Understanding Guided Reading
advertisement

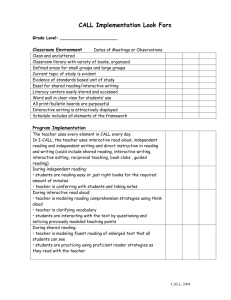
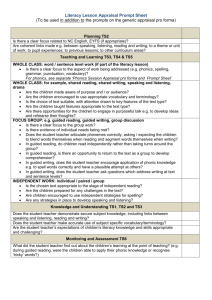
SSI Reading Curriculum Training Mandi Bush, Taylor Davis, Joanna Kysar SSI Reading Netschool Page • Scope and Sequence • Resources • Middle School ELA SSI: http://moodle.nisdtx.org/enrol/instances.php ?id=11046 • Enrollment Key: curriculum2014 Scope and Sequence Mandatory Resources • The Continuum of Literacy Learning by Pinnell and Fountas • Text and Lessons for Content-Area Reading by Daniels and Steineke • Text and Lessons for Teaching Literature by Daniels and Steineke • Comprehension and Collaboration by Harvey and Daniels • DRA2 • Leveled Readers Optional Resources • Literacy Navigator by Pearson • Novels from book room • Literature textbook The Continuum of Literacy Learning by Pinnell and Fountas What is The Continuum of Literacy Learning? • A large body of literacy learning as it happens over time • Addresses interactive read aloud and discussion, writing, guided reading, spelling/phonics skills, reading response, etc. • A common vision of children’s progress • Go to for guided reading groups in SSI DRA2 for Progress Monitoring What is DRA2? • Help identify students’ skills and plan for timely instruction in reading, engagement, fluency, and comprehension. • Monitor student growth on a variety of crucial skills and strategies that successful readers utilize. • Prepare students to be successful at meeting today’s classroom and testing expectations. • Provide support and forma to keep parents and other stakeholders informed about the level of student reading and achievement. Research Based • “It can also be used more frequently [than annual or semiannual] with struggling readers to ensure continued progress.” • Four different field tests were conducted. Two with each edition. • Based on current research in reading from sources such as National Reading Panel Report and Reading for Understanding • DRA2 helps students become good readers by scaffolding and encouraging them to work towards the skills and qualities good readers have. (pg. 6 and 7) DRA2 Materials • • • • • • • • • 28 Benchmark Assessment Books Teacher Guide Blackline Masters (book and CD) 30 Student Assessment Folders DRA2 Organizer Box 29 Hanging Folders Assessment Procedures Overview Card DRA2 Clipboard Training DVD Book Information • 20 books are leveled for on or above fourth through eighth grade (40-80) • Bridge Pack- eight books for those below fourth grade level • Each level consist of two fiction and two nonfiction books ranging between 12-16 pages in length with word count starting at 400 (20) and ending at 2,000 (80). • Most on-level students are able to read silently an entire text in 10-15 minutes. • List of books are on pages 13-20. Basic Steps to Conducting the DRA2 • Step 1: Student Reading Inventory- reading habits (10-15min) • Step 2: Reading Conference- oral reading fluency (6-10min) Choose level based on previous student performance data in Aware and choose fiction or nonfiction based on what was studied the six weeks. If oral reading is in the shaded area- stop the test and move down a level • Step 3: Independent Student work- independent reading and demonstration of comprehension ability (30-40min) • Step 4: Analyzing Student Performance- use teacher observation guide (10min) • Step 5: Input data to AWARE • Use data to select level for guided readers and to help guide instruction (especially one-on-one or small group) • DRA2 will be completed at the end of each six weeks for progress monitoring Understanding Guided Reading What is Guided Reading? • Guided reading is meant to work with students at their instructional reading level, giving them the chance to read a book during the guided reading format that they may not be able to read independently. • Guided reading is made up of a text introduction, reading of the text, discussing/revisiting the text, teaching for processing strategies, word work, and extension. • During guided reading, students are processing the text independently and are supported by a text introduction and a discussion after reading the text. • Guided reading groups are homogeneous but also flexible. Students should move around as necessary. • Consistent guided reading will help students take on the skills they need to be successful readers. Teacher Role in Guided Reading • Teachers use guided reading to get to know their students as readers. • In guided reading, a teacher helps individual students learn how to process a variety of increasingly challenging texts with understanding and fluency within a small group setting. • Guided reading allows the teacher to meet the needs of all students within the class. • Guided reading provides a setting for teachers to demonstrate reading strategies to students. Parts of a Guided Reading Lesson • Text introduction: unlock the text and provide scaffolds that will allow the reader to understand the text. – Point out challenging words and their meanings – Activate background knowledge that will get students interested in the text and encourage connections – Have students make predictions – Talk about the author – Talk about text features, pictures, and organization with in the text • Reading the text: Listen to students read out loud from where they are in their independent reading and ask a quick comprehension question or two, making your way around to all members in the guided reading group. – – – – – Prompt for fluent reading Prompt for self-monitoring to make sure students are comprehending their reading. Prompt for self correcting Check for comprehension Demonstrate how to read fluently and/or search for and use information from the text Parts of a Guided Reading Lesson Cont. • Discussing and Revisiting the text: Ask students a question or questions from within, beyond, and about the text to ensure that you are having a conversation surrounding all different types of thinking about the text. – – – – Within the text (recall and summarize) Beyond the text (prediction, connection, and synthesize) About the text (analyze and critique) Use The Continuum of Literacy Learning by Pinnell and Fountas (page 324-355) for questioning guide • Teaching for Processing Strategies: Provide a brief, explicit teaching point focused on the reading process by modeling your thinking to students. – Solving words, monitoring and checking, searching for and using information, summarizing, maintaining fluency, predicting, making connections, inferring, synthesizing, analyzing, and critiquing – Use what was taught in Text and Lessons for Teaching Literature and Text and Lessons for Content Area Reading by Daniels and Steineke within guided reading groups. Parts of a Guided Reading Lesson Cont. • Working with Words: Give students a 1-2 minute exposure to a word study concept appropriate to their group’s level that would help them as readers and/or writers. The concept doesn’t have to relate to the guided reading. – – – – – – Spelling principle Greek/Latin root words Homographs/homophones Commonly misused grammar concepts Punctuation rules Use The Continuum of Literacy Learning by Pinnell and Fountas (page 324-355 and pages 369-404) for word work ideas • Extending the Understanding of the Text: Ask students to extend their understanding of the text by doing some writing about their reading, researching something surrounding the reading, etc. – – – – Diary entry from character’s perspective Letter or e-mail from one character to another Research a concept mention in the text Use The Continuum of Literacy Learning by Pinnell and Fountas (page 92-99) for ideas. Leveled Readers with The Continuum for Guided Reading • Use The Continuum of Literacy Learning by Pinnell and Fountas • Page 240- a guided reading lesson for using with the leveled readers. • Page 247- text characteristics for guided reading Text and Lessons for ContentArea Reading and Text and Lessons for Teaching Literacy by Daniels and Steineke Take a Look and Teach a Lesson • Find a partner and choose a lesson from your assigned book (Teaching Literature or Content-Area Reading) to teach to us. • You and your partner will have 20 minutes to find a lesson and prepare to present. • You will have approximately 5 minutes to teach the 20-50 minute lesson- condense! Book Clubs and Inquiry Circles: Taking it a Step Further Comprehension and Collaboration by Harvey and Daniels • Focus is on Chapter 10: Literature Circle Inquiry –Different than tradition book clubs –Four different stages (page 201) • Immersion • Investigation • Coalesce • Go Public Questions/Concerns? Thank you and enjoy the rest of your summer!