RET Presentation - CURENT Education
advertisement

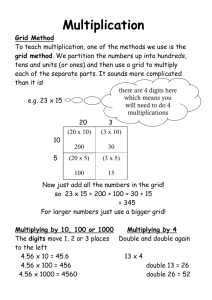
Connecting Middle School Content to the Power Grid Jill K. Lawrence Gresham Middle School CURENT RET Mid-Term Presentation July 1, 2014 Knoxville, Tennessee Challenges • Little to no flow of content progression between grade level curriculum K-8 Ex. Biomes part of 6th grade, adaptations for survival in biomes part of 8th grade content. Not addressed in 7th grade curriculum. • Little to no flow of content within 7th grade curriculum Rocks, minerals, plate tectonics, use of resources, simple machines, Newton’s Laws, speed, waves, cell biology, organ systems, reproduction, transport, heredity. • Inquiry, technology, engineering practices embedded in content throughout the year • Three tasks-at times in conflict Prepare for state assessments (achievement and growth, part of evaluation) Prepare for high school, career and/or college ready Engaging, rigorous, and relevant problem based learning opportunities • Department specifies order of content and instructional time per topic/unit 2 Program Focus – addressing the challenges • Inquiry, technology, engineering start of year instruction 7th and 8th grade – Inquiry skills and the power grid. Engineering design and the power grid. Technology and the power grid (SMART grid). • Integrate power grid into units of study throughout the year. • Maintain a 3-ring binder Organized by standards/units of study Cumulative for 7th and 8th grade studies • Culmination of summer RET at CURENT Inquiry, technology, engineering power grid introductory unit fully designed Framework for power grid integration into 7th and 8th grade curriculum outlined – lessons to be developed throughout the year Fully developed magnet and electricity unit with hands on experiences – 8th grade 3 INQUIRY, TECHNOLOGY, ENGINEERING – INTRODUCTION/FIRST 2-3 WEEKS OF ACADEMIC YEAR SETTING THE TONE AND LAYING THE FOUNDATION 7TH AND 8TH GRADE 4 Curriculum Requirements – 7th and 8th grade • Inquiry SPI 0707.Inq.1 Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. SPI 0707.Inq.2 Select tools and procedures needed to conduct a moderately complex experiment. SPI 0707.Inq.3 Interpret and translate data in a table, graph, or diagram. SPI0707.Inq.4 Draw a conclusion that establishes a cause and effect relationship supported by evidence. SPI 0707.Inq.5 Identify a faulty interpretation of data that is due to bias or experimental error. • Technology and Engineering SPI 0707.T/E.1 Identify the tools and procedures needed to test the design features of a prototype. SPI 0707.T/E.2 Evaluate a protocol to determine if the engineering design process was successfully applied. SPI 0707.T/E.3 Distinguish between the intended benefits and the unintended consequences of a new technology. 5 Guiding Questions Questions to investigate (pre and post assessment) 1. What is the power grid? 2. Why should engineers study historical data regarding the power grid? 3. What are the issues facing the power grid? 4. What is a Smart grid? 5. What is the engineering design process? 6. Explain how you used the engineering design process throughout this learning experience. 6 Day 1 questions to get students thinking, writing, and talking. What do you expect to happen when you flip the light switch? Turn on the hot water? Plug in your cell phone, TV, lamp, etc? What is it that makes it possible for the things in your house and in the school to work? Magic? Where does it come from? How is it made? How does it get to all the houses, businesses, industry? 7 Progression of Learning Day 1: Constructing house for power grid -group work, collaboration, decision making, planning Day 2: Part 1: Observations and predictions CURENT circuit board demonstrations -review/connect 6th grade content circuits Part 2: Wire houses (2 lights), 2 street lamps -test with two 1.5V batteries in series 8 Day 3: Individual power plant vs community power plant Wind Turbine challenge – day 1of 2 Day 4: Wind Turbine Challenge –Day 2 of 2 Compare classroom model with power grid Reading: Generating, moving and fuels that make electricity (NEED pgs 38-40 Energy Info Book) Relate week’s lessons/activities to engineering design process. Students write a summary of their understanding regarding what is engineering and what is the engineering design process? 9 Simple graphic to be used for comparison with classroom model of grid 10 Week 2 – Analyze data, graphing, drawing conclusion, future of the grid Day 1-3: NEED lesson: Energy Analysis Activity 1: Think about how your use of electricity has changed as you have gotten older. Do you have a cell phone? What age did you get the phone? Does it have a data plan? What do you do on your cell phone? Do you have your own tv? Cable? DVR? What age? How much time spent watching? Video game consul? How many? What age? What type? How much time do you spend playing video games? Personal computer, kindle, iPod, tablet, etc? What age were you? 11 Where did it all begin? How has it changed/evolved? History of power, pg 44, NEED Intermediate Energy Infobook Students will read short article and create a time line summarizing the events from the article. Teacher will present some additional information regarding the development of the power grid to be added to the timeline. 12 • Activity 2: Energy Production and Consumption. Graph historical data to determine trends and answer questions. Energy consumption by sector (pgs 46-50, NEED Intermediate Energy Infobook) Groups assigned sector to read information document provided by teacher. Create poster/presentation to share with class 13 Activity 2: data and graphing questions • How has per capita consumption of energy changed in the last 60 years? • How has the percentage of energy we import from other countries changed in the last 60 years? • How has the mix of energy sources changed in the last 60 years for production, consumption, fossil fuels, uranium (nuclear) energy, and renewable energy sources? 14 Thinking about the future • Day 4: As demand for more electricity increases, what does this mean for the power grid? Managing a power grid simulation http://tcipg.mste.illinois.edu/applet/The+Power+Grid# Either whole class, individual student, small groups depending on technology available Smart Grid Introductory Video http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/tech/power-grid.html Toward a Smart Electric Grid Interview/article http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/tech/toward-smartelectric-grid.html 15 Day 5 – wrap up and reflect Reflect on your experience for the past 2 weeks and respond to the following questions: 1. What is the power grid? 2. Why should engineers study historical data regarding the power grid? 3. What are the issues facing the power grid? 4. What is a Smart grid? 5. What is the engineering design process? 6. Explain how you used the engineering design process throughout this learning experience. 16 7th grade- power grid connections (lessons to be developed as the school year progresses) • Earth Science: 7 (Fall semester) Use of renewable and non-renewable resources to generate power • Physical Science: 11 (Fall Semester) Solar cars (speed, distance, time) • Life Science 1: Cell Structure and Organ Systems Analogy: compare power grid to organ systems, levels of organization • Life Science 3: Photosynthesis and Respiration Comparison of solar panels to chloroplast 17 8th grade unit power grid connections • Life Science 5: Biodiversity and Change Diversity of sources for power generation and transmission Human behaviors/adaptations to various situations Grid collapses, resources depleted, cost increase, environment • PS 9.1: Chemical Reactions Conservation of matter, conservation of energy Batteries and the power grid – electric cars • PS 9.2: Properties of Matter Atomic structure, conductors • PS 12.1: Magnetism and electricity • PS 12.2: Earth’s magnetic field and gravity Compare earth’s magnetic field with magnetic field of magnets, electromagnets 18 Electricity and Magnetism Curriculum Requirements – 8th grade Forces in Nature SPI SPI 0807.12.1 Recognize that electricity can be produced using a magnet and wire coil. SPI 0807.12.2 Describe the basic principles of an electromagnet. 19 PS 12.1 Magnetism and Electricity Overview • • • • Lesson 1 – Properties of Magnets Lesson 2 – Electromagnets and solenoids Lesson 3 – Electric Induction Lesson 4 – Generating power and the power grid (review from start of school year Individual Research –introduce research project, options and have students select topic 20 PS12.1 Lesson 1 – Properties of Magnets • Activities Use magnets to move car from Point A to Point B Use magnets to separate magnetic materials from non-magnetic materials Magnetize a nail. How many paper clips can you pick up? Map magnetic poles using compasses View magnetic field lines using iron filing boxes Design a simple experimental procedure to identify magnetic poles of unmarked magnets. Are all magnets created equally? Design a simple test to determine if all magnets have the same strength. 21 PS 12.1 Lesson 2 – Electromagnets and solenoids • What is a solenoid? What do solenoids have in common with magnets? How can you change the strength of a solenoid? Degree of deflection investigation • What is an electromagnet? Compare and contrast solenoids and electromagnets. Bar magnets and electromagnets. How can you change the strength of an electromagnet? Magnetize a nail. How many paper clips can you pick up? Compare with nail magnetized using a bar magnet. Degree of deflection challenge. Design an electromagnet that is stronger than a bar magnet. 22 PS 12.1 Lesson 2 – Electromagnets and solenoids • Simple motor and toy motor Analyze systems. Get both motors working. Explain the science behind what is going on. 23 PS 12.1 Lesson 3 – Electric Induction • Generators Test different amounts of coil to light a bulb Explain how the magnet is causing the bulb to light without a battery. • Analyze variety of items and diagrams and explain how they work in terms of electricity, magnets, electromagnetism, and/or solenoids. 24 PS 12.1 Magnetism and Electricity • Lesson 4 – Magnetism, electricity and the power grid Individual Research –introduce research project, options and have students select topic 25 Possible topics for student research 1. smart grids-explain what a smart grid is and how it works. Make a case for integrating smart grid technology into our current power grid system and homes. 2. micro grids: Microgrids are being explored as solutions for the strain on our current power grid. What are microgrids and how will understanding electromagnets and magnetism help in the development of a microgrid? Where and why are microgrids already being used? 3. electric cars: How does understanding about magnets, electromagnets, and induction of magnetism and electricity apply to the development of electric car technology? What are the issues that the electric grid will face as more and more electric cars come off the production line and become come onine in terms of using the grid? 26 References and Acknowledgements • • • National Energy Education Development Project (need.org) Public Broadcasting Service smart grid videos Power and Energy in the Home, TCIPG Education, University of Illinois • Thank you to Dr. Mehmet Aydeniz for letting me know about the RET program with CURENT Thank you to Dr. Chien-Fe Chen for the opportunity to participate in the RET experience at CURENT and for her guidance throughout the experience. Thank you to Mr. Erin Wills for the soldering lessons, circuit lessons, helping bring the mag-lev device and the generator to reality, helping with determining the necessary supplies, and for the wealth of knowledge on a daily basis. Thank you to Mr. Nick Sirek for the model of the simple motor. Thank you to Mrs. Jessica Minton for her collaboration, carpentry skills, and insights throughout this experience. Thank you to Tim for helping in the machine shop with the mag-lev device. Thank you to Bob Martin for the supplies to build the simple motors. Thank you to all the RET’s for your collaboration and support during this experience. • • • • • • • 27