XP Describe the components of a computer system
advertisement

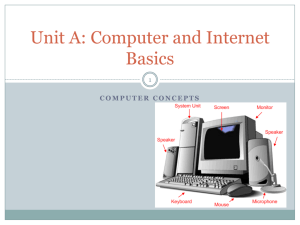
XP Essential Computer Concepts Tutorial 1 1 Describe the components ofXP a computer system A computer system consists of much more than just a computer; it also includes peripheral devices and software. The computer's physical components (such as the main circuit board and the motherboard) are referred to as hardware. The peripheral devices are additional components that are needed to accomplish input, output, and storage functions. Software refers to the intangible components of the computer system, such as the programs that the computer needs to perform specific tasks. 2 XP A typical computer with input and output devices This figure shows a typical computer system configuration with some potential input and output devices. 3 Data is input, processed, stored, and output XP This figure shows a typical processing cycle of data. The user enters data via the keyboard, it is processed by the CPU, it may be sent to another workstation or to a printer, and it is usually saved on a storage device. 4 Compare the types of computers XP There are four basic types of computers: – Microcomputers – Minicomputers – Mainframes – Supercomputers These classifications are based on size, speed, and cost. 5 XP Which type of computer is used for what type of processing? Microcomputers, or personal computers (PCs), come in several forms: – Desktop – Tower – Notebook – Personal digital assistants (PDA) Minicomputers are larger than microcomputers, and have the capability of processing tasks for many users. A mainframe computer is larger and more powerful than a minicomputer and can handle many more users. – Typically used for centralized storage, processing, and data management The supercomputer is the largest and fastest of all the computers and is used for high-volume computing tasks. 6 XP Typical microcomputer types This figure shows the various types of microcomputers available today. 7 Define microcomputer hardware in terms of input and output devices XP Many components can make up the hardware for a microcomputer. Each type of component performs a different function. Input devices provide a method for inputting data and commands. Typical input devices include a keyboard, a mouse, or another pointing device. Output devices enable you to view the results of your work and the processing work of the computer. Typical output devices are monitors and printers. 8 XP Typical input devices This figure shows several devices used for inputting data to the computer. Keyboards Mouse Other pointing devices 9 Define microcomputer hardware in XP terms of processing and storage Processing hardware is the most critical component of a computer system. It includes the microprocessor (a silicon chip designed to manipulate data) and the memory that stores data and instructions. All of the data that is generated through your input or the computer's processing needs to be stored in a fashion that can later be retrieved. This is done through storage devices and media, such as magnetic storage devices (floppy disks and hard disk drives), tape drives, and optical storage devices (CDROM and DVD drives). 10 Storage devices and RAM storage XP Data is frequently transferred from a storage device to RAM for processing, and transferred back to the storage device after processing. 11 Store data on a magnetic disk XP This figure shows how data is stored on a magnetic disk, be it a hard drive or a floppy drive. 12 XP An optical storage device This figure shows the basic way in which data is stored on an optical storage device. 13 XP Examine data representation and the ASCII code A computer does not understand the characters that are used in human languages. A computer must represent every signal as either “on” (with a 1) or “off” (with a 0). These numbers are called binary digits or bits. A series of 8 digits is called a byte. 14 XP How numbers appear in binary form This table shows how various decimal numbers would be represented in binary form. Note that each number requires 8 bits, which makes up one byte. 15 XP Learn about ASCII code In ASCII code, which is commonly used by microcomputers, each byte represents a unique character (such as a letter, a number, or a typographical symbol). The storage capacity of the processor or storage hardware is represented as the number of bytes that the device can handle. These capacities are expressed in kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), or gigabytes (GB). 16 How letters and symbols appear in ASCII code format XP This figure shows how several letters and symbols would appear inside the computer when converted into ASCII format. Note that each character still requires one byte (8 bits) of storage. 17 Describe how peripheral devices are connected to a microcomputer XP In order for peripheral devices to be useful, they must have a way of communicating data with the microprocessor. Each device has a port and a cable that connects into the computer (either externally or internally). These ports connect to a controller card that provides the electrical connection to the main computer board. 18 Microcomputers use ports for input and output operations There are several types of ports available with XP microcomputers: – – – – – USB Parallel Serial SCSI MIDI Each has different capabilities for data transmission, and each is designed to work with different peripheral devices. 19 Identify microcomputer ports This figure shows the various types of ports in use on modern microcomputers. Notice that each port requires a different connector format. Sound Card Ports XP Modem Video Ports Port Parallel Port Keyboard PS/2 Mouse USB Port DB-9 Serial Port Power cable DB-25 Serial Port 20 Connect a printer to the computer XP A printer must be connected to a computer port before it can be used. It is connected via a cable that has a connector on one end that fits into the printer port. The other end has a connector that fits into the computer’s port. 21 XP Identify the hardware and software used to establish a network connection A network enables you to share data and resources with others. A typical network configuration is a local area network (LAN), in which the computers and devices are located relatively close to each other. If a computer is connected to a network, it is referred to as a workstation. – Each workstation requires a network interface card to create the communications channel between the network and the computer – The computer workstation must also have network software to establish communications protocols Each device on the network is referred to as a node. 22 XP A typical LAN configuration This figure shows a typical network with several workstations connected to a server, and a printer connected to the network that can be accessed by any workstation. 23 Explain how Internet access, e-mail, andXP the World Wide Web affect the use of computers The Internet, which was originally developed for the government to connect researchers around the world who needed to share data, is the largest network in the world. It can be used to send messages from one user's computer to another - commonly called e-mail. It can also be used to access the World Wide Web - a huge database of information stored on network servers around the world. You can use a Web browser to search for and view the information available on any topic or to go to a specific location. 24 XP A Web page on the World Wide Web The variety of text, images, sounds, etc. that can be displayed on the Internet, as well as the format in which they appear, is virtually limitless. This figure is an example of what one page of one Web site looks like. 25 Discuss the types of system software and their functions XP The fundamental operations of your computer are managed by the system's software. There are four types of system software. – Operating system software controls basic input and output, allocates system resources, manages storage space, maintains security, and detects equipment failure – Utilities aid the operating system by taking over some of its responsibility for allocating hardware resources – A device drive aids the computer in communicating with individual peripheral devices – Computer programming languages are used by programmers to write computer instructions 26 Software works with your hardware XP to perform basic functions Many of the components of the system software work hand-in-hand with each other to assist you in accomplishing your tasks. This figure shows the operating system software working with the word processing software in order to print a document. 27 Identify popular application XP software Application software (commonly referred to as a computer program) enables you to perform specific tasks with your computer. Some typical tasks are: creating documents and spreadsheets, managing databases, and creating graphics and multimedia presentations. All of these applications have features and tools built into them that aid you in achieving the best results for the project on which you are working. 28 Application software can beXP purchased and installed This figure shows a popular application software product - Microsoft Office. 29 XP A word processing application This figure shows a typical window for a word processing application program. In this case, the red line underneath the word ‘bigin’ indicates a potential spelling error that was caught by the program. 30 XP A typical spreadsheet application Spreadsheet application programs allow you to organize data in a grid of rows and columns. The data can be used in calculations and formulas. 31 XP Use presentation software Presentation software allows you to create slide shows that can be shown via your computer. 32 XP Describe how data is shared among different types of application software The ability to use data created in one application in another application is one of the most powerful developments in the software industry. In the Windows environment, this is done through object linking and embedding (OLE). Embedding copies the source data from one application into a different application. – The copy will remain in its new location regardless of what happens to the original Linking creates a continuous connection between original source data and the copied data. – Whenever the source data is updated or changed, so too is the data in the linked application 33