Human Body Jeopardy!
advertisement

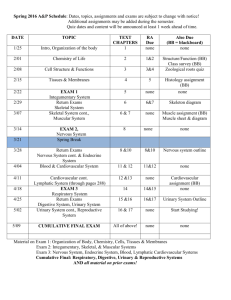
Systems Review Game Click on the number to get to the question. Click on (answer) to see the answer. Click on the picture to return to the main page. Skeletal Muscular Cardiovascular Respiratory Digestive Urinary 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Skeletal 100 How does the skeletal system allow movement? (answer) Joints Skeletal 200 Name 3 types of joints and where they are located in the body. (answer) Pivot – neck Hinge – elbow, knee Ball-and-socket – shoulder, hip Gliding – wrist, ankle Skeletal 300 What is the importance of water in the skeletal system? Explain. (answer) Lubricant – reduces friction at joints and keeps them moving smoothly Skeletal 400 What are the 4 main functions of the skeletal system? (answer) Protects internal organs Makes red blood cells Allows movement Stores minerals Skeletal 500 Why does the skeletal system depend on the muscular system? (answer) The skeleton is built to move, but doesn’t have the capability to move on its own. The muscles attach to bones to make them move. Muscular 100 What is the primary function of the muscular system? (answer) movement Muscular 200 What are the 2 types of muscle action? Explain. (answer) Voluntary – move under your control Involuntary – move without you thinking Muscular 300 What are the 3 types of muscle? Where in the body can each be found? (answer) Cardiac – only in the heart Smooth – lines the walls of digestive tract Skeletal – attached to bones Muscular 400 Skeletal muscles must work in pairs to move bones. What are these pairs? Explain. (answer) Flexor – contracts to bend a body part Extensor – contracts to straighten a body part Muscular 500 Why would some muscles fail to work properly if a bone is broken? (answer) Skeletal muscle is attached to bone, and if the bone is broken the flexors and extensors wouldn’t be able to pull on the bone to move the joint. Cardiovascular 100 What is another name for the cardiovascular system? (answer) Circulatory system Cardiovascular 200 What are the 5 parts that make up this system? Explain each of their functions. (answer) Heart – pumps blood Blood – delivers oxygen and nutrients Artery – takes blood away from the heart Capillary – allows an exchange of materials from blood cells to other body cells Vein – takes blood back to the heart Cardiovascular 300 What is the difference between systemic and pulmonary circulation? (answer) Systemic – circulation of blood from the heart to the body and back to the heart Pulmonary – circulation of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart Cardiovascular 400 Why is water important in the cardiovascular system? (answer) Temperature Regulator – absorbs heat to help keep body temperature constant Cardiovascular 500 Why are other systems dependent on the cardiovascular system? (respiratory, digestive, urinary) (answer) The blood will transport (pick up and deliver) oxygen, nutrients and waste materials around the body Respiratory 100 What is the primary function of the respiratory system? (answer) To bring in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide Respiratory 200 What are the structures that make up the respiratory system? (answer) Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, bronchioles, and alveoli. Respiratory 300 Explain the importance of the alveoli. (answer) Alveoli filter oxygen from the air and pass it into the blood stream through capillaries. At the same time, carbon dioxide is passed into the alveoli from the blood to be removed from the body. Respiratory 400 What is the role of water in cellular respiration? Explain. (answer) Metabolite – water helps the cells perform chemical reactions such as cellular respiration Respiratory 500 What is the difference between breathing and respiration? (answer) Breathing is inhaling and exhaling air. Respiration is getting and using oxygen. Digestive 100 What are the structures that make up the digestive system? (answer) Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, small intestine, liver, gallbladder, and large intestine. Digestive 200 What are the two types of digestion? Explain. (answer) Mechanical digestion – physically breaking, ripping, smashing (etc.) into smaller pieces Chemical digestion – using substances to breakdown into smaller molecules Digestive 300 What is the role of water in regards to digestion? (answer) Solvent – water helps to dissolve nutrients so the body can use them Digestive 400 What are the organs that assist with digestion, but are not part of the digestive tract? Explain their functions. (answer) Liver – stores nutrients, makes bile, breaks down toxins Gallbladder – stores bile and squeezes it into the small intestine to break down fat. Pancreas – protects the small intestine from stomach acid in chyme, by neutralizing the acid Digestive 500 Why is the small intestine so long? Explain. (answer) Villi are fingerlike projections in the small intestine that absorb nutrients from food. It is long so that it can get as many nutrients as possible from the food. Urinary 100 What are the structures that make up this system? (answer) Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra Urinary 200 What is the tube in which urine leaves the body? (answer) Urethra Urinary 300 Where does urine get stored before it can be expelled from the body? (answer) Urinary bladder Urinary 400 What is the primary function of the urinary system? (answer) To remove waste from the blood that was made in the body. Urinary 500 What are nephrons? Explain how they function. (answer) Nephrons are microscopic filters in the kidneys. They filter the waste and water out of the blood which makes urine. Most of the water and the nutrients are returned to the blood and the blood is recirculated. The urine leaves the kidneys in tubes called ureters.