights or property are harmed. Criminal law offers a means by which the state can prosecute the perpetrators of illegal acts. Constitutional law provides a framework for the creation of law, the protection of human rights and the election of political representatives. Administrative law is used to review the decisions of government agencies, while international law governs affairs between sovereign states in activities ranging from trade to environmental regulation or military action. 38 FBI—Federal Bureau of Investigation The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is an agency of the United States Department of Justice that serves as both a federal criminal investigative body and an internal intelligence agency (counterintelligence). The FBI has investigative jurisdiction over violations of more than 200 categories of federal crime.[2] Its motto is a backronym of FBI, "Fidelity, Bravery, Integrity". Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Remarks of Attorney General John Ashcroft How American ensure the security of Internet Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference law enforcement/ computer hacker/ prosecute/ prosecutor cybercrime/cybercriminal/disrupt/disruption/anonymity espionage/traffick/pornography/ facilitate / extortion asset/ infrastructure/ fraud/ fictitious/perpetrate/ stagger misperception/compound/ incentive/sponsor Semantic Variations Stem rupt, pend Antonyms rarely→ frequently permission→ prohibition dispute→ agreement recommend→ disapprove prejudice→fairness Step 4. Reading skills---------Outlining In reading a passage ,outlines are helpful if the reader wants to see how the details explain or develop the main idea, and to put these part into a whole, which makes it easier for readers to understand and remember the important ideas. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1). Step 5. Reading in Depth Courts A. Civil and Criminal Courts B. How Courts Works to Settle Disputes C. The Trial D. Reaching a Verdict E. Appeals Step 6. Assignment 44. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 45. Cloze 46. Preview : Unit 16 : World War II 39 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 16: World War II I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information World War II World War II, or the Second World War (often abbreviated as WWII or WW2), was a global military conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, which involved most of the world's nations, including all of the great powers: eventually forming two opposing military alliances, the Allies and the Axis. It was the most widespread war in history, with more than 100 million military personnel mobilized. In a state of "total war," the major participants placed their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities at the service of the war effort, erasing the distinction between civilian and military resources. Marked by significant events involving the mass death of civilians, including the Holocaust and the only use of nuclear 40 weapons in warfare, it was the deadliest conflict in human history, resulting in 50 million to over 70 million fatalities. The war is generally accepted to have begun on 1 September 1939, with the invasion of Poland by Germany, and subsequent declarations of war on Germany by France and most of the countries of the British Empire and Commonwealth. Germany set out to establish a large empire in Europe. From late 1939 to early 1941, in a series of campaigns and treaties, Germany conquered or subdued much of continental Europe; amid Nazi-Soviet agreements, the nominally neutral Soviet Union fully or partially occupied and annexed territories of its six European neighbors. Britain and the Commonwealth remained the only major force continuing the fight against the Axis in North Africa and in extensive naval warfare. In June 1941, the European Axis launched an invasion of the Soviet Union, giving a start to the largest land theatre of war in history, which, from that moment on, tied down the major part of the Axis military power. In December 1941, Japan, which had been at war with China since 1937,[3] and aimed to dominate Asia, attacked the United States and European possessions in the Pacific Ocean, quickly conquering much of the region. Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 An American Named Edward R .Murrow reports on Britain under the bombs during the Second War Hilter’s air raids on London began in the first week of September of 1940 Under the bombing ,the people of London did their daily jobs as usual Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference Raid /siren/ordeal Semantic Variations Stem Spec9t)/ spic, spir Synonyms immense→ eventual→ vanquish→ fatal→ upheaval→ Step 4. Reading skills---------Outlining In reading a passage ,outlines are helpful if the reader wants to see how the details explain or develop the main idea, and to put these part into a whole, which makes it easier for readers to understand and remember the important ideas. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details Step 5. Reading in Depth Edward R. Murrow Reports on Britain under the Bombs Step 6. Assignment 47. Review the vocabulary and do related exercises 41 48. Cloze 49. Preview : Unit 17 : Housing 4. After–class reading : Newspapers, Magazines , Simplified Classics, and others Unit 17: Housing I:Teaching Aims and Requirements : In this unit students are required to: 1. Practice reading strategies such as predicting, skimming, guessing, etc. 2. Grasp some new words and expressions to enrich student’s vocabulary; 3. Do some oral work such as pre-reading questions, and interaction activities to help to develop the students’ oral communicative abilities; 4. Appreciate the articles in this unit and learn some reading skills; 5. Get to know the origin and making-up of English words; 6. Learn something about current national and international news; 7. Do some other after-class exercises to improve students’ comprehensive skills II: Teaching Focus 1. Comprehension and Appreciation of the Text; 2. Vocabulary 3. Reading Strategy; 4. Fast reading and exercises. III: Procedure: 1. Greeting; 2. The whole plan for this semester; 3. Begin the new lesson: 1). Answer the pre-reading questions orally; 2). Allow students 3 minutes to go over the text rapidly for the main idea; 3). Do the guesswork of vocabulary; 4). Study the Text extensively; 5). Learn some related information; 6). Assignment Step 1. Related Information Housing Step 2: Comprehension and Appreciation of Text 1 Show Me the Way to Go Home Both economical ,emotional and psychological pressures make young people return To their parent’s home. 42 Step 3. Teaching Points for Reference sociologist/ psychologist/ homecoming compromise /obligation/ accommodation/spontaneously sneak/ naïve/ hassle/ generate/ tension/ naïve cozy/crawl/ spacious Semantic Variations Stem sens/sent, stru/struc Antonyms separate→ attached harmful→ helpful mobile→ fixed spacious→ limited delight→displeasure Step 4. Reading skills---------Outlining In reading a passage ,outlines are helpful if the reader wants to see how the details explain or develop the main idea, and to put these part into a whole, which makes it easier for readers to understand and remember the important ideas. Fast Reading : A. Skimming: key words and expressions → topic sentences → main idea B. Scanning: details 1). Step 5. Reading in Depth Mobile Homes Step 6. Assignment 1. Review the vocabulary and learn the glossary and do related exercises 2. Cloze 3. After–class reading : Unit 18: Drama 4. Prepare for final examination The End 43