University of Maine General Education Course Requirements
advertisement

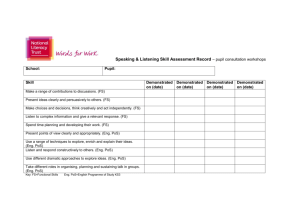
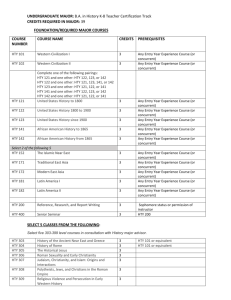
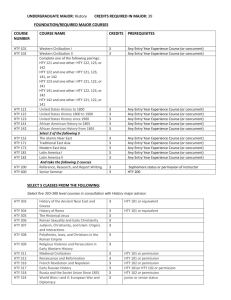
University of Maine General Education Course Requirements & Acceptable Transfer of Courses from Maine’s Community Colleges Transfer courses in the following table have been acquired from the database accessible at https://peportal.maine.edu I. Science Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Science include: ANT 210, ANT 260, ANT 317, ANT 473, ANT 474 , ANT 477, ANT 478 , ANT University of Maine General Education Requirements for Science 479, AST 109, AST 110, AST 114, AVS 145, BIO 222, BIO 100, BIO 200, BIO 205, BIO 208, BIO 223, BIO 310, BIO 326, BIO 327, BIO 432, BIO 464, BMB 207, BMB 208, BMB 209, BMB 210, CHY 101, CHY 102, CHY 121, CHY 122, CHY 123, CHY 124, ERS 100, ERS 101 , ERS 102, ERS 103, ERS 104, ERS 108, ERS 110, ERS 111, ERS 191, ERS 200, ERS 201, ERS 210, ERS 211, ERS 240, ESC 343, ESC 400, FSN 101, FSN 121, GEE 298, HON 312, HON 320, HON 321, HON 322, HON 323, HON 324, HON 325, HON 326, INT 289, PHY 101, PHY 102, PHY 105, PHY 107, PHY 108 , PHY 111, PHY 112 , PHY 121, PHY 122, PSE 100, PSE 105, PSE 110, PSE 140, PSE 141, PSE 413, SFR 100, SFR 101, SFR 102, SFR 111, SFR 112, SFR 215, SMS 100, SMS 108, SMS 110, SMS 111, SMS 120, SMS 211, WLE 200, WLE 201, WLE 260, WLE 423 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) BIO 101 and BIO 102, BIO 131 and BIO 132, BIO 115 and BIO 116 and BIO 117 and BIO 118, CHY 101, CHY 102, GEO 101, PHY 121 and PHY 122, PHY 121, PHY 142 and PHY 143, PHY 242 and PHY 243, CRJ 250 BIO 109, BIO 111, BIO 209, BIO 121 and BIO 122 and BIO 124 and BIO 126, CHE 114, CHE 116, CHE 100, CHE 100, CHE 111, CHE 113, SC 407, CHE 112, CHE 115, PHY 109, PHY 111, PHY 121 and PHY 122, SCO 401, PHY 112, PHY 123 and PHY 124, SCO 402 BS 115 and BS 115L, BIO 102, BIO 213 and BIO 214, CHE 112, CHE 115, PHY 111, PHY 211 BIO 112 and BIO 113, BIO 130 and BIO 120, NUR 114 BIO 120 and BIO 121, BIOL 120 and BIOL 121, BIO 125 and BIO 124, BIOL 125 and BIOL 126, BIO 109, BIOL 190, AHS 120 and AHS 121 and AHS 122 and AHS 123, BIO 130 and BIO 131 and BIO 132 and BIO 133, BIOL 130 and BIOL 131 and BIOL 135 and BIOL 136, BIOL 132 and BIOL 138, CHEM 104, CHM 102, CHM 106, CHEM 104, CHM 102, CHM 106, CHEM 120, CHM 111, CHEM 125, CHM 112, ENV 204, ENV 114, ENVR 115, NUT 111, NUTR 110, PHYS 150, PHY 114, PHYS 155, BIOL 115, HORT 100, PST 113, HORT 130, PST 120, OCEA 105, OCO 111, CJ 240, CJUS 230, LET 120 BIO 125 and BIO 135, BIO 225 and BIO 235, CHY 110, CHY 110, NUT 170 BIO 126 and BIO 127 and BIO 136 and BIO 137, CHM 106, CHM 116, CUL 108 II. A. Human Values and Social Contexts: Western Cultural Tradition Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Western Cultural Tradition include: ANT 173, ANT 221, ANT 330, ANT 473, ANT 474 , ARH 155, ARH 156, ARH 251, University of Maine General Education Requirements for Western ARH 252, ARH 253, ARH 255, ARH 257, ARH 258, ARH 264, ARH 265, ARH 268, ARH 351, ARH 362, ARH 363, ARH 366, ARH 368, ARH 452 , ARH 492, Cultural Tradition ARH 493, ARH 494, ARH 495, AVS 153, CAN 101, CLA 101, CLA 102 , CLA 400, CLA 401, CMJ 201, CMJ 211, CMJ 375, CMJ 444, ECO 335, ECO 336, ECO 343, ENG 131, ENG 222, ENG 235, ENG 241, ENG 242, ENG 243, ENG 244, ENG 245, ENG 246, ENG 248, ENG 251, ENG 252, ENG 253, ENG 256, ENG 271, ENG 451, ESS 315, FRE 463, FRE 464, FRE 495, GEO 349, GER 401, GER 406, GER 413, GER 420, GER 495, HON 314, HON 321, HON 327, HON 333, HON 334, HON 335, HON 336, HON 337, HTY 103, HTY 104, HTY 105, HTY 106, HTY 109 , HTY 110, HTY 412, HTY 198 , HTY 210, HTY 218, HTY 276, HTY 278, HTY 279, HTY 280, HTY 332, HTY 338, HTY 349, HTY 403, HTY 404, HTY 407, HTY 409, HTY 410, HTY 411, HTY 416, HTY 420 , HTY 423, HTY 426, HTY 429, HTY 450, HTY 455, HTY 456, HTY 461 , HTY 462 , HTY 463, HTY 464 , HTY 467, HTY 468, HTY 477, HTY 478, HTY 483, HTY 491 , HTY 492, HTY 494 , INT 101, INT 334, INT 441, LAT 203, LAT 204, MLC 276, MLC 495, MSL 350, MUL 202, NAV 202, NAV 310, PHI 100, PHI 102, PHI 103, PHI 104 , PHI 105 , PHI 200, PHI 210, PHI 212, PHI 214, PHI 220, PHI 223, PHI 230, PHI 235, PHI 236 , PHI 240, PHI 244, PHI 250, PHI 260, PHI 262, PHI 312 , PHI 317, PHI 342, PHI 343, PHI 344, PHI 352 , PHI 353, PHI 354, PHI 364 , PHI 382, PHI 420, POS 120, POS 201, POS 273, POS 301, POS 302, POS 303, POS 304, POS 305, POS 307, POS 401, SFR 220, SFR 480, SPA 307, SPA 403, SPA 406, SPA 495, SVT 221, THE 112 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) ENG 112, ENG 113, HIS 131, HIS 132, HIS 151, HIS 201, PHI 111, PHI 151, POS 160, ACE 234, ACET 234 ENG 227, ENG 228, HIS 101, EMS 225 ENG 212, HIS 111, HIS 112, HIS 202, PHI 110, PHI 101, PHI 201 ENG 224, ENG 234, HIS 123, HIS 125, HIS 119, HIS 207 CNM 201, CNMS 155, HONR 225, LITR 225, HIST 130, HTY 131, HUM 106, HIST 135, HTY 132, HIST 202, HTY 202, HIST 145, HTY 211, PHI 101, PHIL 100, HIST 170, HTY 220, POS 100, POLS 250, POLS 110, POS 104 HIS 112, HIS 113, HIS 117, HIS 119, HIS 115, HUM 210 ENG 224, ENG 225, ENG 222, HIS 110, HIS 120, HIS 101, HIS 102, PHI 102, PHI 110, POS 105 II. B. Human Values and Social Contexts: Social Contexts and Institutions Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Social Contexts and Institutions include: ARH 270, ARH 368, BLS 101, BUA 220, BUA 331, CET 451, CHF 200, CHF 201, University of Maine CHF 351, CMJ 100, CMJ 102, CMJ 103, CMJ 202, CMJ 211, CMJ 250, CMJ 314, General Education Requirements for Social CMJ 375, CMJ 380, CMJ 405, CMJ 410, CMJ 412, CMJ 420, CMJ 451, ECO 100, Contexts and Institutions ECO 120, ECO 121, ECO 180, ECO 190, ECO 329, ECO 368, ECO 377, ECO 443, ECO 471, ECO 475, EDB 202, ENG 280, FAS 101, FAS 220, FAS 420, GER 307, HON 170, HON 315, HON 322, HON 328, HON 333, HON 338, HON 339, HON 340, HON 341, HTY 103, HTY 104, HTY 105, HTY 106, HTY 107, HTY 108, HTY 112, HTY 198, HTY 210, HTY 220, HTY 241, HTY 278, HTY 280, HTY 338, HTY 436, HTY 437, HTY 442, HTY 449, HTY 462, HTY 463, HTY 473, HTY 474, INT 333, INT 490, INT 491, INV 180, INV 392, KPE 485, LBR 200, LST 101, LST 201, MES 201, MLC 421, MSL 350, NAS 101, NAS 102, NAS 270, NAV 202, NAV 310, NUR 415, PAA 100, PAA 200, PAA 220, PAA 233, PAA 380, PAA 425, PAA 430, PAX 201, PAX 250, PAX 260, PAX 360, PAX 400, PHI 100, PHI 105, PHI 212, PHI 214, PHI 232, PHI 233, PHI 235, PHI 236, PHI 244, PHI 345, PHI 353, PHI 432, POS 100, POS 203, POS 241, POS 243, POS 302, POS 306, POS 335, POS 336, POS 337, POS 344, POS 350, POS 352, POS 353, POS 354, POS 363, POS 368, POS 372, POS 374, POS 380, POS 381, POS 383, POS 384, POS 385, POS 386, POS 467, POS 474, POS 475, POS 484, PSY 100, PSY 230, SFR 222, SFR 225, SFR 444, SFR 446, SOC 101, SOC 201, SOC 202, SOC 205, SOC 214, SOC 220, SOC 240, SOC 314, SOC 318, SOC 319, SOC 329, SOC 330, SOC 337, SOC 338, SOC 482, SPA 420, SPA 496, SWK 320, SWK 365, SWK 440 , THE 112, THE 405, WST 101, WST 103, WST 270, WST 480 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) BUS 122, SOC 220, PSY 114, SOC 230, HUM 121, COM 101, SPE 111, COM 100, SPE 101, ECO 202, ECO 201, HIS 131, HIS 132, HIS 151, HIS 152, PHI 111, POS 150, POS 151, POS 205, LRC 024, PSY 101, PSY 201, SOC 101, SOC 210, WST 101 BUS 132, ECO 221, ECO 201, ECO 222, EDB 202, ENG 212, ENG 213, HIS 101, EMS 225, HUO 309, PSY 101, SOC 101, SOC 214 BUS 116, PSY 215, COM 104, ECO 114, EC 213, ECO 113, HIS 111, HIS 112, HIS 101, PHI 110, PSY 101, PY 114, SOC 101, SY 116, SOC 204, SOC 205 BUS 119, ECE 200, COM 111, ENG 211, ECO 111, HIS 121, HIS 125, HIS 117, HIS 119, BUS 215, POL 101, PSY 101, SOC 111, SOC 211, SOC 215 BUS 200, BUSN 260, ECE 111, ECED 110, CNMS 105, ENG 113, ENGL 110, CNM 201, CNMS 155, ECO 204, ECON 120, ECO 205, ECON 125, HIST 130, HTY 131, HUM 106, HIST 135, HTY 132, HIST 170, HTY 220, POLS 105, POS 101, SSC 208, POLS 115, POS 109, SSC 203, PSY 100, PSYC 100, SSC 206, PSY 215, PSYC 215, SOC 100, SOCI 100, SSC 202, SOC 201, SOCI 201 BUS 132, ENG 206, ECO 200, HIS 112, HIS 113, HIS 117, HIS 119, HUM 210, PSC 101, PSY 101, SOC 101, SOC 102 BUS 244, ECE 111, PSY 180, SPE 101, ECO 120, ECO 110, COM 101, HIS 110, HIS 120, HIS 101, HIS 102, PHI 102, POS 101, PSY 101, PSY 202, SOC 101, SOC 210, SOC 201 II. C. Human Values and Social Contexts: Cultural Diversity or International Perspectives Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Cultural Diversity or International Perspectives include: ANT 101, ANT 102, ANT 120, ANT 140, ANT 207, ANT 212, ANT 221, ANT University of Maine General Education Requirements for Cultural ANT 249, ANT 250, ANT 256, ANT 270, ANT 300, ANT 317, ANT 330, ANT ANT 426, ANT 430, ANT 441, ANT 445, ANT 450, ANT 451, ANT 452, ANT Diversity or International Perspectives ANT 458, ANT 461, ANT 465, ANT 466, ANT 469, ANT 470, ANT 477, ARH 245, 423, 454, 100, ARH 155, ARH 251, ARH 252, ARH 253, ARH 255, ARH 257, ARH 258, ARH 268, ARH 270, ARH 362, ARH 363, ARH 368, ARH 369, ARH 493, ARH 494, BLS 101, BLS 338, BUA 328, CAN 101, CLA 101, CLA 102, CLA 400, CLA 401, CMJ 314, CMJ 360, CMJ 366, CMJ 401, CMJ 405, CSD 222, DIS 300, DIS 400, ECO 329, ECO 339, ECO 340, ECO 449, ENG 131, ENG 236, ENG 237, ENG 243, ENG 246, ENG 256, ENG 450, FAS 101, FAS 220, FAS 250, FAS 420, FRE 101, FRE 102, FRE 103, FRE 104, FRE 117, FRE 201, FRE 202, FRE 218, FRE 305, FRE 306, FRE 307, FRE 309, FRE 310, FRE 315, FRE 350, FRE 397, FRE 398, FRE 400, FRE 401, FRE 404, FRE 405, FRE 406, FRE 407, FRE 408, FRE 413, FRE 430, FRE 440, FRE 442, FRE 457, FRE 463, FRE 464, FRE 465, FRE 490, FRE 495, FRE 498, FSN 270, GEE 250, GEO 100, GEO 201, GEO 275, GEO 349, GER 101, GER 102, GER 121, GER 203, GER 204, GER 223, GER 305, GER 306, GER 307, GER 401, GER 402, GER 403, GER 409, GER 490, GER 495, GER 497, HON 316, HON 323, HON 329, HON 334, HON 338, HON 342, HON 343, HON 344, HTY 107, HTY 108, HTY 109, HTY 110, HTY 112, HTY 218, HTY 220, HTY 241, HTY 275, HTY 332, HTY 349, HTY 350, HTY 403, HTY 408, HTY 410, HTY 411, HTY 412, HTY 416, HTY 423, HTY 424, HTY 426, HTY 436, HTY 437, HTY 442, HTY 449, HTY 450, HTY 452, HTY 453, HTY 454, HTY 460, HTY 473, HTY 474, HTY 477, HTY 483, HTY 484, HTY 494, INT 101, INT 441, INT 486, INT 490, INT 491, ISE 213, LAT 203, LAT 204, LAT 247, LAT 248, LAT 451, LAT 452, LAT 453, LAT 454, LAT 481, LAT 482, LAT 497, LAT 498, MLC 175, MLC 190, MLC 276, MLC 495, MUL 120, NAS 101, NAS 102, NAS 270, NAS 401, NAS 490, NAV 310, NMD 213, NUR 415, NUR 452, PAX 201, PAX 350, PAX 370, PAX 400, PAX 401, PAX 491, PHI 223, PHI 236, PHI 286, PHI 287, PHI 317, PHI 343, PHI 346, PHI 364, PHI 382, POS 120, POS 241, POS 243, POS 273, POS 336, POS 337, POS 344, POS 368, POS 370, POS 372, POS 374, POS 467, POS 475, PSY 423, SFR 226, SOC 201, SOC 202, SOC 208, SOC 304, SOC 314, SOC 329, SOC 330, SOC 338, SOC 371, SOC 404, SPA 101, SPA 102, SPA 203, SPA 204, SPA 301, SPA 305, SPA 306, SPA 307, SPA 308, SPA 309, SPA 350, SPA 403, SPA 405, SPA 406, SPA 409, SPA 411, SPA 412, SPA 444, SPA 490, SPA 495, SPA 496, SPA 497, SPA 498, SWK 330, THE 300, THE 460, VOX 100, VOX 101, VOX 102, VOX 103, VOX 104, VOX 105, VOX 106, VOX 107, VOX 108, VOX 109, VOX 110, VOX 111, VOX 130, VOX 131, VOX 132, VOX 133, VOX 134, VOX 135, VOX 136, VOX 137, VOX 138, VOX 139, VOX 140, VOX 141, VOX 160, VOX 161, VOX 167, VOX 168, VOX 190, VOX 205, VOX 206, VOX 207, VOX 208, VOX 209, VOX 210, VOX 240, VOX 270, VOX 290, WST 101, WST 103, WST 235, WST 250, WST 270, WST 340, WST 360, WST 371, WST 430, WST 480 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) ANT 101, REL 101, HUM 151, FRE 101, FRE 102, GEY 101, POS 205, POS 160, SPA 101, SPA 102, WST 101 PHI 105, SOC 214, KOR 101, KOR 102 PHI 106, FRE 101, FRE 102, GER 101, GER 102, GER 201, GER 202, SOC 204, SPA 101, SPA 102, SPA 201 SOC 215, SPA 102 ANTH 105, ART 110, FRE X99, FRE 101, FREN 101, FRE 102, FREN 102, GRMN 100, GRMN 200, MUS 125, MUSI 125, POLS 100, POS 100, POLS 110, POS 104, SPA X90, SPA 101, SPAN 101, SPA X91, SPA 102, SPAN 102, SPA 203, SPAN 201, SPAN 202 HIS 170, SPA 101, SPA 103 ANT 102, HUM 110, ART 110, FRE 101, G 243, POS 105, SOC 210 II. D. Human Values and Social Contexts: Population and Environment Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Population and Environment include: ANT 212, ANT 250, ANT 420, ANT 431, ANT 435, ANT 464, ANT 475, AVS 152, University of Maine BIO 222, BIO 342, BIO 455, BMB 110, CET 412, CHE 480, DIS 300, DIS 450, General Education Requirements for ECO 180, ECO 190, ECO 341, ECO 377, ECO 381, ECO 477, EES 100, EES 324, Population and Environment ERS 102, ERS 103, ERS 108, ERS 110, ERS 121, ERS 191, ERS 201, ERS 210, ERS 441, ESC 426, ESC 446, FAS 120, FAS 240, FSN 270, GEE 250, GEO 100, GEO 201, GEO 212, GEO 275, GEO 425, HON 317, HON 324, HON 330, HON 335, HON 339, HON 342, HON 346, HTY 212, HTY 275, HTY 404, HTY 465, HTY 479, INT 105, INT 302, INT 400, ISE 112, MES 101, MES 201, MES 301, NUR 452, PAA 327, PHI 232, PHI 432, PSE 105, PSE 121, SFR 111, SFR 112, SFR 220, SFR 455, SMS 100, SMS 108, SMS 230, SMS 482, SOC 371, WLE 230, WLE 323, WST 230, WST 371 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) GEY 101 NONE FOUND NONE FOUND NONE FOUND ENV 111, ENVR 110, ENV 205, ENV 114, ENVR 115, OCEA 105, OCO 111 HIS 170 SCI 101 II. E. Human Values and Social Contexts: Artistic and Creative Expression Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Artistic and Creative Expression include: ANT 423, ARH 100, ARH 155, ARH 156, ARH 251, ARH 252, ARH 255, ARH 257, University of Maine General Education Requirements for Artistic ARH 258 , ARH 264, ARH 265, ARH 268, ARH 270, ARH 362, ARH 363, ARH 368, ARH 369, ARH 492, ARH 493, ARH 494, ART 100, ART 110, ART 120, ART 225, and Creative Expression ART 270, ART 370, ART 325, ART 370, ART 371, ART 372, ART 380, ART 499, CMJ 106, CMJ 261, CMJ 351, CMJ 366, CMJ 434, CMJ 466, DAN 101, DAN 102, DAN 103, DAN 105, DAN 121, DAN 122, DAN 123, DAN 130, DAN 205, DAN 297, DAN 397, DAN 497, ENG 205, ENG 206, ENG 222, ENG 231 , ENG 235, ENG 236, ENG 241, ENG 242 , ENG 244, ENG 245, ENG 249, ENG 251 , ENG 252, ENG 253, ENG 280, ENG 309, FRE 430, FRE 463, FRE 464, GER 413, GER 420, HON 180, HON 309, HON 318, HON 325, HON 331, HON 336, HON 340, HON 343, HON 345, HTY 484, INT 101, ISE 104, MLC 421, MUL 101, MUL 150, MUO 101, MUO 103, MUO 109, MUO 111, MUO 112 , MUO 113, MUO 114, MUO 121, MUO 132, MUO 141, MUO 143, MUO 149, MUO 150, MUO 155, MUO 160, MUO 165, MUS 201, MUS 210, MUS 298, MUY 101, MUY 310, NMD 104, NMD 240, NMD 250, NMD 270, NMD 341, NMD 370, NMD 371, NMD 372, PAX 250, PHI 104, PHI 262, PHI 351, PHI 431, POS 355, SPA 420, THE 111, THE 117, THE 118, THE 200, THE 216, THE 340, THE 405, THE 415, WST 250, WST 360 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) HUM 151, ART 101, ART 102, ENG 211, ENG 112, ENG 113, MUS 101, THE 101 ART 110, ART 112, ENG 172, ENG 227, ENG 228, ENG 212, ENG 213 ART 114, ART 111, ENG 210, ENG 212, MUS 101 ENG 239, ENG 224, ENG 234 ART 110, ARTH 145, ARTH 155, ART 175, ARTS 110, ART 153, ARTS 130, CNM 130, CNMS 115, ART 200, ARTS 140, ARTS 120, CNM 272, CNMS 245, CNM 272, CNMS 245, ENG 200, ENGL 200, MUSI 100, MUS 100, CNM 180, CNMS 165, CNM 180, CNMS 165, CNM 272, CNMS 245, TEL 240, TEL 225, ENG 202, LITR 220 ART 105, ENG 208 ART 110, ART 120, ENG 201, ENG 224, ENG 225, COM 101, MUS 101, THE 123 III. Quantitative Literacy (Math) Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Quantitative Literacy include: ANT 462, CMJ 402, COS 120, COS 125, COS 215, COS 220, COS 225, COS 226, University of Maine ECE 105, ECO 480, ECO 485, HON 313, HON 320, HON 327, HON 328, HON General Education Requirements for 329, HON 330, HON 331, HON 332, HON 345, HON 347, KPE 372, MAT 101, Quantitative Literacy MAT 103, MAT 107, MAT 108, MAT 115, MAT 122, MAT 126, MAT 127, MAT 215, MAT 232, NUR 200, NUR 201, NUR 301, PAA 315, PHI 250, PSY 241, SFR 205, SOC 310, TME 151, TME 152 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) CPT 130, MAT 125, MAT 132, MAT 280, MAT 135 CPT 120, MAT 107, MAT 108, MAT 217, MAT 225, MAT 226, NUR 105, NUR 134, NUR 136, MAT 122, MAT 221 and MAT 222 CPT 119, CPT 228, MAT 225, MAT 226, MAT 227, MAT 220, NUR 118, NUR 118, NUR 122 CIS 109, MAT 220, NUR 116, NUR 118, NUR 116, NUR 118, NUR 226, MAT 151, MAT 221 CMPT 125, CPT 102, MAT 115, MATH 110, MAT 215, MATH 220, MAT 140, MATH 190, MAT 220, MAT 225, MAT 216, NUR 117, NURS 125, NUR 117, NURS 125 CTT 130, MAT 115, MAT 119 CIS 276, MAT 120, MAT 227 IV. Demonstrated Writing Competency (Writing Intensive) Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Demonstrated Writing Competency include: ANT 300, ANT 421, ANT 454, ANT 461, ANT 464, ANT 470, ANT 474, ARH 351, University of Maine ARH 361, ARH 362, ARH 363, ARH 366, ARH 368, ARH 369, ARH 452, ARH General Education Requirements for 492, ARH 493, ARH 494, ARH 495, ART 499, AVS 401, AVS 402, BIO 388, BIO Demonstrated Writing Competency 392, BIO 400, BIO 402, BIO 426, BIO 438, BIO 447, BIO 450, BIO 454, BIO 463, BLE 492, BMB 460, BMB 464, BMB 490, BUA 268, BUA 310, BUA 330, BUA 351, BUA 480, CET 356, CET 451, CHB 361, CHB 363, CHF 322, CHF 423, CHF 430, CHY 393, CIE 225, CIE 366, CIE 413, CLA 101, CLA 102, CMJ 236, CMJ 237, CMJ 332, CMJ 340, CMJ 347, CMJ 355, CMJ 401, CMJ 466, CMJ 470, CMJ 483, COS 301, COS 397, COS 490, COS 497, CSD 490, ECE 214, ECE 342, ECE 403, ECO 449, ECO 470, ECO 475, ECO 489, ECP 101, ECP 214, ECP 225, ECP 341, ECP 342, ECP 366, ECP 413, ECP 488, EDB 202, EES 400, EET 100, EET 452, ENG 129, ENG 205, ENG 206, ENG 212, ENG 222, ENG 271, ENG 301, ENG 307, ENG 308, ENG 309, ENG 317, ENG 395 , ENG 402, ENG 405, ENG 415, ENG 416, ENG 418 , ENG 430, ENG 436, ENG 440, ENG 442, ENG 443, ENG 444, ENG 445, ENG 446, ENG 447, ENG 449, ENG 450, ENG 451, ENG 453, ENG 454, ENG 455, ENG 456, ENG 458, ENG 459, ENG 460, ENG 465, ENG 467, ENG 470, ENG 471, ENG 472, ENG 480, ENG 481, ENG 490, ERS 200, ERS 315, ERS 316, ERS 441, ESC 316, ESC 452, FAS 270, FRE 305, FRE 306, FRE 401, FRE 413, FSN 301, FSN 425, GER 305, GER 307, HON 211, HON 212, HON 499, HTY 311, HTY 461, HTY 494, HTY 498, INT 256, INT 333, INT 334, INV 282, ISE 102, ISE 302, KPE 271, KPE 383, KPE 425, LAS 101, LAT 247 , LAT 248, MAT 261, MEE 341 , MES 101, MES 201, MES 301, MET 234, MSL 402, MUH 201, NMD 498, NUR 200, NUR 301, NUR 304, NUR 333, NUR 411, PAA 390 , PAX 250, PAX 260, PHI 343 , PHI 344 , PHI 346, PHI 354 , PHI 364 , PHI 382, PHI 432, PHI 475 , PHY 441, PHY 442, POS 301, POS 302, POS 303, POS 304, POS 305, POS 364, POS 365, POS 385, POS 401, POS 467, POS 499, PSE 101 , PSE 410, PSE 425, PSY 423, PSY 491, PSY 494, SFR 225, SFR 476, SFR 492, SFR 498, SFR 499, SMS 203, SMS 306, SMS 400, SMS 404, SOC 390, SPA 305, SPA 306, SPA 307, SPA 309, SPA 444 , SVT 221, SVT 475, SWK 440, THE 300, THE 340, THE 460, UST 300, WLE 201, WLE 455, WST 480 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) ENG 211, ENG 201, ENG 220, ENG 201, ENG 220, ACE 234, ACET 234 EDB 202, EPC 21 and EPC 22, ENG 172, ENG 121, ENG 211, ENG 215, HUO 303, ENG 121, ENG 211, ENG 215, HUO 303, NUR 105, NUR 134, NUR 136 ENG 210, ENG 212, ENG 219, NUR 118, NUR 122 ENG 239, COM 221, NUR 116, NUR 118, NUR 226 ENG 200, ENGL 200, NUR 117, NURS 125 ENG 208, BUS 205, ENG 201, ENG 205 ECE 190, ENG 201, ENG 211 V. Ethics Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Ethics include: ANT 245, ANT 249, ANT 414, ANT 425, ANT 448, AVS 145, AVS 150, AVS 151, University of Maine AVS 153, AVS 249, AVS 346, AVS 349, BUA 220, BUA 449, CHB 111, CHB 477, General Education Requirements for Ethics CHB 479, CHB 493, CHF 351, CHF 452, CIE 410, CMJ 489, COS 490, DIS 400 , ECO 333, ECO 381 , ENG 235 , ENG 236, ENG 238, ENG 243 , ENG 244, ENG 245 , ENG 246, ENG 249, ENG 253, ENG 430, ENG 435, ENG 436, ENG 440, ENG 442, ENG 443, ENG 444, ENG 446, ENG 447, ENG 451, ENG 453, ENG 454, ENG 455, ENG 456, ENG 457, ENG 458, ENG 459, ENG 460, ENG 465, ENG 467, ENG 481, FAS 270, FSN 436, GEE 298, HON 308, HON 319, HON 326, HON 332, HON 337, HON 341, HON 344, HON 346, HON 347, HTY 424, HTY 460, HTY 479, INT 302, INT 400, INT 491, ISE 213, MSL 402, NAV 304, NMD 213, NUR 455, PAA 100, PAA 200, PAA 327, PAX 351, PAX 491, PHI 100, PHI 102 , PHI 104, PHI 210 PHI 220, PHI 223, PHI 230, PHI 232, PHI 233, PHI 235, PHI 236, PHI 240, PHI 244, PHI 286, PHI 287, PHI 312, PHI 317, PHI 342, PHI 343, PHI 344, PHI 345, PHI 346, PHI 354, PHI 432, POS 201, POS 301, POS 303, POS 305, POS 307, POS 353, POS 370, POS 384, POS 401, POS 484, PSE 121, PSE 430, SFR 446, SFR 491, SOC 208, SOC 304, SOC 337, SOC 404, SVT 325, TSO 398, WST 101, WST 230, WST 410 Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) BUS 122, SOC 230, PHI 111, PHI 151, WST 101 BUS 132, EMS 225 BSC 216, BA 116, BUS 116, PHI 110, PHI 101 BUS 119, BUS 215 BUS 200, BUSN 260, PHIL 100, POLS 250 BUS 132, HUM 210 BUS 244, ENG 222, PHI 102, PHI 110 VI. Capstone Experience Courses meeting the General Education Requirements for Capstone Experience include: ANT 492, ANT 493, ARH 499, ART 499, AVS 401, AVS 402, BIO 388, BIO 392, University of Maine BIO 402, BIO 426, BIO 438, BIO 447, BIO 450, BIO 454, BIO 463, BLE 492, BMB General Education Requirements for 491, BUA 449, CET 458, CHB 479, CHF 423, CHF 424, CHY 498, CHY 499, CIE Capstone Experience 411, CMJ 481, CMJ 483, CMJ 484, CMJ 485, CMJ 489, COS 397, COS 495, COS 497, COS 499, CSD 491, ECE 403, ECO 470, ECO 475, ECO 489, EDG 499, EES 400, EES 489, EET 350, EET 451, EET 452, ENG 490, ENG 496, ENG 499, ERS 498, ERS 499, FRE 495, FSN 401, FSN 520, GER 495, HON 498, HON 499, HTY 498, INT 494, ISE 450, ISE 451, KPE 427, LAS 499, MAT 401, MEE 487, MEE 488, MET 462, MET 463, MET 464, MET 465, MLC 495, MUS 498, NMD 498, NMD 499, NUR 411, NUR 447, NUR 455, PAA 493, PAA 495, PHI 475, PHY 400, PHY 481, PHY 482, POS 499, PSE 425, PSE 430, PSY 491, PSY 494, SFR 404, SFR 454, SFR 491, SFR 492, SFR 498, SFR 499, SMS 400, SMS 404, SOC 499, SPA 495, STT 490, STT 491, STT 494, STT 496, STT 497, STT 499, SVT 490, SWK 495, THE 415, UST 499, WLE 450, WLE 455, WST 480, Equivalent Courses at Maine’s Community Colleges Central Maine Community College (Auburn) Eastern Maine Community College (Bangor) Kennebec Valley Community College (Fairfield/Hinckley) Northern Maine Community College (Presque Isle) Southern Maine Community College (South Portland/Brunswick) NONE FOUND NONE FOUND NONE FOUND NONE FOUND NONE FOUND Washington County Community College (Calais) York County Community College (Wells) <to be compiled> <to be compiled> University of Maine General Education Requirements The General Education Requirements cover six broad areas: I. Science II. Human Values and Social Contexts III. Quantitative Literacy IV. Demonstrated Writing Competency V. Ethics VI. Capstone Experience The following updated requirements, descriptions and student learning outcomes become effective for the fall 2014 semester. Student learning outcome objectives were added recently to each broad area to meet the accreditation requirements of the New England Association of Schools and Colleges (NEASC) I. Science Preamble Students are required to complete two courses in the physical or biological ¬sciences. This may be accomplished in two ways: 1. By completing two courses with laboratories in the basic or applied sciences; 2. By completing one approved course in the applications of scientific knowledge, plus one course with a laboratory in the basic or applied sciences. Definitions and Explanations 1. A laboratory course in the applied physical or biological sciences brings basic knowledge to bear on the solution of practical problems in engineering, medicine, agriculture, forestry, and other fields for which natural science forms the foundation. Normally applied science courses require one of the basic natural sciences (biology, physics, chemistry, geology) as a prerequisite, and carry at least 4 degree credits. 2. A course in the applications of scientific knowledge has the following attributes: a) it focuses on one or more basic or applied natural sciences b) it includes significant blending of presently accepted science with its application in common situations; c) it discusses both the applications and limitations of the relevant scientific methodology; d) it includes as a major component of the course the observation of natural phenomena coupled with the gathering of data and its quantitative analysis, and its interpretation in an expository format; e) its overall focus is on guiding students towards the scientific literacy necessary for modern life rather than on training future science professionals. A science course, laboratory or applied, will have the following student outcomes embedded within the course. The outcomes are based on “The Nature of Science” as published in “Science for All Americans Online” at http://www.project2061.org/ publications/sfaa/online/chap1.htm (sponsored by American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS)). Retrieved February 2012. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the general education area of Science will be able to: 1. Explain what makes knowledge scientific, i.e., “…things and events in the universe occur in consistent patterns that are comprehensible through careful, systematic study.” (AAAS) 2. Demonstrate the appreciation that scientific knowledge is subject to change as new observations and interpretations challenge current understanding. 3. Recognize that valid scientific information is durable, i.e., it is continually affirmed as new observations are made. 4. Perform scientific inquiry including aspects of the scientific method, such as observation, hypothesis, experiment, and evaluation. Note: Covered in laboratory science courses but not necessarily in applied science courses. II. Human Values and Social Contexts Students are required to complete 18 credits in this broad area selected from lists of approved courses to satisfy each of the five sub-categories below. Courses that satisfy requirements in more than one sub-category may be counted in each appropriate sub-category. A. Western Cultural Tradition B. Social Contexts and Institutions C. Cultural Diversity or International Perspectives D. Population and the Environment E. Artistic and Creative Expression A. Human Values and Social Contexts: Western Cultural Tradition Preamble The Western Cultural Tradition involves the historical and/or philosophical examination of the basis of Western culture. Subject areas may include, but are not limited to, artistic, economic, education, historical, legal, linguistic, literary, performative, philosophical, political, rhetorical, scientific, and social dimensions of the Western cultural tradition and its impact. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the General education area of the Western Cultural Tradition will be able to: 1. Examine the sources, transmission, development and outcomes among ideas, institution, artifacts, and values within the traditions of the West. 2. Recognize and explore the complexity and variety among ideas, traditions, institutions, archaeological and historical texts and artifacts and values that inform the cultural traditions of the West. 3. Analyze and think critically about how societies are or have been defined by such cultural traditions. B. Human Values and Social Contexts: Social Contexts and Institutions Preamble Courses included in the Social Contexts and Institutions category focus upon the ways in which social contexts shape and limit human institutions (defined broadly to include customs and relationships as well as organizations). The specific focus may be upon ways in which social contacts and institutions interact with human values, the role of institutions in expressing cultural values, or the social and ethical dimensions attendant upon particular academic disciplines. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the general education area of Social Context and Institutions will be able to: 1. Identify, describe and analyze social contexts and human institutions 2. Recognize and critically evaluate the interaction between social contexts and human institutions C. Human Values and Social Contexts: Cultural Diversity or International Perspectives Preamble A course included in the Cultural Diversity or International Perspectives category satisfies one or more of the following criteria: (a) it places primary emphasis on the experiences, perspectives, and cultural work of one or more groups who are not dominant within a particular culture; (b) it has a primary goal encouraging students to become aware of the diversity of American culture and to discover their roles within that diversity; or (c) it places primary emphasis on the relationships among or within different cultures in the past or present; (d) it introduces students to a culture other than their own through an intermediate or advanced course in the language of that culture. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the Cultural Diversity or International Perspectives general education area of will be able to do at least one of the following: 1. Recognize the experiences, perspectives, and cultural values of one or more groups who live within a culture different than their own. 2. Describe the diversity of American culture and reflect on their personal roles within that diversity. 3. Identify and assess how different cultures have related to each other either in the past or the present. 4. Achieve intermediate or advanced mastery of a language other than English. D. Human Values and Social Contexts: Population and Environment Preamble Courses included in the Population and Environment sub-category help students to understand how humankind interacts with our finite physical and biological environment. This understanding can be fostered in different ways. Some courses may emphasize technical, scientific problems and solutions. Others may focus on institutional, historical, and political dimensions, and others may focus on the cultural, ethical, and philosophical issues underlying current environmental problems. Courses fulfilling this requirement should address at least one of the following: 1. the role of both local and global environmental change on the quality of human life; 2. the pervasive role of human population growth on environmental quality and the quality of life, both in industrial and developing countries; 3. the influence of historical, cultural, religious, economic, educational, and political factors on population growth and environmental quality; 4. the ethical and philosophical assumptions underlying environmental policies and thinking about nature and the place of humans in nature; 5. possible sustainable solutions to the population/environment problems. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the general education area of Population and Environment will be able to do at least one of the following: 1. Recognize and understand the role of both local and global environmental change on the quality of human life, 2. Describe the influence of diverse factors, such as philosophical, cultural, religious, economic, educational, and political, on population growth and environmental quality, 3. Understand the concepts and principles necessary to evaluate contemporary issues of population growth, natural resource conservation, and environmental protection, 4. Interpret diverse types of information about environmental issues, to develop their own perspectives on these issues, and to communicate these perspectives effectively, 5. Understand and describe technical and/or scientific approaches for addressing problems that arise in the relationship between human population and the environment. E. Human Values and Social Contexts: Artistic and Creative Expression Preamble Courses included in the Artistic and Creative Expression category engage the student in creative thinking and processes. A primary objective is to develop skills and intellectual tools required to make artistic and creative decisions, and to participate in, evaluate, or appreciate artistic and creative forms of expression. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the general education area of Artistic and Creative Expression will be able to: 1. Participate in, identify or evaluate artistic and creative forms of expression. 2. Develop skills and/or intellectual tools central to the artistic and creative process or its critique. III. Quantitative Literacy Preamble Students are required to complete at least six credit hours in Quantitative Literacy. Quantitative literacy is the ability to formulate, evaluate, and communicate conclusions and inferences from quantitative information. Students will develop their quantitative literacy during their undergraduate experience through courses targeted at quantitative literacy and through frequent exposure to quantitative problems and analyses both inside and outside their major. Student Learning Outcomes Upon completion of general education study in quantitative literacy, students will understand the role that mathematics and quantitative thinking plays in solving and communicating information about real world problems and relationships. Students will be able to: 1. Translate problems from everyday spoken and written language to appropriate quantitative questions. 2. Interpret quantitative information from formulas, graphs, tables, schematics, simulations, and visualizations, and draw inferences from that information. 3. Solve problems using arithmetical, algebraic, geometrical, statistical, or computational methods. 4. Analyze answers to quantitative problems in order to determine reasonableness. Suggest alternative approaches if necessary. 5. Represent quantitative information symbolically, visually, and numerically. 6. Present quantitative results in context using everyday spoken and written language as well as using formulas, graphs, tables, schematics, simulations, and visualizations. Instructors of courses offering General Education credit in the area of Quantitative Literacy will indicate how the Student Learning Outcomes will be achieved on their syllabi. Assessment practices are, for the most part, embedded within the courses awarding general education credit and are appropriate to the content and goals of each course and program. IV. Demonstrated Writing Competency Preamble Students are required to write throughout their academic careers and must demonstrate competency both at the introductory level and within their majors. To fulfill this requirement, students must: 1. Complete ENG 101, College Composition with a grade of C or better, or earn transfer credit by challenging the course successfully through presentation of a portfolio of past work demonstrating mastery of course outcomes. 2. Complete at least two writing-intensive courses, at least one of which must be within the academic major. Definitions and Explanations In a writing-intensive course: 1. students must have an opportunity to revise their writing in response to feedback from the instructor; 2. a substantial portion of the student's final grade must be based upon the quality of the written work, and 3. course enrollment should normally be limited to 25 students or less. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the general education area of Demonstrated Writing Competency will be able to: 1. Critique and revise their writing. 2. Achieve the intended purpose in the writing task, with awareness of audience. 3. Identify and fully develop ideas to a specific thesis. 4. Organize ideas effectively. 5. Adhere to proper mechanics and style. 6. Achieve clarity of expression in language, argument, rhetorical form, and idea. V. Ethics Preamble Students are required to take a course or a series of courses placing substantial emphasis on discussion of ethical issues. The ethics requirement can be satisfied by 1. a stand-alone course in which ethics constitutes a substantial focus of the course, or 2. a well defined series of courses required in a particular curriculum, wherein the treatment of ethics in any one course may be somewhat less, but which taken together sum to a substantial emphasis on ethics. Courses that satisfy the ethics requirement must have a theoretical component and have one or more of the following attributes: a) they teach methods of ethical analysis b) they deal intensively with ethical issues associated with a particular discipline or profession; c) they engage the student in the study of ethical questions arising through the interpretation of literature or history, or social scientific analysis designed to include ethical evaluation. In order for a course to be approved under this criterion, the treatment of ethics must be substantial rather than merely incidental. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the general education area of Ethics will be able to do one or more of the following: 1. Understand and describe main issues and concepts relevant to ethical theory. 2. Demonstrate their ability to work effectively with ethical issues and theories through their analysis and evaluation of the theoretical, literary, historical or artistic texts through which fundamental ethical ideas and problems are presented. 3. Critically evaluate the ethical ideas they are studying and apply these ideas to situations of everyday life. VI. Capstone Experience Preamble Every program must include an approved capstone experience. The goal is to draw together the various threads of the undergraduate program that bear directly upon the academic major in an experience that typifies the work of professionals within the discipline. Normally, the Capstone would conclude at the end of the student's senior year. Students should consult closely with their academic advisor to explore the range of options available for meeting this requirement. The capstone experience should have the following attributes: 1. the experience must be of significant depth and require innovation, creativity, reflection and synthesis of prior learning; 2. the experience must result in a thesis, report, presentation, or performance that demonstrates mastery of the subject matter 3. faculty/student interaction should be an integral part of the experience. 4. minimum student effort in the capstone should reflect the equivalent of three credits of work 5. Interdisciplinary experiences and opportunities for group participation in the capstone experience should be encouraged. Student Learning Outcomes Students completing the general education area of Capstone Experience will be able to: 1. Synthesize knowledge, skills, and dispositions gained throughout the student's major concentration of study. 2. Demonstrate competence within the discipline through professional conduct and, as appropriate, critical reasoning, analytical ability, and creativity. 3. Demonstrate effective communication skills.