The Diploma in Business Studies - Shareworld Development Institute
advertisement
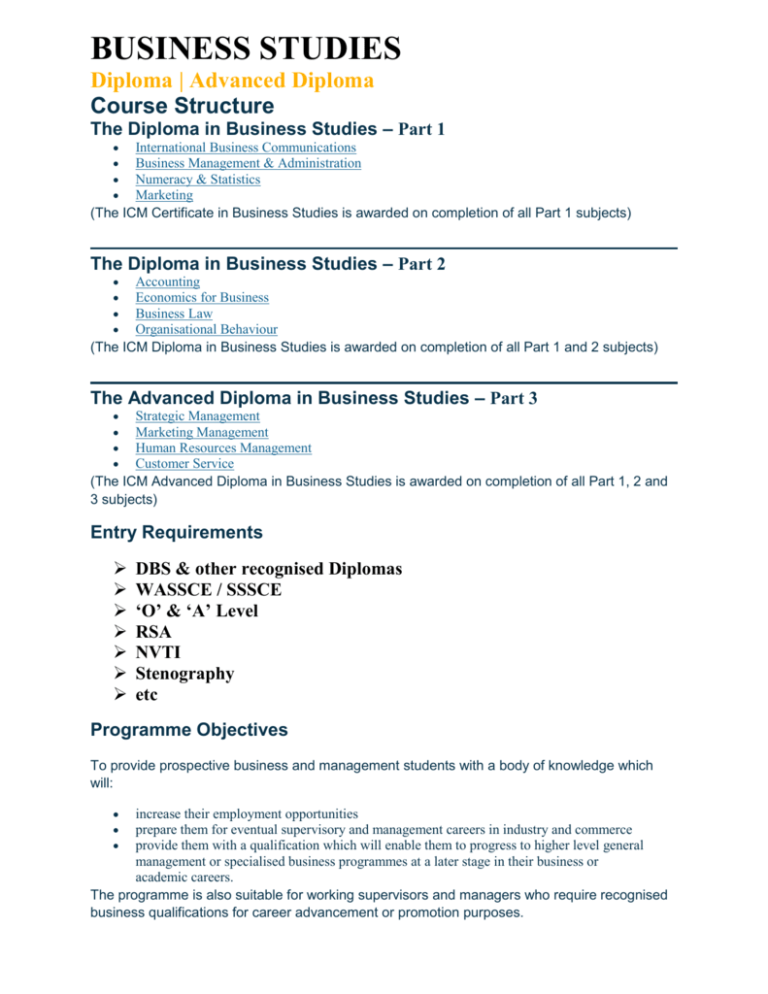
BUSINESS STUDIES Diploma | Advanced Diploma Course Structure The Diploma in Business Studies – Part 1 International Business Communications Business Management & Administration Numeracy & Statistics Marketing (The ICM Certificate in Business Studies is awarded on completion of all Part 1 subjects) The Diploma in Business Studies – Part 2 Accounting Economics for Business Business Law Organisational Behaviour (The ICM Diploma in Business Studies is awarded on completion of all Part 1 and 2 subjects) The Advanced Diploma in Business Studies – Part 3 Strategic Management Marketing Management Human Resources Management Customer Service (The ICM Advanced Diploma in Business Studies is awarded on completion of all Part 1, 2 and 3 subjects) Entry Requirements DBS & other recognised Diplomas WASSCE / SSSCE ‘O’ & ‘A’ Level RSA NVTI Stenography etc Programme Objectives To provide prospective business and management students with a body of knowledge which will: increase their employment opportunities prepare them for eventual supervisory and management careers in industry and commerce provide them with a qualification which will enable them to progress to higher level general management or specialised business programmes at a later stage in their business or academic careers. The programme is also suitable for working supervisors and managers who require recognised business qualifications for career advancement or promotion purposes. The Diploma in Business Studies – Part 1 International Business Communications Main Topics of Study: The process of communication The objectives of communication The meaning of words Non-verbal communication The context or situation Barriers to communication Why? Who? Where? When? What? How? Planning the message Summary – how to communicate Speaking effectively Basic speaking skills Qualities to aim for when speaking Summary – good speaking Listening Listening- the neglected skill Reasons for improving listening Are you a good listener? Ten aids to good listening Summary – good listening Human interaction and non-verbal communication Metacommunication and paralanguage The language of silence The language of time Body language or kinesics The underlying psychology: NLP, El and TA Conflict between verbal and non-verbal communication Summary – the importance of paralanguage in human interaction Talking on the telephone Telephone problems Basic telephone rules Switchboard operators Making a call Gathering information by telephone Answering the telephone Voicemail Mobile phone manners Summary – good telephoning Interviewing Interviewing weaknesses What is an interview? The purposes of the interview Types of interview information How to plan an interview Structuring the interview How to question and probe Summary – Interviewing Being interviewed for a job Preparing – the organisation Preparing – know yourself At the interview Tips to remember Summary – being interviewed for a job Communicating in groups Advantages of groups Disadvantages of groups Factors affecting group effectiveness Summary – making groups and committees work Running and taking part in meetings Chairing meetings Decision-making methods Responsibilities of participants Duties of officers and members The agenda The minutes Videoconferencing and audio-conferencing Formal procedure Giving a talk Techniques of public speaking Preparation Developing the material Opening the talk Closing the talk Visual aids Use of notes Practising the talk Room and platform layout Delivery of the talk Summary – being a good speaker Using visual aids General principles Whiteboards Flip charts Build-up visuals Physical objects Models and experiments Overhead projector Data projector Slide projector Videos Closed circuit television and video Points to remember about visual aids Video and DVD hire and purchase Summary – being in control of visual aids Faster reading How do you read? The physical process of reading Ways of increasing your vocabulary Summary – faster reading Better reading Determine reading priorities Scanning Skimming SQ3R method of reading Summary – better reading Writing business letters Why good letter-writing matters Backing up the phone call or meeting Planning a letter Layout and style The structure of a letter Dictating Standard letters Summary – writing business letters Applying for a job What sort of job do you want? What is available and what are they looking for? The application itself Job-hunting on the Internet Summary – applying for a job Writing reports What is a report? Types of report Essentials of a good report What is the purpose of the report? Fundamental structure Format, layout, headings and numbering Long formal reports House style How to get started Setting your objective Researching and assembling the material Organising the material and planning the report Writing the first draft Editing the report Producing the report Summary – report writing Memos, messages, forms and questionnaires Memos E-mail Fax Postcards and reply cards Text messaging Forms and questionnaires Summary – other writing tasks Visual communication When to use charts and graphs Presentation of statistical data Presenting continuous information Presenting discrete or non-continuous information Presenting non-statistical information effectively Getting to grips with grammar Why does grammar matter? What is grammar? How good is your English? The parts of speech in brief The framework of English The architecture of the sentence Common problems with English Subject-verb agreement Problems with verbs Problems with adjectives Problems with adverbs Problems with pronouns Problems with prepositions and conjunctions Problems with ellipsis Problems with negatives Revision of grammar Appendices A Punctuation made easy B Using capitals C Using numbers D Business cliches or ‘commercialese’ E Commonly misused and confused words F Ten (simple?) rules of spelling G Commonly misspelled words H Tips on modern business style I Differences between men and women communicating Business Management & Administration Main Topics of Study: The Organisational Background to Business Administration The Management Framework to Business Administration What are Business Administration and Management? The Board of Directors Functions within an Organisation The ‘Systems’ Approach to Organisation Planning-Control Feedback Cycles Characteristic Features of Organisations The Structure of Organisations and the Need for Authority The Features of Bureaucratic and Non-Bureaucratic Organisations Traditional Principles and Types of Organisation More about Systems & Subsystems The Structure of Business Enterprises The Pattern of Organisations Business Types including; Sole-Trder Enterprises, Partnerships, Limited Partnerships, The Limited Liability Company, Non-Profit-Making Units (Clubs & Societies), Public Enterprises Public Sector Organisations; Autonomous Public Corporations, Nationalised Industries, Local Government Institutions, Central Government Departments Functions within Organisations The Production Function: The Production Process and Types of Production Site Selection & Factory Planning Plant & Equipment Materials & Materials Handling Production Administration Costing Aspects of Production Work Study Maintenance & Production CAD, CAM & CIM The Purchasing Function: The Nature of Purchasing and the Role of the Purchasing Officer Purchasing Department Procedures, Inventory Control, Stores Control and Economic Order Quantity The Research & Development Function: The Functions of the Research & Development Department Basic Research Problem-Based Research Ideas Generation Applied Research & Development Patents, Trade Marks & Service Marks Research & Development in the Business Organisation The Marketing Function: Introduction to Marketing and The Marketing Philosophy Market Analysis & Research Promotion, Publicity & Public Relations Pricing Policy Credit Control Sales Administration Transport & Distribution (Logistics) Export Marketing Personnel Department: The Need for Staff The Functions of the Personnel Department and a Personnel Policy Employee Records Promotion, Transfer, Termination & Dismissal The Administrative Officer’s Role Industrial Relations Practice The Remuneration of Staff Office Administration: The Role of the Administrative Officer Facilities Management – The ‘New-Look’ Office Administrator The Office & its Functions The Clerical Function, Business Correspondence, Mail Inwards, Mail Outwards, Systems for Producing Business Correspondence. Meetings, Conferences, Functions and Delegation Other Responsibilities of the Administrative Officer: The Organisation & Methods Department Security Aspects of Business Risk Management The Environment of Organisations What is a Claimant? Assessing the Impact of Claimants Numeracy & Statistics Main Topics of Study: Using a Calculator: Approximations Estimation Degrees of Accuracy The Keys of a Calculator Standard Form Fractions: Types of Fraction Equivalent Fractions Operations Involving Fractions The Conversion Between Fractions & Decimal Fractions Ratio and Proportion: Ratio Division in a Given Ratio Direct Proportion Scale Diagrams & Models Measurement: Metric and Imperial Units Conversion Between Metric & Imperial Units Percentages: Percentages Finding a Percentage of an Amount Increasing & Decreasing an Amount by a Given Percentage Expressing One Quantity as a Percentage of Another Wages & Salaries: Basic Pay Overtime Rates Commission Piecework Deductions from Pay Travel: Foreign Currency Time Timetables Sampling, Surveys, Questionnaires: Surveys Censuses Samples Sampling Methods Bias Questionnaires Pilot Surveys Hypothesis Testing Classification & Tabulation of Data: Tabulation Classification of Data Tally Charts Frequency Tables Statistics on Display: Pictorial Representation of Data Pictograms Bar Charts Pie Charts Line Graphs Frequency Polygons Drawing Inferences from Diagrams Averages & Range: The Arithmetic Mean The Mode The Median The Use of Mean, Mode & Median The Mean & Median of a Frequency Distribution Range Cumulative Frequency: The Cumulative Frequency Curve (or Ogive) The Median The Interquartile Range Percentiles Probability: Introduction Probability From Theory and Experiment Simple Probabilities Simple Laws of Addition Possibility Space Networks & Decision Trees: Networks Decision Trees Algebra: The Basics of Algebra Indices Brackets Common Factors Equations Harder Equations Trial & Improvement Flow Diagrams Sequences Formulae Graphs: Graphs & Curves The Interpretation of Graphs Graph Plotting Conversion Graphs Cartesian Coordinates Straight Line Graphs Gradients & Intercepts Geometrical Shapes: Lines & Angles Polygons Circles & Angles Tessellations 2D Representation of 3D Objects Mensuration: Perimeters of Polygons Area The Circumference and Area of a Circle Volume Time & Travel Graphs: Distance-Time Graphs with Straight Lines Distance-Time Graphs with Curves Velocity-Time Graphs Growth & Decay Further Algebra: Simultaneous Equations Inequalities Removing Brackets Rearranging Formulae Marketing Main Topics of Study: Concept & Process of Marketing The Marketing Concept: Evolution of Marketing Business Orientations Societal Issues & Emergent Philosophies Customer & Competitor Orientation Efficiency & Effectiveness Limitations of the Marketing Concept Marketing process overview: Marketing Audit Integrated marketing Environmental Analysis SWOT Analysis Marketing Objectives Constraints Options Marketing planning Costs and benefits: Benefits of Building Customer Satisfaction Service and Customer Care Relationship Marketing Customer Retention Customer Profitability Total Quality Marketing Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning Macro-environment: Environment Scanning Political, Legal, Economic Socio-cultural, Ecological & Technological Factors Micro-environment: Stakeholders (Organisation’s Own Employees, Suppliers, Customers, Intermediaries, Owner’s Financiers, Local Residents, Pressure Groups & Competitors) Direct & Indirect Competitors Porter’s Competitive Forces Buyer Behaviour: Dimensions of Buyer Behaviour Environmental Influences Personal Variables – Demographic, Sociological, Psychological-motivation, Perception & Learning Social Factors Psychological Stimuli Attitudes Other Lifestyle & Life Cycle Variables Consumer & Organisational Buying Segmentation: Process of Market Selection Macro & Micro Segmentation Bases for Segmenting Markets: Geographical, Demographic, Psychographic & Behavioural Multivariable Segmentation & Typologies Benefits of Segmentation Evaluation of Segments & Targeting Strategies Positioning Segmenting Industrial Markets Size Value Standards Industrial Classification Marketing mix Products: Products & Brands – Features, Advantages & Benefits The Total Product Concept Product Mix Product Life-cycle & Its Effect on Other Elements of the Marketing Mix Product Strategy New Product Development Adoption Process Place: Customer Convenience & Availability Definition of Channels Types & Functions of Intermediaries Channel Selection Integration & Distribution Systems Franchising Physical Distribution Management & Logistics Ethical Issues Price: Perceived Value Pricing Context & Process Pricing Strategies Demand Elasticity Competition Costs Psychological Discriminatory Ethical Issues Promotion: Awareness & Image Effective Communication Integrated Communication Process Promotional Mix Elements Push & Pull Strategies Advertising Above & Below the Line Packaging Public Relations & Sponsorship Sales Promotion Direct Marketing & Personal Selling Branding On-line Marketing Different Marketing Segments & Contexts Consumer Markets: Fast-moving Consumer Goods Consumer Durables Co-ordinated Marketing Mix to Achieve Objectives Organisational Markets: Differences From Consumer Markets Adding Value Through Service Industrial Non-profit Making Government Re-seller Services: Nature & Characteristics of Service Products – Intangibility, Ownership, Inseparability, Perishability, Variability Heterogeneity – the 7Ps Strategies Service Quality Elements of Physical Product Marketing Tangible & Intangible Benefits International Markets: Globalisation Standardisation Versus Adaptation The EU / Benefits & Risks Market Attractiveness International Marketing Mix Strategies The Diploma in Business Studies – Part 2 Accounting Main Topics of Study: Introduction to Accounting: What is Accounting? Business Organisations and Sources of Finance Introducing Financial Statements: The Profit and Loss Account and the Balance Sheet The Role of the Accountant and the Accounts Office Supply Information for Management Control: The Purpose of Management Information The Use of Cost Centres and Coding of Costs Providing Comparisons on Costs and Income A Brief Introduction to Wages Control Accounts: Sales and Purchase Ledger Control The Construction of Financial Statements: Financial Statements: The Calculation of Profits Adjustments: Accruals, Prepayments and Drawings Adjustments: Bad Debts and Provisions for Debtors Depreciation of Fixed Assets Partnership Accounts Company Accounts Accounts of Clubs and Societies The Extended Trial Balance Using Accounting Information: Accounting Ratios and Preparing Reports Accounting Standards: Statements of Standard Accounting Practice and Financial Reporting Statements (SSAPs and FRSs) Accounting for Stocks Manufacturing Accounts Marginal Costing Budgeting Economics for Business Main topics of study: The Nature & Scope of Economics: The Nature & Scope of Economics The Development of Economic Society The Economic Problem: Scarcity Choice and Opportunity Cost Alternative Economic Systems Production: The Economic Background to Production Specialisation and the Division of Labour Business Organisations Factors of Production The Scale of Production and Economies of Scale The Location of Production The Theory of Price Determination: Demand Supply Price Determination Concept of Elasticity Applications of the Demand and Supply Model Market Structures: Competitive Markets – the Institutions where Price is Decided Monopoly Oligopoly Imperfect Competition (Monopolistic Competition) Public Policy Towards Competition Factor Markets and Rewards to Factors: Rewards to Factors: Distribution Theory Land & Rent Labour & Wages Capital & Interest Entrepreneurship & Profit Economic Rent Market Failure: Market Imperfections Externalities Public Goods and Merit Goods Imperfect Information Dealing with Market Failure Money & Banking: Functions of Money Financial Institutions Central Banking Macroeconomics: Basic National Income Accounting Use of National Income Statistics Economic Policy Circular Flow Analysis Consumption, Savings and Investment National Income Equilibrium Multiplier and Accelerator Unemployment & Inflation: Types of Unemployment Costs of Unemployment Causes of Inflation Costs of Inflation Economic Policy Instruments: Taxation, Government Spending and Budgets Fiscal Policies Money and Monetary Policy Supply Side Measures and Privatisation International Trade: Absolute & Comparative Advantage The Principle of Free Trade Protection – Types and Causes Free Trade, Customs Unions and Single Markets The European Union and Other Free Trade Areas GATT and WTO Balance of Trade and Payments Dealing with Balance of Payments Problems Globalisation and International Monetary Issues: Exchange Rate Determination Fixed and Floating Exchange Rate Systems Trade and Economic Development Transnational Enterprises Globalisation Business Law Main Topics of Study: Contracts Formation of Contract: What is a Contract? The Intention to Create Legal Relations Offer Termination of an Offer Acceptance Agreement without Offer & Acceptance The Nature of Consideration Executory, Executed & Past Consideration Sufficiency of Consideration Privity of Contract Terms of Contract: The Terms of Contract Incomplete Contracts Conditions & Warranties Oral Evidence Relating to Contracts in Writing Representations & Contract Terms Implied Terms The Required Form of Contracts Exclusion Clauses The Unfair Contract Terms Act 1977 The Unfair Terms in Consumer Contracts Regulations 1994 Vitiating Factors: Contractual Capacity Mistake Misrepresentation Duress Undue Influence Void & Illegal Contracts Discharge of Contract: How a Contract Comes to an End Performance Agreement Breach of Contract Frustration Remedies Available for Breach of Contract Damages Action for the Price Equitable Remedies Limitation to Actions for Breach Quasi-Contract Agency: The Creation of Agency The Duties of an Agent The Rights of an Agent The Authority of an Agent Liability of the Parties Agents Acting for Undisclosed Principals Termination of Agency Special Types of Agent Sale of Goods Definition of a Contract for the “Sale of Goods”: Types of Goods The Price Terms Implied by the Sale of Goods Act 1979 & Changes made by the Sales & Supply of Goods Act 1994 (S.14) Time of Performance Seller’s Title Description of the Goods Sale by Sample Satisfactory Quality & Fitness for Purpose Passing of Property & Risk Nemo Dat Quod Non Habet Delivery Acceptance & Rejection Remedies of the Parties, Romalpa Clauses The Supply of Goods & Services Act 1982 Consumer Credit and Protection Consumer Credit: Forms of Consumer Credit What is a Regulated Agreement? The Classification of Regulated Agreements The Protection of Debtors Lenders Liability Termination of Credit Agreements Extortionate Credit Bargains Consumer Credit Licensing, Advertising & Canvassing Credit Cards Consumer Protection: Consumer Protection Trade Descriptions Consumer Safety Product Liability Tort and Negligence Tort: Tort & Other Wrongs Wrong & Damage Distinguished Remoteness of Damage Vicarious Liability Strict Liability Defences to an Action in Tort Contributory Negligence Remedies in Tort Conversion Nuisance Defamation Definition Libel and slander Action and defences Negligence: Negligence Duty of Care Breach of Duty of Care Res Ipsa Loquitur Consequential Harm Negligent Mis-statement Company Law The Nature of a Company The Company as a Legal Entity The Veil of Incorporation Companies & Partnerships A Company’s Liability in Tort & Crime Public & Private Companies Holding & Subsidiary Companies Formation of a Company Promoters & Pre-Incorporation Contracts Registration Procedures Commencement of Business Company Contracts Memorandum & Articles Purpose & Contents of the Memorandum The Company Name Registered Office Objects Articles of Association Alteration of the Articles The Memorandum & Articles as Contracts Meetings Types of Meeting Convening a Meeting Proxies Types of Resolution The Assent Principle Liquidations & Other Insolvency Procedures Methods of Dissolution Liquidations Compulsory Liquidation Voluntary Liquidation Liquidation Committee Contributories Powers of Liquidators Duties of Liquidators Alternatives to Liquidation Administration Orders Voluntary Arrangements Directors Appointment Shareholdings Termination of office Disqualification Powers and dealings Partnerships: Definition Organisational Behaviour Main Topics of Study: Introduction to Organisations Organisation Structure Structural Perspective Elements of Organisation Structure Types of Job Line, Staff & Functional Structures Formal & Informal Organisations Designing Organisation Structure Centralisation & Decentralisation Management Scientific Management Taylorism Gilbreth Gantt Fordism Bureaucracy & Roles Organisational Structuring Rules Roles Bureaucracy or Adhocracy Classical Management Theory Henri Fayol Applicability of Theory Modern Classical Management Theory Contingency Approach Contingency & Organisational Structure Determinism Versus Strategic Choice Technological Determinism Environmental Determinism Strategic Choice Environmental Strategic Choice People in Organisations Communication & Perception Interpersonal Communication Perception Non-Verbal Communication Motivation Motives as Goals of Human Behaviour Motives as Individual Decision-Making Processes Social Process of Motivating Others Empowerment Learning Learning Process Behaviourist Approach to Learning Cognitive Approach to Learning Behaviour Modification Techniques Socialisation & Feedback Personality Definition Personality Types & Traits Stress & its Management Development of the Self Nomothetic & Idiographic Psychometrics Groups and Teams in Organisations Group Formation Group Level Analysis of Organisational Behaviour Historical Background to study of Groups Concept of a Group Formal & Informal Groups Homans Theory of Group Formation Stages of Group Development Group Structure & Process Group Structure Status Structure Power Structure Linking Structure Role Structure Group Structure & Group Process Leadership Structure Communication Structure Group Control Group Influences on Individuals’ Motivations Group Influences on Individuals’ Perceptions Group Socialisation of Members Group Influences on Individuals’ Attitudes & Behaviours Conformity to & Rebellion Against Authority Group Effectiveness Effectiveness, Productivity & Satisfaction Factors Affecting Group Behaviour Making Groups Perform Group Cohesion Development and Change: Issues and Challenges Organisational Change The Contemporary Imperative Project Management & Participative Management Resistance to Change Understanding Change Business Process Re-Engineering Change Agent Organisation Development Goals & Processes Levels & Models of Intervention OD Techniques OD Applications OD Consultant Corporate Culture Rise of Corporate Culture Concept Models of Corporate Culture Corporate Culture & Economic Performance Changing Cultures Corporate Culture & Management Control National Cultures Technology & Change Definitions & Predictions Determinism or Choice Politics of Technology Characteristics of Mass Production Socio-Technical Systems Analysis & Design Competing Socio-Technical Paradigms Advanced Technology & the Changing Nature of Work Management Power and Control Leadership & Management Style Functions of Leaders & Managers Leaders as Special People Leaders & Followers Context Culture Changing Leadership Style Managing Conflict Perspectives on Organisational Conflict Functional & Dysfunctional Conflict Coordination & Conflict Organisational Power & Politics Organisations – Rational or Political Organisational Politics Organisational Power Power & Influence Management Control Perspectives on Management Control Nature of Management Control Mechanisms Strategies & Problems of Management Control Psychological Need for Control Social Control The Advanced Diploma in Business Studies – Part 3 Customer Service Main Topics of Study: Introduction: What is Customer Service? Importance of Customer Service Understanding Customer Satisfaction Excellent Customer Service Five Needs of Every Customer Cost of Losing a Customer Challenges and Solutions Challenges of Customer Service Elements of Success Barriers to Excellent Customer Service Power of Perceptions Understanding Expectations Levels of Expectations Scope of Influence Reputation Management Techniques for Exceeding Customer Expectations Keys to Credibility Importance of Values Ethics in Customer Service Current Status of Customer Service New Trends in Customer Service Problem Solving Role of Problem Solving in Customer Service Creativity & Problem Solving Problems as Opportunities Confronting Conflict Problem Solving Process Problem Solving Strategies Development of Negotiation Skills Professional Approaches to Apologising & Conveying Bad News Barriers to Problem Solving & Decision Making Importance of Follow Up Management and Strategy Strategy & Formulating a Plan for Success Why a Strategy Planning Importance of Infrastructure Culture High Touch & Low Touch Customers Segmenting the Market Developing a Strategy Empowerment Importance of Mission & Purpose Statement Steps to Empowering Customer Service Providers Co-Production of Customer Service Why Co-Production Works Design of Systems Communications Communications in Customer Service Building Customer Intelligence Methods of Communication Listening Voice Inflection as a Customer Service Tool Telephones & Customer Service Words to Use/Avoid Power Phrases Power of Eye Contact Appeal to the Senses Communication & Technology Managing Difficult Customers Coping with Challenging Customers Who are Challenging Customers Why they are Challenging Characteristics of Challenging Customers Respect Empathy Accepting Mistakes Benefits from Dealing with Challenging Customers Motivation and Leadership Motivation What is Motivation Needs & Wants Motivating Factors Understanding Morale Self-Concept & Motivation Improving Self-Concept Power of Self Motivation Teamwork Motivating Others Leadership in Customer Service Leadership Defined Knowing Yourself Formal & Informal Leaders Coach or Counsellor Characteristics of Excellent Leaders Leadership & Goals Creating a Customer Service Culture Benefit of Job Aids Leadership without Position The Boss as a Customer Customer Retention & Measurement of Satisfaction: What is Customer Retention Value of Existing Customers Churn Developing & Improving the Customer Retention Programme Measurement of Satisfaction Sources of Information Benefits of Measuring your Effectiveness Determining your Effectiveness Surveys & Reality Business Benefits from Measuring Satisfaction Customer Service in a Changing Marketplace: Today’s Changing Marketplace The Customer of the 21st Century New Technology Call Centres The Internet Enhancing Service Experiences & Building Customer Loyalty Excellence in Customer Service: Excellence as the Goal Getting Started Rewards of Excellent Customer Service Human Resources Management Main Topics of Study: Individuals & Groups: Individual Differences Perceptions Communications Motivation Industrial Psychology Behavioural Theories Research Studies Groups Group Dynamics Personal & Group Goals Manpower Planning: Recruitment & Selection Interviewing Selection Testing Validation of Testing Procedures Training Systems Approach to Training On-Job Vs Off-Job Induction Programmes Personnel Records Use of Computers Job Analysis: Job Description Job Specification Person Specification Job Rotation Job Enlargement Job Enrichment Job Evaluation Development of a Human Relations Approach: Role of Personnel Department Nurturing Human Assets in a Business Career Development Counselling Welfare Participating in Decision-Making Supportive Management Styles Industrial Relations: The Role of the Trade Union Moves Toward Industrial Democracy Strikes, Cause, Effect & Avoidance Marketing Management Main Topics of Study: Marketing Management: The Critical Role of Marketing in Organisations & Society Laying the Groundwork through Strategic Planning Managing the Marketing Process & Marketing Planning Analysing Marketing Opportunities: Marketing Information Systems & Marketing Research Analysing the Marketing Environment Analysing Consumer Markets & Buyer Behaviour Analysing Business Markets & Organisational Buying Behaviour Analysing Competitors Researching & Selecting Target Markets: Measuring & Forecasting Market Demand Identifying Market Segmentation & Selecting Target Markets Designing Marketing Strategies: Marketing Strategies for Differentiating & Positioning the Marketing Offer Developing, Testing & Launching New Products & Services Managing Products through their Product Life Cycle Deciding on International Market Entry Methods of Entry International Marketing programmes Planning Marketing Programmes: Managing Product Lines, Brands & Packaging Managing Service Business & Ancillary Services Designing Pricing Strategies & Programmes Selecting & Managing Marketing Channels Managing Retailing & Wholesaling Designing Communication & Promotion-Mix Strategies Designing Effective Advertising Programmes Designing Direct Marketing, Sales-Promotion & Public Relations Programmes Managing the Sales force Managing Direct Marketing Operations Implementing Marketing Programmes Controlling Marketing Activities Strategic Management Main Topics of Study: Nature of Strategic Management: Definitions Stages of Strategic Management Key Terms in Strategic Management Strategic Management Model Benefits of Strategic Management Business Ethics & Strategic Management Business & Military strategy Strategies in Action: Types of Strategies Integration Strategies Intensive Strategies Diversification Strategies Defensive Strategies Guidelines for Pursuing Strategies Mergers & Leveraged Buyouts Generic Strategies Strategic Management in Governmental Organisations Strategic Management in Small Firms Business Mission: Importance of a Clear Mission Nature of a Business Mission Components of a Mission Statement Writing & Evaluating Mission Statements External Assessment: Nature of an External Audit Economic Forces Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Political, Governmental & Legal Forces Technological Forces Competitive Forces Sources of External Information Forecasting Tools & Techniques Competitive Analysis Industry Analysis Internal Assessment: Nature of an Internal Audit Relationships Among Functional Areas Management Marketing Finance Productions Operations R&D Computer Information Systems Internal Audit Checks Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix Strategy Analysis & Choice: Nature of Strategy Analysis & Choice Long Term Objectives Comprehensive Strategy Formulation Framework Input Stage Matching Stage Decision Stage Cultural Aspects of Strategy Choice Politics of Strategy Choice Role of Board of Directors Strategy Implementation, Management Issues: Nature of Strategy Implementation Annual Objectives Policies Resource Allocation Managing Conflict Matching Structure with Strategy Restructuring & Reengineering Linking Performance & Pay to Strategies Managing Resistance to Change Managing the Natural Environment Creating a Strategy-Supportive Culture Production Operations Concerns when Implementing Strategies Human Resource Concerns when Implementing Strategies Implementing Strategies, Other Issues: Nature of Strategy Implementation Marketing Issues Finance Issues R&D Issues Computing Information Systems Issues Strategy Review, Evaluation & Control: Nature of Strategy Evaluation Strategy-Evaluation Framework Published Sources of Strategy-Evaluation Information Characteristics of an Effective Evaluation System Contingency Planning Auditing Using Computers to Evaluate Strategies Guidelines for Effective Strategic Management