Scatter Diagram of Bivariate Measurement Data
advertisement

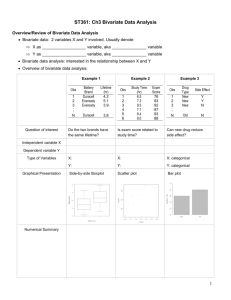
Scatter Diagram of Bivariate Measurement Data Bivariate Measurement Data Example of Bivariate Measurement: Some questions for Bivariate Data • Are the variables related? • Can we quantify the strength of their relationship? • Can we predict one variable from the other? • Let x, y be the two variables of a bivariate data. • The variable x is marked along the horizontal axis and y on the vertical axis on a graph paper. • The pairs (x, y) of observations are then plotted as dots on the graph. • The resulting diagram is called a scatter diagram or scatter plot. The correlation Coefficient • If the scatter plot of (x,y) is a line, we say x and y has a linear relation. • The to measure how “linear” a relation is, we use the correlation coefficient. The correlation Coefficient, r • The value of r is always between -1 and 1. • The magnitude of r indicates the strength of a linear relation, whereas its sign indicates the direction. Calculation r