차세대 인터넷 망관리 기술
advertisement

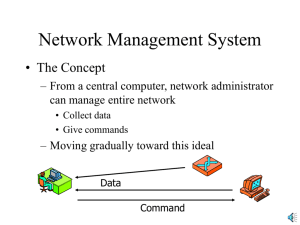
차세대 인터넷 망관리 기술 2000. 12. 12 이재용 연세대학교 전기전자공학과 jyl@nasla.yonsei.ac.kr 차세대 인터넷 ~2002 TCP/IP 기반의 유선 Web 응용 서비스 ~2005 QoS 제공 기반의 Web 응용 서비스 (Intserv/Diffserv) 개 인: ADSL (1.544Mbps) 사무실: 고속 LAN (10Mbps) 유·무선 고속 통합 인터넷 무선 인터넷 무선 모뎀 (64Kbps) IMT-2000 (128K ~ 2Mbps) All-IP 무선 인터넷 개 인: 6Mbps 사무실: 10Mbps Traditional SNMP Management Basic Functions Admin framework DB Server For Long-term Analysis NMS Functions handling MIB browser Applications Fault mgmt Configuration mgmt Accounting mgmt Performance mgmt Security mgmt Periodic polling Using SNMP Agent Agent Agent Device Device Device Other functions DB interface 차세대 인터넷 망 관리 요구사항 통합 망으로 인한 관리 망 크기의 증대 확장성 (Scalability) 새로운 서비스 출현으로 인한 서비스 관리 유연성 (Flexibility) End-to-End QoS 보장 관리 강인성 (Robustness) 고속화에 따른 관리 End-to-end Scope 분산 관리 Paradigm의 필요성 - 구조 •관리 통신 •Agent •Master - 관리 객체 분산 망 관리 동향 (1) 구조적 측면 OSF (Open Software Foundation) DME(Distributed Management Environment) IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) AgentX (Agent Extensibility Protocol) ITU/TMN ODMA (Open Distributed Management Architecture) FIPA (Foundation for Intelligent Physical Agents)/OMG Mobile Agent 분산 망 관리 동향 (2) 관리 객체 측면 OMG CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) SUN etc. Java RMI(Remote Method Invocation) JMX(Java Management eXtension) IETF RMON I, RMON II Functional MIB (Expression MIB, Event MIB, Scheduling MIB) ITU Event Notification / M-Action WBEM Architecture Other Windows Management App Management App DCOM / XML DCOM / XML Managed Node Common Information Model (CIM) CIM Object Manager COM Object Providers XML Managed Objects CMIP CMIP Objects SNMP SNMP Objects RPC DMI Objects Win32 Win 32 Objects BMC software 구조 CORBA-based Inter-domain Manager Using Web HTML JAVA Applet JAVA Applet CORBA (Orbix Web) HTML(CGI) WEB Browser RMI CORBA – based Inter-domain Manager ORB CORBA/SNMP gateway CORBA/SNMP gateway SNMP Sub-domain Agent Agent Agent CORBA Sub-domain Agent Agent Agent CMIP Sub-domain Agent Agent Agent 망관리에서의 분산화 : Event Notification/M-Action NM client의 load를 줄여줌 Event filtering / Correlation NMS Notification 이 요구됨 M-Action Event 발생은 미리 작성된 Scenario에 의함 Event 발생에 대한 reaction Server Server Server Action 은 NMS에 의존하므로 신속한 대응 미흡 망관리에서의 분산화 : RMON Host a Host b Host c Interface 2 Subnet X RMON Probe NMS Subnet Y Interface 1 Host d Host e - Network-layer address에 근거한 통계자료 모음 (nlHOST) • Control table Subnet Spec Subnet Spec X Y RMON 1 - Subnetwork-wide 통계 제공 - Off-line 관리 (data gathering) - alarm defing and event reporting - frame filtering and capturing RMON 2 - End-to-End 통계자료 제공 • email, file transfer.www에 따른 응용계층 트래픽을 감시 • host들에서 특정 application의 트래픽을 기록 가능 단점 RMON 장비의 CPU, memory 낭비 • Data Table Host related statistics Host related statistics Host related statistics •• • # of input packets / octets # of output packets / octets 망관리에서의 분산화 : Mobile Agent Distributed Management : Management by Delegation (MbD) 지적능력을 스스로 갖고 새로운 프로세스를 만 들어 낼 수 있다 (Autonomy) NMS Script (code, data, state) Server간에 이동이 가능하다 (Mobility) (remote execution 또는 migration) Results Server Server 분산된 일을 server를 지나며 수행 가능 (Intelligence) 비동기적으로 망 관리 수행 가능 (Asynchronousity) 망 관리에서 확장성과 유연성을 중대시한다 표준화그룹 : FIPA, OMG MASIF Server Platform : Aglet,Concordia,grasshopper, Voyager * FIPA : Foundation for Intelligent Physical Agent * OMG : Object Management Group * MASIF : MOBILE Agent System Interoperability Facility Distributed Objects Common Object Request Broker Architecture Web-Based Enterprise Management Java Management eXtensions CORBA (1) Object Management Architecture standardized by OMG Joint Inter-Domain Management (JIDM) group Sponsored by Open Group and the TMF (Telecommunication Management Forum) Provide tools that enable management system based on CMIP, SNMP, and CORBA to work together. Provide CMIP/CORBA and SNMP/CORBA inter-working. Map between GDMO/ASN.1 and CORBA IDL. Map between SNMP SMI and CORBA IDL. CORBA (2) Manager Client (Caller) Object (Callee) Stub Skeleton Middleware(ex. ORB) SNMP CMIP IDL CORBA Objects Network ASN.1 Objects Object Request Broker (ORB) SNMP domain Web 기술과의 통합을 시도 Orbix Web from IONA CorbaWeb from academia GDMO Objects CMIP domain CORBA domain WBEM Desktop Management Interface(DMI)에서 제기됨 Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) 초기에는 HMMS, HMMP, and HMOM로 구성됨 Drastic upheaval of WBEM Common Information Model (CIM) CIMOM이 HMOM을 대치. HTTP 과 XML 을 수용함. Current work Integrating CIM with CORBA and Java-based management. Developing SNMP/CIM, DMI/CMI, and CMIP/CIM gateway. Java technologies Java RMI Can be combined with Object Serialization. Management objects (SNMP or CMIS/CMIP objects) are mapped into distributed Java objects. JMAPI (Java Management API) Based on Java RMI Set of tools and guidelines to build management applets. Supports the most common SNMP MIB (MIB-II) JMX (Java Management eXtension) A management framework destined for object-oriented web-based management. SNMP API, WBEM API, (already specified) and TMN API (currently under definition) SNMP-to Java MIB compiler (translates the managed objects into MBean Component) JMX JMX Architecture Instrumentation level : give instant manageability to any object Agent level : provide management agent. Manager level : provide management component operating as manager or agent. JMX Components JMX Manageable Resource JMX Agent JMX Manager Services for management Addition Management Protocol APIs Interacting with other management environments. Key Component of JMX Proprietary Management Application Web Browser Proprietary Management Application Manager Level JMX Manager Protocol Adaptors Agent Level MBean Server Service Object 2 Instrumentation Level Object 1 Object 3 Java virtual machine MBean (registered in the server) Java virtual machine Plain JavaBeans Component (not registered) AgentX (Agent Extensibility Protocol) Motivation for AgentX Distributed management의 필요성 Hierarchical framework. Management applications의 분산된 agent에 대한 투명한 접근 Managed objects의 동적인 확장 MIB 장비로부터 SNMP protocol engine을 분리 MIB 구현 모듈의 동적인 추가 AgentX Framework Manager SNMP SNMP Entity AgentX Dispatcher AgentX Master-Agent Extensibility protocol SubAgent SubAgent SubAgent Master agent Agent 역할로서 SNMP 프 로토콜 메시지의 송수신. MIB에는 거의 직접적으로 접근하지 않음. Subagent(s) Master-agent에 의해 처 리되는 SNMP 메시지로부 터 “Shielded”됨. MIB을 직접 접근. AgentX Roles – Master Agent 기능 Subagent로부터 AgentX session 확립 요구를 받아들임. Subagent로부터 MIB region의 등록 접수 현재 등록된 MIB region에 따라, AgentX 프로토콜이 MIB에 접근 Subagent를 위해 notification을 전달해줌. AgentX Roles - Subagent 기능 Master-agent와 함께 AgentX session 시작 Master-agent에게 MIB region을 등록 등록된 MIB region내에서 OID와 실제 variable을 bind 시킴 Variable에 대한 관리 동작을 수행 관리 객체 (MO: Managed Object)를 초기화 시킴 Notification을 주도 Example: Management with AgentX Subagent From a manager’s point of view, an extensible agent behaves exactly as would a monolithic agent. Mail Server Email MIB AgentX NMS SNMP Subagent Master Agent AgentX MIB Registry WWW MIB AgentX The master agent is MIB ignorant and SNMP omniscient while the subagent is SNMP ignorant and MIB omniscient. WWW Server Subagent 10baseT Hub Repeater MIB AgentX Protocol Operations 18 Protocol operations are defined. 7 PDUs for Master agent Subagent direction 10 PDUs for Subagent Master agent direction 1 PDU for both Master agent and subagent. Master agent Subagent Get-PDU, GetNext-PDU, Get-Bulk-PDU, TestSet-PDU, CommitSetPDU, UndoSet-PDU, and CleanupSet-PDU. Subagent Master agent Open-PDU, Close-PDU, Register-PDU, Unregister-PDU, Notify-PDU, Ping-PDU, IndexAllocation-PDU, IndexDeallocation-PDU, AddAgentCaps-PDU, and RemoveAgentCaps-PDU. Both side Response-PDU OID Registration Subagents may register single instances: E.g., 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.2.0 = HOST-RESOURCESMIB.hrSystemDate.0 Subagents may register OID regions: E.g., 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.[1-22].7 = IF-MIB.ifIndex.7 – IFMIB.ifSpecific.7 Only a single subagent can be “authoritative” for a particular OID region. Priority values are used to identify the authoritative subagent if regions overlap. Transport Layer Mappings AgentX defines the following transport mappings: AgentX over TCP The master agent accepts TCP connection requests for the well-known port 705. Subagents connect to the master agent using 705 port number. AgentX over UNIX-domain Sockets The master agent creates a well-known UNIX-domain socket endpoint called “/var/agentx/master”. AgentX PDUs are not encoded using the BER They are transmitted as a contiguous byte stream. (Unlike SNMP PDUs) Security Considerations Community NMS USEC for v3 Master Agent No mechanism Subagent Agent session 동안 SNMP 보안 관련 정보가 subagent에게 전달되 는 방법이 없다. Implementations and Products JAX – A Java AgentX Sub-Agent Toolkit http://www.ibr.cs.tu-bs.de/projects/jasmin/jax.html CMU AgentX Implementation http://www.net.cmu.edu/groups/netdev/agentx/ Compaq True64 UNIX version5.0 mailto: daniele@zk3.dec.com Epilogue Envoy http://www.isi.com UC Davis, SNMP suites ucd-snmp.ucdavis.edu Frank Fock, Agent++ http://www.fock.de/agent++ AgentX Limitations Requires relatively complex operations on the master agent side in order to realize SNMP lexicographical ordering and access control efficiently. Only a single subagent can be “authoritative” for a particular OID regions. Only one network device which has same MIB can be managed at the same time. Security mechanism is not considered. Functional MIBs Expression MIB Event MIB Scheduling MIB Remote Operations MIBs Notification Log MIB Expression MIB expValueEntry expObjectEntry A table of object definitions for each Used by expExpressionEntry row (OID, wildcard…) A table of values from evaluated expressions Produce expExpressionEntry Result Information about a single expression (Interval, Prefix…) Produce Error expErrorEntry Information about errors in processing an expression 목적: 망관리 시스템에서 네트워크 트래픽 overhead를 줄이기 위함 MIB variable에 대한 expression computation 수행 Expression 구성시 3가지 MIB object sampling 형태 지원 absolute, delta, changed (boolean sampling). Event MIB 목적 MIB variable이 threshold를 지나치거나, 변화된 값을 가질 때 event를 발생시키기 위함 다른 MIB과의 관계 [RFC1757] RMON alarm, event group의 능력에 대한 superset 제공 [RFC1905] SNMPv2의 Manager-Manager MIB의 계승/보완 [RFC2573] SNMPv3 Management Target과 Notification MIB 의 서비스에 의존 [RFC2982] 분산 관리 Expression MIB을 보완한다. Scheduling MIB schedEntry schedOwner SnmpAdminString, schedName SnmpAdminString, schedDescr SnmpAdminString, schedInterval Unsigned32, schedWeekDay BITS, schedMonth BITS, schedDay BITS, schedHour BITS, schedMinute BITS, schedContextName SnmpAdminString, schedVariable VariablePointer, schedValue Integer32, schedType INTEGER, schedAdminStatus INTEGER, schedOperStatus INTEGER, schedFailures Counter32, schedLastFailure SnmpPduErrorStatus, schedLastFailed DateAndTime, schedStorageType StorageType, schedRowStatus RowStatus 목적 주기적 또는 주어진 날짜와 시 간에 수행될 action에 대한 scheduling 동작 Control object를 변경시켜 schedule을 enable/disable 시킴 다른 관리 기능에 의해 활성화/ 비활성화 되는 schedule을 미 리 구성할 수 있게 함. Remote Operations MIBs Ping MIB Remote host에서 관리 응용으로 하여금 Ping 수행 가능케 함. Traceroute MIB Remote host에서 Traceroute 수행케 함. Lookup MIB Remote host에서 Name lookup 가능케 함. Notification Log MIB 목적 Local loggin 기능의 형태로 다른 MIB에게 common infrastructure 제공 주로 sender의 Notification을 위해 사용되나 receiver도 사용 가 능. nlmLogEntry nlmStatsLogEntry nlmConfigLogEntry A table of Notification A table of logging log statistics entries statistics control entries. (logged or bumped) (entry limit, filter…) contains A table of Notification log entries (variables…) has nlmLogVariableEntry A table of variables to go with Notification log entries (values…) Script MIB Overview of the Script MIB(1) Defined in RFC2592 SNMP-compliant MIB Script MIB 분산된 장소로 Script 전달 Script를 위한 argument 전달 동작중인 script의 monitor, control이 원격으로 가능 Running script로 부터 결과 받음. Overview of the Script MIB(2) • Consists of six tables mib - II scriptMIB(mib-2 64) smObjects smLangTable smExtsnTable smScriptObject smScriptTable smCodeTable smRunObjects smLaunchTable smRunTable – – – – – – Language Extension Script Code Launch Run • OID is (mib-2 64) Table (1) Language Table Agent가 지원하는 언어 정보 제공. E.g. Java, and Tcl etc. Extension Table Language 확장에 대한 정보 제공 Local resource나 network protocol에 대한 interface제공 가능. Table (2) Script Table Script MIB을 지원하는 network 장비에 설치된 모든 script를 나 열 Script를 설치/제거, script 상태를 변경/읽기 등을 가능케하는 object 가짐. 지정된 URL로 부터 script를 Agent에 의해 영원히 설치되고, 받아 질 수 있음. Code Table SNMP set operation에 의해 Agent에게 script를 도착하게(push) 함. Table (3) Launch Table 준비된 script를 서술 List의 각 entry는 Script에서 전달된 argument Script 수행중의 신뢰도, 허가등을 나타냄. Run Table 최근 끝나거나, 돌고 있는 script list Manager로 하여금 동작되고 있는 script에 대한 정보 추출이나 제 어 가능케 함. Operations of Script MIB Manager Script Repository HTTP or other push script pull script smLangTable Java JDK1.1.8 Perl 5.004 ③ ① smScriptTable Preinstalled Preinstalled Dynamic -loaded Dynamic -loaded SNMP agent ② ⑤ ④ smLaunchTable smRunTable ⓢ Info Access ⓢ args secutiry Launch ⓢ args state result ⓢ Info Access ⓢ args secutiry Launch ⓢ args state result ⓢ Info Access ⓢ args secutiry Launch ⓢ args state result ⓢ Info Access ⓢ args secutiry Launch ⓢ args state result Network Node Applications of Script MIB Scripts as Agent Scripts as Mid-level manager Monitoring Service testing (QoS monitoring) Service management and control Fault handling Scripts as Agent Agent를 확장하거나 구현 표준 MIB로 부터 관리정보를 computing하는 서비 manager 스 제공 Agent의 확장성 제공. Launch script Retrieving result Internet Server Script Repository Polling Script MIB agent MIB-II (ex. tcpConnTable) response Scripts for monitoring Monitoring Detecting irregular condition Collecting accounting data More scalable The number of node to be monitored MIB objects per node Significantly decrease M : Manager A : Agent manager mid-level M manager A M A management traffic. Pre-process monitored data A A More flexible Easy to add nodes to be monitored Easy to modify the set of MIB objects monitored. A A Script for service testing Service testing (QoS monitoring) manager Checking the availability and the static and dynamic parameters of a given services. Internet Server Launch script Introducing new MIB module Lacks flexibility for new services Send test packet result Service testing by Script MIB Receive services MIB Agent User Rapidly adaptable to new situation. Script MIB agent is located where potential users are (differ from central manager). Script MIB can be installed on several remote location which require service monitoring. Script for service deployment and control Local mid-level managers can control server processes are running on the same node as the processes. Web server manager Download script Check service The Script MIB offers a convenient solution for the rapid development and installation of network services. example) Remote service deployment on programmable switch. Programmable switch Control network Scripts for fault handling Web server (repository) ②Choose manager Adequate script ③Install script ①Fault notification ④Execution ⑤Remove script Fault handlings can be distributed to mid-level manager as script. Central manager only required to decide which fault handling procedure to apply. Procedures ① ② ③ ④ ⑤ Fault identification Choose adequate script Install script Start and execute script Remove script References (1) Sun, “Java Management Extension White Paper,” http://java.sun.com/products/JavaManagement WBEM Initiative, Online: http://www.dmtf.org/wbem CORBA, Online: http://www.omg.org/ M. Daniele et al., “Agent Extensibility (AgentX) Protocol Version 1,” , RFC2741, January 2000. L. Heintz et al., “Definitions of Managed Objects for Extensible SNMP Agents,” , RFC2742, January 2000. R. Kavasseri and Bob Stewart, “Event MIB,” , RFC2981, October 2000 R. Kavasseri and Bob Stewart, “Distributed Management Epression MIB,” , RFC2982, October 2000. References (2) Bob Stewart and Ramanathan R. Kavasseri, “Notification Log MIB,” , internet draft, draft-ietf-disman-notif-logmib-16.txt, February 2000. Kenneth White, “Definitions of Managed Objects for Remote Ping, Traceroute, and Lookup Operations,” , RFC2925, September 2000. D. Levi and J. Schönwälder, “Definitions of Managed Objects for Scheduling Management Operations,” , RFC2591, May 1999. D. Levi and J. Schönwälder, “Definitions of Managed Objects for the Delegation of Management Scripts,” , RFC2592, May 1999 References (3) J Schönwälder, “Emerging Internet Management Technologies,” IM’99 Tutorial, 1999. Jürgen Schönwälder, Jürgen Quittek and Cornelia Kappler, “Building Distrubuted Management Applications with the IETF Script MIB,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 18, no. 5, May 2000. David Levi, “Introduction to the Script MIB,” Simple Times, vol. 7 no. 2, Nov. 1999. Éamonn McManus, “Script MIB Implementation Experience,” Simple Times, vol. 7 no. 2, Nov. 1999. Frank Strauß, “Script MIB Performance Analysis,” Simple Times, vol. 7 no. 2, Nov. 1999. Jürgen Quittek and Cornelia Kappler, “Practical Experiences with Script MIB Application,” Simple Times, vol. 7 no. 2, Nov. 1999.