D. Major Compromises
advertisement

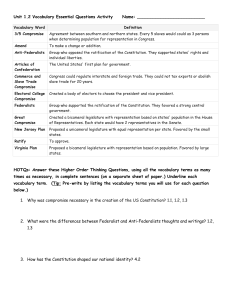
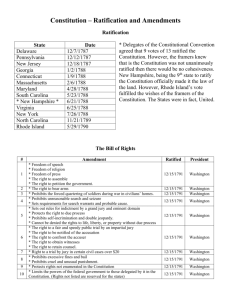
D. Major Compromises • Major disagreement arose over the question of representation in the new government • Virginia Plan – James Madison – Introduced by Edmond Randolph – Favored large states – Representation would be based on the size of a state’s population – Wanted national sovereignty to replace state sovereignty • New Jersey Plan – William Patterson – Favored small states – Each state was given equal representation • Results in bickering, name-calling, wig-pulling, and almost a full stop of the convention E. Great Compromise • Connecticut Compromise – Roger Sherman • Created a two house lawmaking body called Congress – Senate – States had equal representatives – House of Representative – States represented according to its population F. Slavery Compromises • Commerce and Slave Trade – Congress was forbidden the power to tax exports of goods from any state • Congress could not interfere with the slave trade for 20 years (1808) • Three-Fifths Compromise • Proposed by James Madison • Decided the question of how slaves would be counted for representation • Counted each slave as 3/5th of a person • Victory for the South because white men would be overrepresented there • “Great as the evil is, a dismemberment of the union would be worse” – James Madison th 3/5 of a Man? G. Approving the Constitution • Needed 9 states to approve the Constitution • Federalist – Supported ratification of the Constitution • Favored a strong central government • Believe the Articles were too weak to keep the states unified • Anti-Federalist – Opposed ratification of the Constitution • Feared strong central governments • Believed Constitution would fail to protect individual rights • Called for a bill of rights Primary Source – Alexander Hamilton – Federalist Papers #84 • “I go further and affirm that bills of rights, in the sense and to the extent in which they are contended for, are not only unnecessary in the proposed Constitution but would even be dangerous. . . . For why declare that things shall not be done which there is no power to do?” H. Constitution is Ratified • • • • Federalist Papers – Written in favor of the ratification of the Constitution – 85 Essays Written by Alexander Hamilton (51), James Madison (29), and John Jay (5) Papers provide insight into the mindset of two of the most brilliant thinkers of the day Regarded as the authoritative documentation of "original intent" – Reached compromise on adding a bill of rights – Critiqued the Articles – Explained how the new government would work Ratification of the Constitution Votes of State Ratifying Convents (1878-1790) State Date For Against Delaware Pennsylvania New Jersey Georgia Connecticut Massachusetts Maryland South Carolina New Hampshire Virginia New York North Carolina Rhode Island Dec. 1787 Dec. 1787 Dec. 1787 Jan. 1788 Jan. 1788 Feb. 1788 Apr. 1788 May 1788 June 1788 June 1788 July 1788 Nov. 1789 May 1790 30 46 38 26 128 187 63 149 57 89 30 194 34 0 23 0 0 40 168 11 73 47 79 27 77 32 • April 30, 1789 – George Washington is sworn in as the 1st President under the new Constitution • “If we get a government that lasts for 20 years were will have accomplished our mission.” – George Washington Primary Source – Benjamin Franklin, 1787 • “I doubt, too whether any other convention we can obtain may be able to make a better constitution. For when you assemble a number of men to have the advantage of their joint wisdom, you inevitably assemble with those men all their prejudices, their passions, their errors of opinion, their local interests, and their selfish views. From such an assembly can a perfect production be expected?”