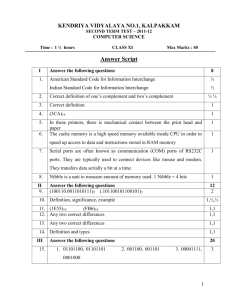
Colorless

Next-Generation ROADMs
October 1, 2012
Sheldon Walklin
CTO, Optelian
Contents
• Introduction
• Wavelength Selective Switch
• Colorless, Directionless and Contentionless
• Flexible Bandwidth ROADMs and Transmission
Beyond 100 Gb/s
• ROADM Control, OpenFlow and SDN
• Conclusion
2
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
Wavelength Selective Switch Functionality
Nx1 WSS
SW 1
VOA 1
Port 1
Common
SW M
VOA M
Port N
3
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
Colorless, Directionless and Contentionless (CDC)
Colorless
Any wavelength can be dynamically added/dropped without having to re-fiber a transceiver.
Directionless
A wavelength can be dynamically added/dropped from any direction without having to re-fiber a transceiver.
Contentionless
A wavelength can be re-used on all directions without any restrictions.
4
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
4-Degree ROADM (Colored)
Com
In
B
Com
Out
WSS
Com
In
A
Com
Out
Com
In
Com
Out
C
•
In general, can build an N-degree
ROADM using
Nx1 WSSs and
1xN splitters.
• The color and direction are fixed by fiber connections.
A B
. . .
C D
. . .
. . .
. . .
Colored add ports
Com
In
D
WSS
Com
Out
A
. . .
B
. . .
C
. . .
Colored drop ports
D
. . .
5
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
Transceiver
Rx
Tx
4-Degree ROADM (Colorless)
Com
In
A
Com
Out
Com
In
B
Com
Out
WSS
Com
In
Com
Out
C
A B C D
. . .
. . .
. . .
Colorless add ports
. . .
Com
In
D
WSS
Com
Out
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
A
WSS
. . .
WSS
. . .
B C
WSS
. . .
D
WSS
. . .
Colorless drop ports
Transceiver
Rx
Tx
6
•
Any transceiver wavelength
(color) can be remotely configured
• The direction is fixed by fiber connections.
•
Reduced number of access ports compared to colored.
Colorless and Directionless
Drop directions
A B C D
Add directions
A B C D
4x1 WSS
1xN WSS
. . .
Colorless drop ports
Wavelength
Contention
Passive combiner
. . .
Colorless add ports
•
Structure for cross connecting between degrees remains the same as shown for the 4-degree
ROADM on earlier slide.
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
7
Colorless, Directionless and Contentionless
(using NxM WSSs) drop directions
A B C D
4xN WSS
. . .
CDC drop ports
add directions
A B C D
Nx4 WSS
. . .
CDC add ports
8
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
Colorless, Directionless and Contentionless
(using Broadcast-and-Select with Tunable Filters)
Drop directions
A B C D
Add directions
A B C D
4x1
SW
4x1
SW
TF TF
CDC drop ports
4x1
SW
TF
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
9
4x1
SW
4x1
SW
CDC add ports
4x1
SW
Colorless, Directionless and Contentionless
(using Adjunct NxM Photonic Switches)
B
Com
In
Com
Out
WSS
•
Use NxM photonic switches to upgrade existing colored
ROADMs to full CDC functionality
Com
In
A
Com
Out
Com
In
Com
Out
C
A
. . .
B
. . .
C
. . .
D
. . .
Com
In
Colorless add ports
D
WSS
Com
Out
A
. . .
B
. . .
C
. . .
D
. . .
Colorless drop ports
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
10
Transceiver
Rx
Tx
Ideal CDC WSS
A
Directions
B C
CDC drop ports
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
CDC ROADM
(module)
D
•
Concept module
•
Non-blocking wavelength switching between any set of ports.
• Per wavelength attenuation control at line egress ports.
• Low insertion loss (up to a few dB)
• Very high reliability.
11
CDC add ports
The Benefit of CDC Functionality s1
R1 s3
R2 s2 s4
R3 s5 s10
R5
R4 s7 s11 s6 R6
R7 s8 s12 s9
R8
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
12
•
Without CDC, cannot automatically restore optical circuit for failure on Span S1 or
S6, or power failure at Node R2 or R4.
• CDC allows more flexibility to remotely reroute optical circuit when optimizing network utilization.
•
Consideration: OTN and/or
Layer 2+ protection and switching capabilities may reduce need for optical circuit dynamic routing.
Flexible Bandwidth ROADMs
1 2 3 4 5 6
Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 Ch5
• Flexible bandwidth (FB) ROADMs (aka gridless ROADMs) allow the passband center and/or width to be dynamically adjusted.
•
Many people advocate that FB ROADMs will be required to support bit rates beyond 100G.
13
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
Considerations for Transmission
Beyond 100 Gb/s
• For 40G and 100G transmission, the client interface has transitioned to parallel optics, while the line interface has retained single-carrier optics for improved transmission capacity. Parallel optics will likely be required on the line interface for bit rates approaching 1 Tb/s and beyond.
• Multi-carrier channels or superchannels are likely to be used for longhaul transmission beyond 100 Gb/s, with PDM-QPSK used for each constituent carrier. PDM-xQAM may be used in Metro (shorter distance) applications.
• Although FB ROADMs may provide improved spectral efficiency, they are not required for transmission beyond 100 Gb/s.
14
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
ROADM Control
Automated Optical Layer
• Controls the power level of each wavelength at ROADM ports to a set target (Automatic Power Balancing)
• Span or link gain control
Automated Wavelength Circuit Provisioning
• Impairment-aware path computation (wavelength routing)
• ROADM switch configuration
15
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
Automated Wavelength Circuit Provisioning
5 done
1 wavelength circuit request
Connection
Controller
4 signaling
2
A-to-Z circuit request with routing constraints viable route(s) and required regen location(s)
3
Path
Computation
Element impairment-aware
Optical
Network
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
16
OpenFlow and SDN
App
OpenFlow
Controller s1
R1 s3
R2 s2 s4
R3 s5 s10
R5
R4 s7 s11 s6 R6
R7 s8 s12 s9
R8
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.
App
App
17
• Centralized dynamic control
•
Simple flow table entry at each ROADM for wavelength connection
•
Smart Apps
– must be aware of topology, resource availability and state, fiber properties, impairment modeling, etc.
•
Opportunity for OpenFlow applications to have multilayer control and visibility
•
Apps can evolve independently of physical network
Conclusion
• Current generation ROADMs use WSS modules and have colored or colorless access ports.
• CDC functionality generally has a higher capital cost and lower access port density, but may provide lower operational costs.
• FB ROADMs may provide improved spectral efficiency, but are not required to achieve transmission beyond 100 Gb/s
• Multi-carrier channels or superchannels will likely be used for long-haul transmission beyond 100 Gb/s, with PDM-QPSK used for each constituent carrier. PDM-xQAM may see application in the Metro
• Automated ROADM networks are well-suited to centralized control, making OpenFlow a good match. This could also facilitate multi-layer control.
18
© 2011 Optelian. All rights reserved.