Kidney and Male GU pathology
advertisement

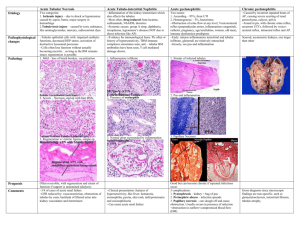
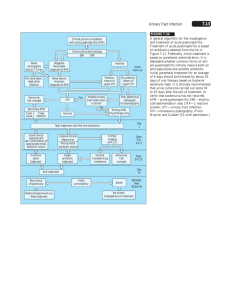
Kidney pathology 2010.1 Tubular & interstitial diseases Kidney - cut surface Co * Calyx B Pelvis * • Outer cortex (Co) • Inner medulla composed of pyramids * • Cortical columns of Bertini (B) between pyramids* • Urine first collects in calyces, pelvis Malpighi and Malpighian “corpuscles” (glomeruli) Glomerular structure • Arterioles • Capillaries • Mesangium (“between capillaries”) • Urinary space surrounds glomerulus within Bowman’s capsule • Urin sp -> prox tubule Normal renal tubules Acute pyelonephritis • • • • • Most severe end of spectrum of UTI Acute bacterial inflammation of kidney E coli, Proteus, Enterobacter, Klebsiella … Abscesses in cortex, medulla Polymorphs in tubules; glomeruli spared • (CMV, polyoma virus in immunocompromised) Acute pyelonephritis Acute pyelonephritis Acute pyelonephritis - clinical • M < 1yr and over 40 yrs; F 1 - 40 yrs • Sudden onset tenderness in costo-phrenic angle • Temp, rigors, cystitis • Most resolve quickly • May recur, become chronic • Complications Pathogenesis of acute pyelonephritis • (Haematogenous spread) • Bacterial adhesins, colonisation, ascending infection • Cystitis • Vesico-Ureteric Reflux & Intrarenal Reflux, congenital or acquired – VUR: Urine, bacteria -> ureter – Inrarenal reflux: Urine enters kidney papillae Predisposing factors • Short female urethra • Obstruction (pregnancy, congenital, stones, tumours, BPH) • Bladder dysfunction • Diabetes • Catheters, cystoscopy, other • Vesico-Ureteric Reflux & Intrarenal Reflux – If no reflux, infection only in bladder Complications of Acute Pyelo • • • • Perinephric abscess Pyonephrosis *Papillary necrosis Fibrous scars, chronic pyelonephritis Chronic pyelonephritis • Scars overlying distended calyces • Chronic inflammation and fibrosis involving tubules and interstitium • Two types – Reflux nephropathy – Chronic obstructive pyelonephritis Reflux nephropathy • • • • Commoner VUR pressure threshold Organisms Refluxing papillae at upper, lower poles • Hypertension at 15-25 yrs Chronic pyelonephritis (reflux) Chronic pyelonephritis - reflux type Chronic pyelonephritis, obstructive • Older patients • Strictures, calculi in ureter, renal pelvis • BPH • Tumours Chronic pyelonephritis - clinical • Chronic renal failure, hypertension • UTI (but often negative urine cultures) • Interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, thyroidization of tubules, thick arteries, FSGS • Accounts for 10 - 20% of patients on dialysis • Other types of pyelonephritis TB (L) & Xanthogranulomatous PN (R) Non-bacterial inflammation of renal tubules, interstitium • Drugs/toxins: penicillins, rifampicin, NSAIDs….. – Immune injury (types I, IV); direct, unknown – Fever, oliguria in 50%, rash – Micro; inflammatory cells, inc eosinophils • Analgesic nephropathy - phenacetin, +/- aspirin, codeine • Assoc with glomerular disease e.g. SLE, renal vasculitis • Gout, multiple myeloma • Renal allograft rejection Acute interstitial nephritis Eosinophils in drug induced interstitial nephritis Acute renal transplant rejection Acute renal failure • Sudden onset of oliguria (<400ml) – Raised serum Creatinine • Cause determines symptoms, prognosis • Overall mortality is 40% – – – – Drugs, toxins Crescentic glomerulonephritis e.g. ANCA+ vasculitis Genitourinary obstruction Shock, ischaemia Acute renal failure - pathology • Most patients have a microscopic lesion - Acute Tubular Necrosis (necrosis of tubular epithelial cells is a “marker” of acute loss of renal function) • Renal tubular epithelium sensitive to toxins, ischaemia • Vasoconstriction -> hypoxia in outer medulla • Two types of ATN: • ATN due to drugs, toxins - PCT cells (95% survival) • ATN due to ischaemia, shock or sepsis - granular casts (20-50% survival) Normal tubules (L) and drug-induced ATN* (R) * ATN, drug-induced ATN due to toxin ATN due to Sepsis/Ischaemia Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in chronic renal disease correlate with progressive loss of renal function QuickTime™ and a Photo - JPEG decompressor are needed to see this picture. Chronic renal failure • Progressive and irreversible loss of renal tissue • Chronic GN, chronic PN, hypertensive nephrosclerosis, diabetes, adult type PCKD • Symptoms - anaemia, dehydration, nausea, metabolic bone disease, etc • Asymptomatic renal insufficiency present prior to this while kidneys’ intact nephrons compensate • Dialysis, transplant or death within 1 year of onset of CRF