Corporate 3G Product Ideation
advertisement

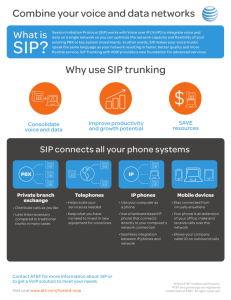
XL Hosted PBX Services SIP Based Services by XL XL Business Solution 2006 This document contains confidential and proprietary information belonging to XL, which information may be used only in connection with the business of XL Agenda • Product Brief • How it Works • How to Connect • How to Survive Slide 2 Product Brief This document contains confidential and proprietary information belonging to XL, which information may be used only in connection with the business of XL Hosted PBX Service Own Managed PBX Hosted PBX PBX / IP PBX PBX / IP PBX Branch A Hosted PBX PBX / IP PBX Branch …n Headquarter Headquarter Branch ..n Branch A • High cost of PBX investment and maintenance • No PBX investment, reduce maintenance cost • Separated PBX System of each office • Integrated PBX System of the offices (Integrated Corporate Telecommunication System) • High cost of internal communication • No Cost of internal communication HQ to Branch Free HQ to Branch call Branch to Branch Free Branch to Branch call Slide 4 XL Hosted PBX Service • Ability to deliver Hosted PBX service Nationwide even Worldwide through XL MPLS Network and NNI (partner) • More cost reduction. Reduce NOT ONLY in the number of elements to purchase, deploy, and manage PBX but ALSO reduce usage cost by getting the benefit of XL VoIP and XL GSM PABX Services • Wide range of service: Convergence Service of Data (Private and Public/Internet), Fixed and Mobile Voice • Most interoperable system: wide range of CPE (minimize investment) XL Hosted PBX Services Bundling w/ XL Products XL Broadband Internet Services Corporate XL MPLS Network XL VoIP XL GSM XL Hosted System Slide 5 Service Features Standard Hosted PBX (PABX Services) GSM PBX Extension Dialing Speed Dial Call Return Last Number Redial Consultation Hold Call Transfer Three-Way Calling Call Waiting Calling Line ID Call Forwarding Do Not Disturb Voice Messaging Voice Portal Web-Based MACs Calling Plans Device Inventory Series Completion Hunt Groups Advance PBX and Multimedia CommPilot Call Manager Click-to-Dial, Phone Lists, LDAP Directory Integration Outlook Integration Call Screening Priority & Distinctive Ringing, Anonymous Call Reject, Selective Call Accept & Reject, Call Screening by Digit Patterns Alternate Numbers Shared Call Appearance Auto Attendant Dial by Name or Extension, Record Greeting Remotely Attendant Console Directory Manager, User Status Voice Mail, VM Waiting Indication, VM to E-Mail, VM Notification, VM Call Back Call Park, Call Pick-Up Account Codes Authorization Codes Call Intercept Call Centers Instant Messaging & Presence Remote Office Music on Hold Find-Me Follow-Me Selective Call Forwarding, Simultaneous Ringing, Call Notify Unified Messaging Agent Login, Call Queuing & Distribution, Statistics As features of GSM PBX services Corporate VoIP As features of Corporate VoIP services Internet As features of Broadband Internet services MPLS B U N D L I N G As features of MPLS services Slide 6 Standard Package • PABX Services (start with 10 extensions, additional: per 10 extensions) – Standard (extension to extension call, call forwarding, call bearing etc.) – Premium (conference call, auto attendant etc.) • VoIP Service enable • GSM PABX Service enable • Access (MPLS Platinum) • CPE will be managed by partner (optional, customer can managed itself) Enterprise LAN WAN MPLS VPN VoIP Port TDM PBX PSTN XL VoIP SIP Custom er LAN PLMN Enterpri se IP PBX XL GSM PBX SIP XL GSM Listed Number Instant Office Services XL MPLS/VPN HOSTED PBX SERVICE XL Hosted PBX System Other XL Services BUNDLING Slide 7 How it works XL SIP Service is powered by Broadsoft This document contains confidential and proprietary information belonging to XL, which information may be used only in connection with the business of XL BroadWorks Open Protocols – SIP: Session Initiation Protocol • – MGCP: Media Gateway Control Protocol • – Access device or network device Application Server or Network Server look ups SSH (TELNET): Secure Shell • – Voice mail storage and retrieval DNS: Domain Name Server • – Voice mail forwarding, call notification e-mail POP3/IMAP: Post Office Protocol / Internet Message Access Protocol • – Web access to Application Server or Network Server, encrypted HTTP transactions for required pages SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol • – OSS provisioning interface for Application Server or Network Server XML over CORBA HTTP/HTTPS: HyperText Transfer Protocol or HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure • – Multi-media streaming CORBA: Common Object Request Broker Architecture • – Call control RTP: Real-Time Transport Protocol • – Call control, IM&P SIMPLE Management access SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol • BroadWorks server traps and performance measurements Slide 9 BroadWorks Proprietary Protocols – MCP: Media Server Control Protocol • – MSS: Media Server Selection • – Application Server to Network Server look up for serving Application Server for user (XML over CORBA) TTREP: TimesTen Replication • – Application Server to Network Server automatic propagation of group and user information (XML over CORBA) LocationAPI: Network Server Portal API • – Attendant Console control and updates SyncAPI: Network Server Synchronization • – Call Manager control and updates ACAP: Attendant Console Protocol • – Application Server to AS/AS to Network Server redundancy active node tracking CPP: CommPilot Push Protocol • – Application Server to Network Server request for list of geographically located Media Servers ASR: Application Server Redundancy • – Application Server to Media Server session control TimesTen Database replication between Application Server and Network Server cluster peers RSYNC • File synchronization (system prompts, greetings) Slide 10 BroadWorks: Call Control Protocols NS2 NGW1 NGW2 NS1 SIP OSS/NMS SIP MSS SIP SIP DNS AS secondary AS primary MCP MS1 MS2 SMTP SIP CS1 POP3 SIP SIP Access MGCP MGCP Access CS2 PC - Browser Slide 11 BroadWorks: Media Streaming Protocols NS2 NGW1 NGW2 NS1 OSS/NMS RTP DNS AS secondary AS primary RTP RTP MS1 MS2 SMTP RTP CS1 POP3 CS2 RTP SIP Access MGCP Access PC - Browser Slide 12 BroadWorks: Redundancy Protocols RSYNC NGW1 NGW2 TTREP OSS/NMS NS2 NS1 DNS SyncAPI SMTP ASR MS1 MS2 AS secondary AS primary CS1 POP3 CS2 TTREP RSYNC PC - Browser SIP Access MGCP Access Slide 13 BroadWorks: User Web Access Protocols NGW1 NGW2 OSS/NMS NS2 NS1 MS1 DNS MS2 LocationAPI SMTP AS secondary AS primary CS1 CS2 POP3 HTTP/HTTPS HTTP/HTTPS CPP/ACAP SIP Access MGCP Access PC - Browser Slide 14 BroadWorks: Management & Vmail Protocols NGW1 NGW2 OSS/NMS HTTP(S)/SSH/Corba NS2 NS1 SNMP HTTP(S)/SSH/Corba MS1 AS secondary AS primary MS2 SSH DNS POP/IMAP POP3 HTTP(S) SMTP CS1 CS2 SMTP SIP Access MGCP Access PC - Browser Slide 15 SIP Overview • Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) – Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard for multimedia conferencing over IP • SIP is an ASCII-based, application-layer control protocol (defined in RFC 3261) that can be used to establish, maintain, and terminate calls between two or more end points • SIP provides the capabilities to: – Determine the location of the target end point – Determine the media capabilities of the target end point—via Session Description Protocol (SDP) – Determine the availability of the target end point – Establish a session between the originating and target end point – Handle transfer and termination of calls • BroadWorks Application Server acts as a back-to-back user agent – Terminates the incoming call-half, applies services and if necessary, originates an outgoing call-half Slide 16 SIP Overview • SIP (Methods) Requests – INVITE—Indicates a user or service is being invited to participate in a call session – ACK—Confirms that the client has received a final response to an INVITE request – BYE—Terminates a call and can be sent by either the caller or the callee – CANCEL—Cancels any pending searches but does not terminate a call that has already been accepted – OPTIONS—Queries the capabilities of servers – PRACK – Provisional acknowledgement – REGISTER—Registers the address listed in the To header field with a SIP server Slide 17 SIP Overview • Types of responses used in response to a Request – SIP 1xx—Informational Responses (for example, 180 Ringing) – SIP 2xx—Successful Responses (for example, 200 OK) – SIP 3xx—Redirection Responses (for example, 302 Temporarily Moved) – SIP 4xx—Client Failure Responses (for example, 404 User Not Found) – SIP 5xx—Server Failure Responses – SIP 6xx—Global Failure Responses – Registration Process – Registration occurs when a SIP client must inform the Application Sever of its location – During this process, the client sends a REGISTER request to the Application Server and includes the address (or addresses) at which it can be reached – Registrations can require Authentication (shared-secret) Slide 18 SIP Overview • Invitation Process – An invitation occurs when one SIP end point (user A) "invites" another SIP endpoint (user B) to join in a call – User A sends an INVITE message to the Application Server requesting that user B join or set up a call – Application Server processes the request and returns an appropriate response (for example, 100 Trying, 487 User Busy) – If necessary, the Application Server initiates a terminating callhalf to user B and mediates the two call-halves – If user A no longer wants to end the call, it sends a BYE message Slide 19 SIP INVITE Message Dialed Digits Originator INVITE sip:2403645138@192.168.5.253;user=phone SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 192.168.5.214:5060 From: "2403649314" <sip:2403649314@192.168.5.253>;tag=0003e3630c9 To: <sip:2403645138@192.168.5.253;user=phone> Call-ID: 0003e363-0c9406d6-124f754f-085ca146@192.168.5.214 Date: Tue, 04 Jun 2002 19:52:42 GMT CSeq: 101 INVITE User-Agent: AccessDevice Unique Callid associates Contact: sip:2403649314@192.168.5.214:5060 Expires: 180 related to a call Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 170 Accept: application/sdp v=0 o=SDP 26088 15595 IN IP4 192.168.5.214 s=SIP Call RTP listen port c=IN IP4 192.168.5.214 t=0 0 m=audio 23890 RTP/AVP 0 8 18 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 all messages Codecs Slide 20 SIP Basic Call Flow SIP Device INVITE BroadWorks 100 Trying 180 Ringing or 183 Session Progressing PRACK (Optional) 200 OK (PRACK - Optional) 200 OK (INVITE - Answer) ACK RTP – two-way voice path BYE ACK Slide 21 MGCP Overview • Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) – Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard for multimedia conferencing over IP • MGCP is an ASCII-based, application-layer control protocol (defined in RFC 2705) that can be used to establish, maintain, and terminate calls between two or more endpoints • MGCP is a client-server protocol. The Call Agent (server) handles all aspects of setting up calls to and from endpoints • MGCP provides the capabilities to: – Determine the location of the target end point – Determine the media capabilities of the target end point—via Session Description Protocol (SDP) – Determine the availability of the target end point – Establish a session between the originating and target end point • BroadWorks Application Server acts as an MGCP Call Agent (CA) Slide 22 MGCP Overview • MGCP messages composed from short list of primitives • NotificationRequest (RQNT)—Instructs the MGCP device to watch for specific events • Notify (NTFY)—Informs the CA when requested events occur • CreateConnection (CRCX)—Creates a connection to an endpoint • ModifyConnection (MDCX)—Changes the parameters associated with an established connection • DeleteConnection—Deletes an existing connection. ACK returns call statistics • AuditEnpoint (AUEP)—Audits an existing endpoint • AuditConnection (AUCX)—Audits an existing connection • RestartInProgress (RSIP)—Is a gateway notification to the CA that an MG or an endpoint is restarting or stopping Slide 23 MGCP Overview • Notification Messages – MGCP device uses these messages to tell the CA of a change of state – Typically involve signaling or events – Examples: • Signals: Ringing, distinctive ringing, ring back tone, dial tone, intercept tone, network congestion tone, busy tone, confirm tone, answer tone, call waiting tone, off-hook warning tone, pre-emption tone, continuity tone, continuity test, DTMF tones • Events: On-hook transition, off-hook transition, flash hook, receipt of DTMF digits Slide 24 MGCP Sample Messages MGCP Endpoint NTFY 353 aaln/s1/3@[192.168.5.77] MGCP 0.1 X: 1 O: L/hd NTFY 200 RQNT 200 4 OK NTFY 354 aaln/s1/3@[192.168.5.77] MGCP 0.1 X: 4 O: D/7702T 200 200 353 RQNT 4 aaln/s1/3@[192.168.5.77] MGCP 0.1 D: (xx.[T#]|0[T#]|0[2-9]xxxxxxxxx|1[2-9]xxxxxxxxx |[2-9]xxxxxxxxx|*xx) Q: loop,discard R: L/hf(I,K), D/[*0-9#T](D), L/hu(E(L/hd;;),N,K), L/oc(E(L/hu, L/hf(I,K);L/ot;),N) X: 4 S: L/dl NTFY 200 CRCX 200 5 I: 68 v=0 o=- 4 0 IN IP4 192.168.5.77 s=Cisco SDP 0 c=IN IP4 192.168.5.77 t=0 0 m=audio 16400 RTP/AVP 0 BroadWorks 200 354 CRCX 5 aaln/s1/3@[192.168.5.77] MGCP 0.1 C: 4 M: recvonly L: a:PCMU Q: loop,discard R: L/hu(E(L/hd;;),N,K), L/hf(I,K) X: 6 200 Slide 25 Call-Half Model: Typical Call Setup Originating Sip Node A (1) SipInviteEvent Terminating Sip Node B Internal Events SIP Call Half Session (A) (2) InvitationEvent (3) InvitationReceivedEvent SIP Call Half Session (B) (4) SipInviteEvent (5) 18x Ringing Event (6) AlertingEvent (7) 18x Ringing Event (8) 200 OK Event (10) AnswerEvent (11) 200 OK Event (9) AckEvent (12) AckEvent RTP Media Slide 26 How to Connect This document contains confidential and proprietary information belonging to XL, which information may be used only in connection with the business of XL Network Architecture Enterprise Data Center Solaris / SPARC AES Servers XL VOIP IP Router APX Universal Gateway Hosted Enterprise VoiceMail PRI XL MPLS XL GSM Lucent Brick* Firewall WAP Enabled PDA IP SIP SIP Phone Router PRI MGCP SIP IAD Analog Phone Windows, SunRay SIP Softphone PSTN MultiLocation PSTN Access IP Enterprise Directory, Call Logs, VoiceMail Messaging & Database, DNS Location 2 Location 1 Slide 28 How to Connect • Customer must have XL MPLS connection • Additional setting will be added by XL in CE (Customer Edge) MPLS Router will ALG (Access Layer Gateway) setting. • After ALG has been set up, the AES will recognize the IP Address Gateway and designated Port for every subscriber. • XL will create SIP subscriber remotely (in AES) based on customer gateway. (subscriber hierarchy in the next slide) • SIP CPE (Customer Premise Equipment) will be set up by customer. The setting will be: – Set IP Address – Set SIP Proxy – Set User ID and Password Slide 29 Application Server User Hierarchy System Provider Service provider Reseller Group or department Small or medium enterprise User End user System Provider Service Provider Service Provider Group Group Group Group Dept Dept Dept Dept Users Users Users Users Virtual System Virtual System Slide 30 CPE of XL Hosted PBX Widest Variety of Endpoints SIP/MGCP End-User Device Options • • • • • • • • Soft-phones Hard-phones Line gateways Trunk gateways IADs VoIP phones Firewalls Remote Survivability/Monitoring Polycom SwissVoice UniData WiFi Uniden Cisco Verilink Lucent APX® AudioCodes Edgewater Citel Microsoft For additional device availability – see pdf file XTen Slide 31 How to Survive This document contains confidential and proprietary information belonging to XL, which information may be used only in connection with the business of XL How to Survive when MPLS goes down Voice call 1 PSTN Voice call 2 XL MPLS XL Hosted PBX • • • • Survivability Gateway Layer 2 Switch 10/100 T1 XL provides gateway which have survivability features (optional) Pre configure (by XL - optional) when first installation in customer Automatically takes over upon WAN failure Automatically exits survivability upon restoral Slide 33 Geographical Redundant Deployment (2007 plan) Site 1 Site X LAN LAN Data Center 1 Data Center 2 National Backbone Server AES Router Managed IP Data Center Retail Sites IP Phone Slide 34 Thank You This document contains confidential and proprietary information belonging to XL, which information may be used only in connection with the business of XL