Document
advertisement

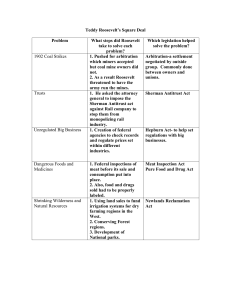
“Teddy Roosevelt’s Square Deal” Notes: Chapter 9 Section 3 NEXT SECTION 3 I.) A Rough-Riding President A. The Rise of Theodore Roosevelt 1. born 1858 in New York City & is sickly & asthmatic as child 2. Life: graduates from Harvard (1880) elected New York Assembly (1881-1884) Image retires to ranch in Badlands (1884-1887) Civil Service Commission (1888-1895) New York City Police Commissioner (1895-1897) Assistant Secretary of the Navy (1897-1898) NEXT forms & joins “First U.S. Volunteer Calvary Regiment” (Rough Riders) during the Spanish-American War (1898) elected governor of New York (1898-1900) becomes Vice President under William McKinley (1900-1901) becomes President after assassination of McKinley (1901-1909) (youngest president at age 42) B. creates the “Modern Presidency” 1. cites federal responsibility for the national welfare 2. Square Deal: Roosevelt’s Progressive reforms to protect the common person against big business SECTION 3 II.) Using Federal Power A. Trustbusting 1. Problem: In 1900’s, trusts control about 4/5 of U.S. industries 2. Goal: Roosevelt wants to curb trusts that hurt public interest 3. “Trustbuster”: in 1902 orders Justice Dept. to sue Northern Securities Company (railroad monopoly) under the Sherman Antitrust Act Outcome: 1904 Supreme Court dissolves the company B. 1902 Coal Strike 1. Issue: coal miners in Pennsylvania go on strike 2. Problem: 5 months in coal reserves run low 3. Outcome: operators to accept arbitration after threat of take over 4. Importance: Sets principle of federal intervention when strike threatens public Continued . . . NEXT C. Railroad Regulation 1. Goal: federal regulation of the railroads 2. Problem: Interstate Commerce Commission has little power to enforce regulations 3. Outcome: Elkins Act (1903): stops rebates, sudden rate changes Hepburn Act (1906): limits passes, set maximum rates 4. Importance: government has more power to regulate railroads SECTION 3 III.) Health and the Environment A. Regulating Foods and Drugs 1. Problem: Upton Sinclair writes “The Jungle”: reveals unsanitary conditions in meatpacking industry 2. Issue: Roosevelt’s creates commission that investigates and backs up Sinclair’s account 3. Outcome: Meat Inspection Act (1906) passed by congress - dictates sanitary requirements - creates federal meat inspection program B. Pure Food and Drug Act 1. Problem: Food, drug advertisements make false claims; medicines often unsafe 2. Outcome: Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) passed by congress - halts sale of contaminated food, medicine - requires truth in labeling Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 3 C. Conservation and Natural Resources 1. Problem: U.S. Forest Bureau established in 1887 but stands by as private interests exploit natural environment 2. Outcome: Roosevelt sets aside more than 148 million acres for forest reserves, sanctuaries, national parks 3. Importance: U.S. belief is conservation part saved for preservation and part saved for development for public Map NEXT SECTION 3 IV.) Roosevelt and Civil Rights A. Civil Rights at the Turn of the 20th Century 1. Roosevelt’s terms as president make no civil rights reforms 2. Appoints a few individual African Americans to civil service jobs - invites Booker T. Washington to White House B. National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) founded 1909 by W. E. B. Du Bois & black/white reformers Goal : full equality among races Image NEXT