Lecture XX: Strategic Analysis II: Internal Capabilities Niels
advertisement

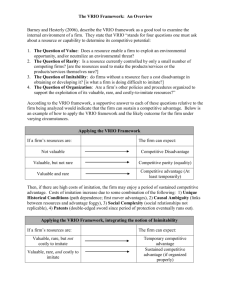
Strategic Management Lecture 03: Strategic Analysis II: Strategic Capability Niels-Erik Wergin What is Strategic Capability? Strategic capability refers to the resources and competences of an organisation needed for success. Internal Factors Internal Analysis (last week: external factors – external analysis) 2 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Why Internal Analysis? Internal analysis provides a comparative look at a firm’s resources and competences • what are the firm’s strengths? • what are the firm’s weaknesses? • how do these strengths & weaknesses compare to competitors? • how can these strengths & weaknesses be utilised to gain competitive advantage? 3 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Resources and Competences Resources: • tangible and intangible assets of a firm • used to conceive of and implement strategies Competences: • skills and knowledge that enable a firm to take full advantage of its resources 4 Two Types of Resources Tangible resources are physical assets of an organisation such as buildings, workers, patents, and finance. Intangible resources are non-physical assets such as information, reputation, knowledge, and skills 5 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Resource Categories 6 Physical resources Financial resources Human resources Intellectual capital Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 What are Competences? Core competences are the skills and abilities by which resources are used by an organization to achieve competitive advantage in ways that others cannot imitate or obtain. e.g.: marketing skills 7 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 The Experience Curve Competences in activities develop over time based on experience, resulting in cost efficiencies • Growth may not be optional • Unit costs should decline year on year • First mover advantage is important 8 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 The Experience Curve 9 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Internal Analysis The VRIO Framework Four Important Questions: • Value • Rarity • Imitability • Organization Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 10 The VRIO Framework If a firm has resources that are: • Valuable, • Rare, • costly to Imitate, and • the firm is Organized to exploit these resources, then the firm can expect to enjoy a sustained competitive advantage. 11 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 The VRIO Framework (1) - Value The Question of Value • in theory: Does the resource enable the firm to exploit an external opportunity or neutralize an external threat? • the practical: Does the resource result in an increase in revenues, a decrease in costs, or some combination of the two? (BMW’s reputation allows it to charge a premium for its cars) 12 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 The VRIO Framework (2) - Rarity The Question of Rarity • if a resource is not rare, then perfect competition dynamics are likely to be observed (i.e., no competitive advantage, no above normal profits) • a resource must be rare enough that perfect competition has not set in • thus, there may be other firms that possess the resource, but still few enough that there is scarcity (several pharmaceuticals sell cholesterol-lowering drugs, but the drugs are still scarce—look at prices) 13 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Applying the VRIO Framework Valuable and Rare If a firm’s resources are: The firm can expect: Not Valuable Competitive Disadvantage Valuable, but Not Rare Competitive Parity Valuable and Rare 14 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Competitive Advantage (at least temporarily) The VRIO Framework (3) - Imitability The Question of Imitability • the temporary competitive advantage of valuable and rare resources can be sustained only if competitors face a cost disadvantage in imitating the resource » intangible resources are usually more costly to imitate than tangible resources (Harley-Davidson’s styles may be easily imitated, but its reputation cannot) 15 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 The VRIO Framework (3) - Imitability The Question of Imitability • If there are high costs of imitation, then the firm may enjoy a period of sustained competitive advantage • A sustained competitive advantage will last only until a duplicate or substitute emerges • If a firm has a competitive advantage, others will attempt to imitate it 16 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 16/03/2016 Applying the VRIO Framework Value, Rarity, & Imitability If a firm’s resources are: 17 The firm can expect: Valuable, Rare, but not Costly to Imitate Temporary Competitive Advantage Valuable, Rare, and Costly to Imitate Sustained Competitive Advantage (if Organized appropriately) Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 The VRIO Framework (4) - Organization The Question of Organization • a firm’s structure and control mechanisms must be aligned so as to give people ability and incentive to exploit the firm’s resources • examples: formal and informal reporting structures, management controls, compensation policies, relationships, etc. • these structure and control mechanisms complement other firm resources—taken together, they can help a firm achieve sustained competitive advantage 18 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Applying the VRIO Framework Valuable? Rare? Costly to Imitate? Exploited by Organization? No Disadvantage No Parity Yes Yes No Temporary Advantage Yes Yes Yes Yes 19 No Competitive Implications Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Yes Sustained Advantage The Resource-Based View Competitive Advantage Resources & Capabilities • Valuable Competitive Advantage will be sustained if: • Rare • Costly to Imitate • Organized to Exploit 20 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 • other firms’ costs of imitation are greater than benefit of imitation • the firm is organized to exploit advantages Benefits of Internal Analysis Tells us: • what the firm should do, given the relative strengths and weaknesses of resources and competences Managers’ Job: • use strategic capability (resources and competences) to achieve competitive advantage VRIO Framework Helps Managers Recognize Sources of Competitive Advantage 21 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009 Case Example: eBay Analyse eBay’s strategic capability Which capabilities provided eBay’s competitive advantage? How would you manage this capability given new entrants and the changing nature of eBay? 22 Strategic Management © Niels Wergin 2009