Explain the function of the sensory register
advertisement

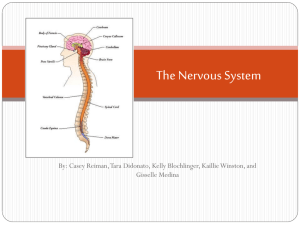
Explain the function of the sensory register Uses part of the brain stem known as the reticular activation system (RAS) and the thalamus which screens the data from the senses to determine their importance to the individual. The sensory register goes through a process called perceptual or sensory filtering. Pg. 40 State two functions of the hippocampus Explain the importance of sense and meaning to learning Relate the cognitive belief system to learning Learning that involves sense and meaning is likely to be stored in long-term memory. It is unlikely for something that does not have sense or meaning to get stored in long-term memory. Memory can happen without meaning or sense but it is less likely to occur. Tell you the functions of the immediate memory Also known as short-term memory. Holds data for about 30 seconds. The importance of the information is determined by the individual’s experiences. If the information is not important it will drop out of immediate memory. Tell you the functions of the cerebellum The ability of the human brain to combine individual items in many different ways. It is how we perceive the world. The cerebellum coordinates movements. Is important for learning, performance, and timing of complex motor tasks. Encodes information and sends it to one or more long-term storage areas. The hippocampus is hippo librarian : ) Decides where to store long-term memories “Belle” or Miss Cerebellum is the secretary in charge of all the details. Define windows of opportunity Windows of opportunity represent important periods in which the brain responds to certain types of input to create or consolidate neural networks. If that type of input is not given during that time, then the person will never develop that skill. Explain how the brain prioritizes incoming information Explain what is meant by the “novel” brain The amygdala encodes an emotional message. The brain is scanning the environment for novelty. It responds to what is unique and different. Tell you the functions of the cerebrum The cerebrum controls thinking, memory, speech, and muscular movement. “Brum” or Mr. Cerebrum is the boss of thinking, memory, speech, and muscular movement. Touch, taste, sight, hearing, smell, Proprioceptive Survivor value is top priority. Emotional experiences. The learners past experiences (sense and meaning). Explain the function of the amygdala It stores the emotional part of a memory, regulates emotions, and makes emotional connections between memories. Name the senses Describe the time limits of the working memory Ebbinghaus concluded that working memory lasted up to 45 minutes. Russell showed that working memory was age dependent and could range from 5-10 minutes for preadolescents and 10-20 minutes for adolescents and adults before boredom or fatigue became factors. Provide an example of how self-concept affects learning It is the way we view ourselves. It is shaped by past experiences. Their experiences can impact their acceptance or rejection of new learning. Explain synapses Synapses are where one nerve cell connects to another nerve cell (though they do not touch). Neurotransmitters go from one cell to another at the synapses. Explain the meaning of sensory preferences People prefer to learn by one sense as opposed to another. This results in auditory, visual, kinesthetic and other learners. Each type of learner will behave differently during learning. Explain the value of humor in learning Humor enhances the climate, promotes mental health, relieves stress and therefore helps with the classroom community. In a lesson humor can be used as an attention-getter which results in increased retention. Describe the capacity limits of working memory It is dependent on the person’s age. Children under 5 have the capacity of 1-3 chunks, ages 5-14 can process 3-7 chunks, and ages 14 and older can process 5-9 chunks. To increase the amount of information to be processed in working memory, make bigger chunks. Explain chunking Chunking is the process where the brain perceives several items of information as a single item. Patterns, sequence, and categories are common ways to chunk information. Explain what is meant by emotional control Emotional control is developed between 2-30 months of age. It has to do with the emotional and rational system evaluating how to get the owner what they want. It can be influenced by parents, and it is difficult to retrain someone when they are older. The ability of a person to use your own emotions to make decisions. And it includes the perception of others emotions. Read emotions and know what to do with that. Describe the sources of brain research What was learned in the past (behaviorist model). The new sophisticated medical equipment (CT, PET, MRI, MEG) has showed more brain work. Explain the function of neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters excite or inhibit the neighboring neuron. There are over 100 different neurotransmitters that have been discovered so far. Explain the function of longterm memory Long-term memory refers to the process of sorting and retrieving information. Long-term storage refers to where in the brain the memories are kept. Explain closure Describe a neuron Closure is a way that a learner’s working memory summarizes for itself a perception of what has been learned. A neuron is a nerve cell. It has thousands of branches, called dendrites, emerging from its core. Information is transferred along a long fiber called an axon. A myelin sheath surrounds each axon.