Advanced Placement United States Government and Politics Mr
advertisement
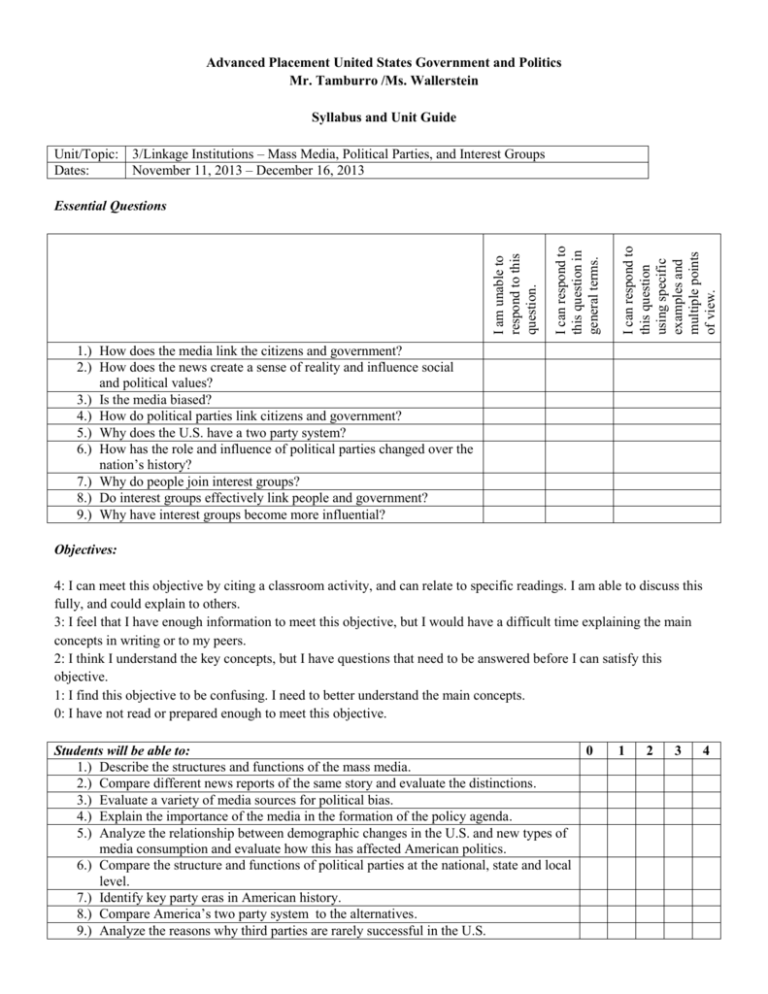
Advanced Placement United States Government and Politics Mr. Tamburro /Ms. Wallerstein Syllabus and Unit Guide Unit/Topic: 3/Linkage Institutions – Mass Media, Political Parties, and Interest Groups Dates: November 11, 2013 – December 16, 2013 I can respond to this question using specific examples and multiple points of view. I can respond to this question in general terms. I am unable to respond to this question. Essential Questions 1.) How does the media link the citizens and government? 2.) How does the news create a sense of reality and influence social and political values? 3.) Is the media biased? 4.) How do political parties link citizens and government? 5.) Why does the U.S. have a two party system? 6.) How has the role and influence of political parties changed over the nation’s history? 7.) Why do people join interest groups? 8.) Do interest groups effectively link people and government? 9.) Why have interest groups become more influential? Objectives: 4: I can meet this objective by citing a classroom activity, and can relate to specific readings. I am able to discuss this fully, and could explain to others. 3: I feel that I have enough information to meet this objective, but I would have a difficult time explaining the main concepts in writing or to my peers. 2: I think I understand the key concepts, but I have questions that need to be answered before I can satisfy this objective. 1: I find this objective to be confusing. I need to better understand the main concepts. 0: I have not read or prepared enough to meet this objective. Students will be able to: 1.) Describe the structures and functions of the mass media. 2.) Compare different news reports of the same story and evaluate the distinctions. 3.) Evaluate a variety of media sources for political bias. 4.) Explain the importance of the media in the formation of the policy agenda. 5.) Analyze the relationship between demographic changes in the U.S. and new types of media consumption and evaluate how this has affected American politics. 6.) Compare the structure and functions of political parties at the national, state and local level. 7.) Identify key party eras in American history. 8.) Compare America’s two party system to the alternatives. 9.) Analyze the reasons why third parties are rarely successful in the U.S. 0 1 2 3 4 10.) Explain the causes of party dealignment 11.) Explain how demographic changes in the U.S. have led to changes in the major political parties. 12.) Identify the different incentives that motivate people to join interest groups. 13.) Compare types of interest groups and different specific interest groups. 14.) Compare interest groups, lobbying firms, and PACs. 15.) Compare PACs and Super PACs. 16.) Evaluate the ways that interest groups attempt to influence elections and government decision making and the limits on their influence. 17.) Describe how the federal government regulates interest groups. 18.) Compare the goals of political parties and interest groups and explain how they can support each other’s goals. Topic and Assignment Schedule Day Date Topics and Activities 1 M 11/11 Review – what are linkage (D) institutions? Intro to Media & Politics: Focus Questions Reading/Viewing Due 2 W 11/13 (B) Distribute research assignment Functions of mass media History of media & politics Edwards 197-207 3 R 11/14 (C) “Making News” exercise Government regulation of media Role of internet in politics Edwards 207-210 Lanahan #79 “From Republic.com 2.0” 4 F 11/15 (D) 5 T 11/19 (B) Media center: research project Edwards 210-217 Read an article on a news source that would be aligned differently than your ideology 6 W 11/20 (C) Intro to political parties Structure and functions of political parties Hippocampus, “The Function of Parties in America” and “Organization of Parties” Wilson 97-101 7 R 11/21 (D) Party platforms: group activity 8 M 11/25 (B) FRQ Media bias History of Parties in U.S. Hippocampus, “Political Party Eras” and “Party Realignment and Dealignment” Wilson 101-107 Assignments Due Pew Research Center News IQ Quiz – Bring in results Questions about Lanahan #79 News Article Analysis discussion Research topic should be chosen before today Review Media & Politics Review Unit 2 Test 9 T 11/26 (C) 10 11 W 11/27 Political videos (21 min) M 12/2 (D) Two-party system vs. multiparty systems Third parties W 12/4 (B) Third parties 12 R 12/5 (C) 13 F 12/6 (D) (Sub plans) T 12/10 (B) 14 Intro to interest groups Assign interest group research project Media center: research project Media Research Project Hippocampus, “Third Parties” Wilson 107-112 Obstacles to Third Parties handouts Wilson 117-119 Wilson 119-122 Interest group handouts 15 W 12/11 16 R 12/12 Wilson 124-132 (D) M 12/16 Unit Test – MC / FRQ All Unit Readings Study for Test (B) **Reminder that any reading assignments are subject to unannounced, open-notes (not text) quizzes.** 17 Roles of interest groups Theories of interest groups How interest groups influence policy Wilson 122-124 Interest group reading assignment Key Terms and Vocabulary amicus curiae briefs broadcast media class action suits coalition coalition government collective good congressional campaign committee critical election Dixiecrats economic protest parties electioneering elite theory equal-time rule faction factional/charismatic personality parties gatekeeper grassroots lobbying / mass mobilization hyperpluralist theory ideological parties interest group investigative journalism linkage institutions litigation lobbying mass media media event narrowcasting New Deal coalition news leaks party dealignment party eras party identification party image party neutrality party platform party realignment patronage / spoils system pluralist theory plurality policy agenda policy entrepreneurs political machine political party press conference national chairperson national committee national convention PACs press secretary print media Progressives proportional representation public interest lobbies Ralph Nader “revolving door” right-to-work law Ross Perot single-issue groups single issue parties single-member districts sound bite spin control Strom Thurmond subgovernments / issue networks / iron triangles Super PACs talking head Tea Party movement third or minor parties ticket splitting v. straight-ticket voting union shop winner-take-all system








