Assessment and care of the newly delivered mother
advertisement

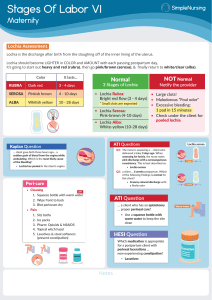
Assessment and Care of the Newly Delivered Mother Normal Postpartum Changes Uterus • Rapid contraction of the uterine muscle and arteries – compresses blood vessels – thrombi form – endometrium undermines site, area heals Normal Postpartum Changes Uterus • Normal size decrease ~1 cm/day • Weight from 1000g to ~50-100g • Size affected by parity, multiple gestation, or bladder distension • After-pains start to in frequency LOCHIA Rubra Serosa Alba Normal Color Red Pink, brown Yellowishtinged white Normal Duration 1-3 days 3-10 days Normal Discharge Bloody w/ clots Abnormal Discharge Foul smell; many lg. clots, saturate pad 10-14 days, Can be longer Serosang., Mostly Fleshy odor musus, no strong odor Foul smell, quickly saturate pad Foul smell, rubra or serosa flow; lasts > 4 wks Factors Affecting Lochia • Factors: – Uterine atony, retained placental fragments/membranes, activity, distended bladder – Duration not affected by choice of feeding method or use of oral contraceptives • Warning signs – Foul-smelling lochia, unusually heavy flow, large clots, rubra continues by PPD4, saturates > 1pad/hr • Final sloughing at 7-14 days Perineum • Perineal lacerations – 1º – 2º – 3º – 4º skin & superficial structures reaches into perineal muscle extends into anal sphincter muscle involves anterior rectal wall Perineum • Comfort measures: warm or cool baths, ice packs, witch hazel pads, anesthetic sprays, po analgesics • Report unusual discomfort, pain, drainage • Continue perineal hygiene Cervix, Vagina, & Pelvic Floor • Cervix & lower uterine segment flaccid immediately PP • Cervix – by 2-3 days has resumed its usual appearance but remains dilated 2-3 cm., 1 cm by end of 1st week – Cervical edema may last several months Vagina • Vagina & vaginal outlet may appear bruised early after delivery; caused by pelvic congestion, disappears quickly after birth • Involutes by contraction – Walls become gradually thicker, rugae return by ~ 3 weeks • Pelvic floor tone regained during first 6 wks PP Return of Menses • Menses – return varies – First menses usually occurs within 7-9 wks PP if non-nursing – Great variation in menses return if BF due to depressed estrogen levels. Usually returns between 218 months Return of Ovulation • First menstrual cycle is usually anovulatory, but 25% may ovulate before menstruation • Mean return of ovulation – ~ 10 wks PP if non-nursing – ~ 17 wks PP if breastfeeding Family Planning • Discuss family planning – Wait until bleeding stops & have seen provider for 6 week follow-up appt. – Discuss with provider at 6 wk. checkup FertilityCare Program, 322-4434 (Creighton Model) • 99.5% effective in spacing pregnancy • Can an infertile couple’s chance of conceiving by 20-80% • Simple charting based on external exams • Can be used to treat GYN conditions: – Infertility, menstrual cramps, PMS, ovarian cysts, abnormal bleeding, PCOS, repetitive miscarriage, PP depression, hormonal abnormalities, chronic discharge, pelvic pain Normal Postpartum Changes Bladder • Extensive diuresis to excrete excess fluid (2-3 L) • capacity, tone • Risk of over-distention and incomplete emptying • Leakage, urinary frequency common • Mild proteinuria (1+) may exist for 1-2 days in ~ half of women Normal Postpartum Changes Bladder • Spontaneous voiding should occur by 6-8 hours PP; enc. Frequent voiding • If cath’d, remove no more than 800 cc at one time • Stress incontinence common • Encourage Kegel exercises • Observe for s/s UTI Hemodynamic/Hematologic • Normal EBL up to 500 ml vaginal birth, up to 1000 ml cesarean birth • By 3rd day PP plasma volume as fluid shifts from extracellular to intravascular • Excess fluid by 2 wks PP by diuresis and diaphoresis • Leukocytosis to 14-16,000 during labor (or higher): remains 2-3 days PP Hemodynamic/Hematologic • Cardiac output peaks immediately after birth (autotransfusion) • Decreases to pre-labor by 1 hour, remains for 24 hours, then to normal levels by 2 weeks • Clotting factors in preg. & early PP – Assess for thrombus formation Gastrointestinal • Relaxin slows GI tract, delays passage of stool • Incontinence 6x more common w/ 3 and 4° lacerations • Prevent constipation - should have BM by 2-3 days PP • Hemorrhoids common GI System • Encourage non-pharmacological methods (fiber, fluids, warm drinks in AM, walking, etc.) • OTC stool softeners • Hemorrhoid OTC preparations • Use care w/suppositories if 3 or 4 lacerations • Skin Musculoskeletal – diaphoresis – stretch marks, pigmentation chg – varicosities, spider veins • Stretched muscles and ligaments return to former state – Diastasis separation 2-3 fingerwidths; lasts ~ 2 wks • Edema decreases 1-3 days PP • Hormonal effects regress over time Neurologic • DTR’s remain normal • Multiple sources of discomfort – Fatigue, afterpains, incisions, muscle aches, breast engorgement or sore nipples, headaches • Sleep disturbances r/t hormones Endocrine • Thyroid - risk of thyroiditis – May develop during first month PP, most likely in weeks 3-4. • Followed by thyroid storm – Life threatening emergency, caused by excessive amounts of thyroid hormones – S/S: fever, marked weakness, extreme restlessness w/wide emotional swings, confusion, psychosis, even coma • Followed by hypothyroidism – Extreme lethargy, fatigue, weight loss or later wt. gain, goiter formation Endocrine: Glucose Metabolism • Levels change r/t absence of pregnancy hormones – Decreased insulin needs if diabetic – Gestational diabetics return to normal – 6 wk 75 gm glucose screen to R/O Type 2 DM (fasting BG ok if no further pregnancies planned) Initial Postpartum Assessment • Vital signs – Vag birth – q. 15 min. x 4, q. 30 min. x 2, then 1 hour, then q. 12 hrs or more frequent if indicated – C/birth – q. 15 min. in PAR; then q. 30 min. x 2, q. 1 hr x 4, then q. 4 hrs until 24 hour post-op; then QID • Physical assessment • Emotional considerations Vital Signs • Temp should be normal. Call if temp for 2 days (> 100.4° F) – Incisions, IV site, breasts, S/S UTI • Pulse remains normal or decreases slightly after birth • BP normal – Assess patients w/ DBP for HTN – Orthostatic BP common – BP can be late sign of hemorrhage Assessment: BUBBLE-HEAD • • • • • • B U B B L E Breasts Uterus Bladder Bowels Lochia/lungs Episiotomy/ lacerations • • • • H E A D Homan’s sign Edema Affect Discomfort Monitoring of Incisions • Assessment of incisions – REEDA scale (Redness, Edema, Ecchymosis, Discharge, Approximation) • Healing – Stitches absorb (10 days) Interventions for Incisions • Episiotomy (perineal) – Wash hands before and after pad change, ice pack 1st 24 hours, change pads frequently, peri bottle after voiding, wipe front to back, wash with soap & water daily, tub/sitz baths – Stitches dissolve in about 10 days – Healing generally takes 4-6 weeks - may take longer for “no pain” (type of epis, ability to heal, infections, etc.) Incisions • Abdominal – Wash with soap & water daily, rinse well; keep clean and dry, soft cloth to whisk away moisture, assess daily for healing, remove steri strips in 7-10 days – Healing takes ~ 6 weeks Cesarean Considerations • Recovery from anesthesia • Auscultate bowel sounds q. 4 hours • Observe for bladder distension, adequate urinary output • Auscultate lung sounds • Ambulate early & often! Pain Control • Perineal pain – Ice, topical anesthetics, Tucks, whirlpool • Oral medications • Protective positioning, splinting (C/S) Other Issues • Restructuring patient education – teaching in antepartum period about self and baby care – age of informed consumer – intrapartum & PP notoriously poor retention of teaching. Need time to rest and “practice” what has been learned earlier. PP Teaching • PP women have transient deficits in cognition, particularlyin memory function, the first day after giving birth (Rana, Lindheimer, Hibbard, & Pliskin, 2005). • Verbal instruction immediately after birth or first PP day will be poorly remembered • Need appropriate written materials • Priorities for most women in 1st 24 hrs PP are rest, time to touch, hold, and get to know their baby, and an opportunity to review and discuss their L&D Other Issues • Providing alternative support services – – – – – Postpartum follow-up clinic/phone calls Lactation services Support groups Home visits Early parenting education Questions???