Our Solar System
advertisement

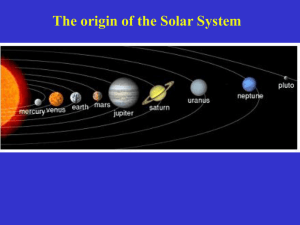
The Universe The Big Bang Theory • Scientists believe that our universe began with a big explosion of gas and dust in space. This explosion is called the Big Bang. • All of this matter and energy in space was concentrated at one point before the Big Bang. • They believe this explosion occurred about 15 billion years ago. • Since that time, the universe has been expanding (getting bigger and more spread out). animation of the formation of the universe: • http://resources.schoolscience.co.uk/PPARC/b ang/bang.htm our solar system • Our solar system consists of the sun, planets, dwarf planets (or plutoids), moons, an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and other objects. • The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, over 61 moons, the asteroids, comets, meteoroids and other rocks and gas all orbit the Sun. This is the compostion of our solar system: Sun: 99.85% Planets: 0.135% Comets: 0.01% ? Satellites: 0.00005% Minor Planets: 0.0000002% ? Meteoroids: 0.0000001% ? Interplanetary Medium: 0.0000001% ? animation of our solar system. • http://janus.astro.umd.edu/javadir/orbits/ssv. html galaxy • Definition: A cluster of hundreds of billions of stars. • Our galaxy is the Milky Way. • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. • Our solar system is on a spiral arm of the Milky Way. The Milky Way Galaxy Types of Galaxies: Elliptical galaxies Huge; contain stars, gas, and dust Held together by gravity Round-to-oval shape Mainly old stars are present Types of Galaxies: Spiral galaxies • Huge; contain stars, gas, and dust • Held together by gravity • Pinwheel shape • Young and old stars are present Types of Galaxies: Irregular galaxies • No regular shape • May show signs of a disk and/or a bulge; • halo is present • Usually rich in gas and dust • Young and old stars are present formation of our solar system • http://www.metacafe.com/watch/1111454/fo rmation_of_the_solar_system_great_animatio n/