geologic time
advertisement
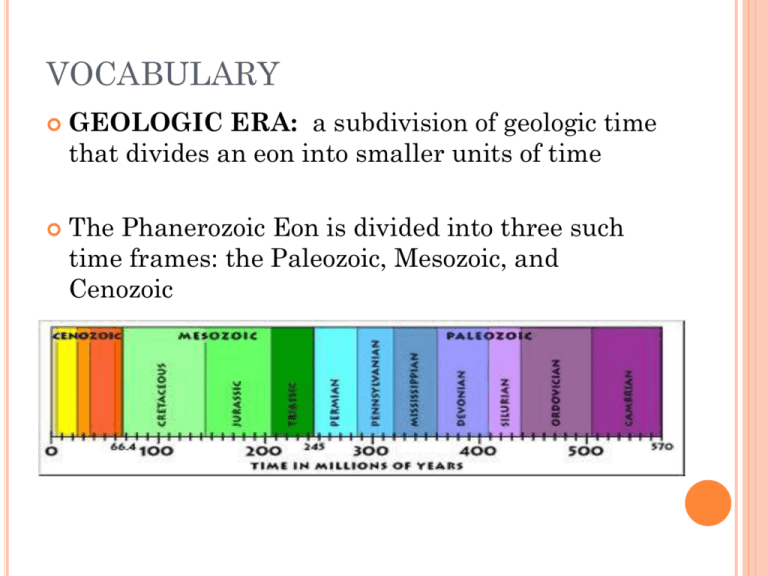
VOCABULARY GEOLOGIC ERA: a subdivision of geologic time that divides an eon into smaller units of time The Phanerozoic Eon is divided into three such time frames: the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic PART I: GEOLOGIC TIME AND THE AGE OF THE EARTH LET’S START WITH SOME BASICS….. Scientists have always wondered how old the earth was. But how were they to determine the Earth’s age? 1ST ATTEMPT: ‘BEGAT’ THEORY 1640 He Archbishop James Ussher calculated, using Hebrew chronology (know as the ‘begat’ theory) CONCLUSION: Earth was created in 4004 BC. FATAL FLAW This is a calculation of recorded history– not how long the earth itself has been around. SALT IN THE OCEAN THEORY 1715 : English Astronomer Edmund Halley (of Comet Halley fame) Salinity of ocean Measured in location and then measured again 10 years later FATAL FLAW Although the Earth’s first waters were indeed fresh water, the salinity of the oceans is actually in equilibrium with the earth’s crust – and does not increase over time. THICKNESS OF THE SEDIMENTARY LAYERS THEORY Late 1800’s Various geologists measured the total thickness sedimentary rocks. They thought that this would lead to an approximate calculation of the age of the Earth. VARIOUS AGE CALCULATION FATAL FLAW They assumed that each rock type had an average rate of deposition This does not hold true Climate, rock type, type of deposition, angle of slope - all affect the rate of sediments being deposited LOSS OF HEAT THEORY 1859: Lord Kelvin in 1859 Argued that the Earth was originally molten and continued to lose heat from the center to the surface at a uniform rate. FATAL FLAW Scientist of his day did not know about radioactive decay This is keeping the earth’s interior hot (not ‘cooling down’) RADIOACTIVE DECAY THEORY 1902 Ernest Rutherford studying radioactive decay Measured the ratio of Uranium to its decay by product Helium FATAL FLAW Over time the helium gas escaped from the rock sample This gave an inaccurate ratio RADIOACTIVE DECAY THEORY REFINED 1911, Arthur Holmes radioactive decay, but used a better set of elements. FATAL FLAW Rocks on the earth’s surface are constantly being recycled via processes associated with erosion, weathering and plate tectonics. This destroys the original ratios METEORITE THEORY Using radiometric age dating techniques on meteorite samples have revealed a still older date for the age of the Earth AGE OF THE UNIVERSE? How does this age compare to the age of the universe? February 2003, NASA’s Wilkinson Microwave Anisotrophy Probe provided scientists with a date GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE Now that scientists had a handle on the age of the earth, they started to think of how to divide it up into sections Think day calendar – year, month, week, NEPTUNIST THEORY Neptunist theories dictated that all rocks had precipitated out of a single enormous flood PLUTONIST THEORY – JAMES HUTTON (FATHER OF GEOLOGY) The interior of the Earth was hot, and that this heat was the engine which drove the creation of new rock: land was eroded by air and water and deposited as layers in the sea; heat then consolidated the sediment into stone, and uplifted it into new lands. DEVELOPING THE IDEA The principles underlying geologic (geological) time scales were laid down by Nicholas Steno in the late 17th century STENO’S LAWS Over the course of the 18th century geologists realized that: Sequences of strata were often eroded, distorted, tilted, or even inverted after deposition; Strata laid down at the same time in different areas could have entirely different appearances; The strata of any given area represented only part of the Earth's long history. FOSSILS William Smith - identification of strata by the fossils they contained Enabled geologists to divide Earth history based on appearance/disappearance of difference plants or animals EARLY ATTEMPTS Scientists divided the rocks of the Earth's crust into four types Each type of rock, according to the theory, formed during a specific period in Earth history Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary NAMES OF THE GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE The process was dominated by British geologists, and the names of the periods reflect that dominance. DIVISION OF THE TIME SCALE LARGEST to SMALLEST …. EON Divided into ERAS Divided into PERIODS Divided into EPOCHS Divided into AGES TODAY’S ACTIVITY CREATE A SCALE MODEL OF GEOLOGIC TIME 1 mm = 1 million years Your list will allow your team to plot major biologic and geologic events HOMEWORK – SGQ #1 Discuss what was happening to the planet during the Precambrian Supereon. Feel free to include drawings or illustrations. Be sure to include by what processes the crust and oceans formed, when and over how much time. TICKET OUT THE DOOR When did the geologic time scale start? TODAY’S VOCABULARY GEOLOGIC ERA: a subdivision of geologic time that divides an eon into smaller units of time. NOTE: The Phanerozoic Eon is divided into three such time frames: the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic represent the major stages in the macroscopic fossil record. EONS …… Largest division of geologic time The Hadean, Archean and Proterozoic Eons (were as a whole formerly called the Precambrian) This covered the four billion years of Earth history prior to the appearance of hard-shelled animals PHANEROZOIC EON – life started to appear in the geologic record Takes us to the present day EONS DIVIDED INTO ERAS PHANEROZOIC EON PALEOZOIC ERA MESOZOIC ERA Early life, mostly in the water Middle life, age of dinosaur CENOZOIC ERA Present life, age of mammals ERAS DIVIDED INTO PERIODS The "Cambrian," (the Roman name for Wales) The "Ordovician," and "Silurian", named after ancient Welsh tribes, were periods defined using stratigraphic sequences from Wales. The "Devonian" was named for the English county of Devon The "Carboniferous" was simply an adaptation of "the Coal Measures," the old British geologists' term for the same set of strata. The The "Permian" was named after Perm, Russia, because it was defined using strata in that region by a Scottish geologist Roderick Murchison. However, some periods were defined by geologists from other countries. "Triassic" was named in 1834 by a German geologist Friedrich Von Alberti from the three distinct layers (Latin trias meaning triad) —red beds, capped by chalk, followed by black shales— that are found throughout Germany and Northwest Europe, called the 'Trias'. The "Jurassic" was named by a French geologist Alexandre Brogniart for the extensive marine limestone exposures of the Jura Mountains. The "Cretaceous" (from Latin creta meaning 'chalk') as a separate period was first defined by a Belgian geologist Jean d'Omalius d'Halloy in 1822, using strata in the Paris basin and named for the extensive beds of chalk (calcium carbonate deposited by the shells of marine invertebrates). IMPORTANT TO NOTE …….. The time scale is depicted in its traditional form with oldest at the bottom and youngest at the top -- the present day is at the zero mark. HOW DO WE DECIDE WHERE TO PUT THE DIVISIONS? Numerous high-resolution radiometric dates have been generated that has led to improved age assignments of key geologic stage boundaries, Also used: Occurrence/disappearance of fossils Global geochemical variations, Milankovitch climate cycles, and Magnetic reversals FOR TODAY FINISH YOUR TIME LINE COLOR CODE ALONG THE TIME LINE TO SHOW THE DIFFERENT ERAS RED = PRECAMBRIAN (pre-life) BLUE = PALEOZOIC (ancient life, mostly in the oceans) GREEN = MESOZOIC (age of reptiles – dinosaurs) YELLOW = CENOZOIC (age of mammals – the Era we are now living in) AFTER TIMELINE…. Questions that go with the activity WORKSHEET: HOMEWORK: Worksheet and SGQ #2 The boundaries for the geologic eras were established because of mass extinctions. What are mass extinctions? When did the five major mass extinctions of the Earth past occur? For each discuss what scientists feel caused them and what species and what % were wiped out. TICKET OUT THE DOOR WHICH ERA DO YOU LIVE IN? Precambrian Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic GEOLOGIC HISTORY OF WESTERN US http://jan.ucc.nau.edu/~rcb7/Text_WUS.html http://cpgeosystems.com/wnamtectonic.html RESOURCE WEBSITES http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/geotime/contents.html






