Day1 - WordPress.com
advertisement

Eng. Nouran Nawar
SNMP Interaction
HP Products
HPOVNNM Installation
OUR LAB
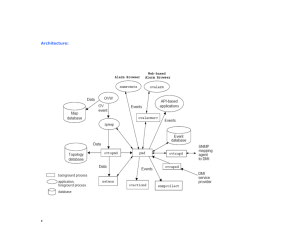
Basic Component on NNM
Home Base
OVW
Home Base Vs. OVW
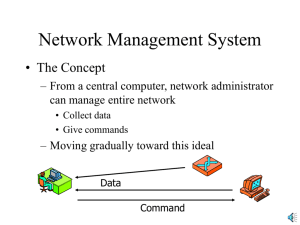
Need to make control from single point.
OSI specific management functional Areas:
Fault Management.
Configuration Management.
Accounting Management.
Performance management.
Security management.
MS : Management Station.
MA : Management Agent.
MN : Management Node.
Polling
SNMP use a simplest command between Manager and Agent,
using UDP/IP. “connection less”
Most of communication start by a manager.
Agent communication is response for manager.
SNMP Traps: Agent start communication when predetermined
even occur.
SNMP Get
AGENT
Response
SNMP
MANAGER
SNMP Set
Response
MIB
Traps
MS
MN
MIB : Management Information Base.
SNMP agent listen to port 161 UDP.
SNMP Manager listen to port 162 UDP “Traps”.
1. GET
2. GET_Next
3. Get_Bulk (v2)
Msgs sent by MS to MN
4. Inform (v2)
5. Set
6. Response
7. Traps
Msgs sent by MN to MS
SNMP v1
GET, Get Next, Set, Trap
SNMP V2
Get Bulk, Inform, SNMP V1
SNMP V3
Proxy Agent, Authentication , SNMP V1, SNMP V2
SNMP V2c
Access to device configuration
Standard Method to set or get data fro MN
MIB: piece of status or configuration
MIB object
NAME + Access + Type + Descr.
Access : read + write
MIB Tree
MIB tree
Management Sub Tree
Symbolic
.iso.org.dod.internet.mgm.mib-2.system.sys.sysDescr.0
=
Instance ID
Numeric
.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0
Fully Qualified MIB object name = object ID dot
notation(.)
Community name to provide a level of security for SNMP.
By default: get community name is “public”
Set community name: modify configuration.
HP open view advanced security
HP open view Dynamic Net value analyzer
HP open view Glance plus
HP open view ISP
HP open view Internet usage
HP open view Network Node manager
HP open view Performance manager
HP open view performance insight
Map to your NW.
Discover layer#2 & layer#3 connectivity
Event Management and Alarm Browser
SNMP data collection, MIB graph for any variable
Data ware house, Archive NW data
Report
Web based GUI
Mange HSRP, MPLS “SPI” smart plug in
NNM Starter Edition “SE”
Small NW, 250 node
NNM Advanced Edition “AE”
Discover unlimited nodes, VLANs, MPLS, VPN, WAN
HP NNM-I Certificate HP0-632
Your machine has a static IP
NOTE: “Changing IP Make the HP Stop working”
IIS windows Component
SNMP
Java J2re “Java 2 Runtime Environment, Standard Edition
1.4.2_06 ” min JPI 1.4.2.01
DNS Suffix and restart.
Delete switch configuration.
Enable SNMP on “our lab sw”.
Give the switch suitable name, IP, GW.
Enable SNMP, put community name, SNMP version, Traps,
All steps CH:26 Cisco_3560_Guide
1.1.1.1.
Save your configuration
http://1.1.1.1:7510
Dynamic views
Node status summary
Alarm browser
Dynamic summary
Discovery progress
Path view
Neighbors view
Internet view
Network view
Node view
Segment view
Cmd ovw
Basic windows Root Internet NW Segment Nodes.
“Ipmap” service create IP sub-map hierarchy.
Relation between maps and sub-maps like parent and child.
Dark blue:
unknown
Unmanaged
Green: normal
Testing
Cyan: warning
Restricted
Yellow: minor
disabled
Orange: major
Red: down
Green
Cyan
Yellow
Orange
Red
Help Symbol legend
View Zoom
View Label
Map Print “Unix only”
Edit find Location an object
Access object properties capabilities you can not change
general attributes rarely changed
Map Map snapshots
cmd ovmapsnap
Edit add to Quick navigator
Need OS login
Edit map
NNM be installed on
machine
Remote administration
Tomcat alarm
Scaled well
Snapshots
View find
Background
File print preview
Quick navigator
Poster printing
Edi find
MS discover itself, using IP, SM. DGW.
Discover DGW.
MS discover ARP cache.
SNMP community must be known.
Every 15 min, repeat polling.
“netmon” services run at background use ICMP and SNMP
over UDP to find nodes at network.
Loadhost command
Cmd loadhosts –m 255.255.255.0
172.169.1.215 3560
172.19.1.213 nouran-pc
Useful commands:
Ovstart –c
Ovstart –v
Ovstop
Ovstatus –c
C:\Program Files\HP OpenView\bin\dvUsersManager.ovpl
It will edit in C:\Program Files\HP OpenView\tomcat\jakarta-tomcat4.0.4\webapps\topology\WEB-INF\dynamicViewsUsers.xml
If it will not work,
C:\Program Files\HP OpenView\tomcat\jakarta-tomcat4.0.4\webapps\topology\WEB-INF
Uncheck <security-constraint> section.
Launcher
Network Presenter
Monitor NW Activity
Discover your network with Netmon
Controlling Netmon discovery
View your network by Network Presenter “read only”.
Start launcher on windows:
Ovw tools hpopenview launcher.
http://172.19.1.212/OvCgi/ovlaunch.exe
Start Launcher on Unix:
http://172.19.1.212:3443/OvCgi/ovlaunch.exe
Tasks: Access to task operation.
Configuration Event Correlation.
Configuration web reporting interface.
Information & Reports:
MIB Browser.
NNM Alarms.
Web Reporting interface.
Tools:
NW Presenter
Alarm Browser
Event corrleation
SNMP Data presenter
SNMP MIB Browser
Web Reporting
Access maps from network presenter.
Open a map other than the default map.
Network presenter needs ovw map is opened.
Any change in ovw reflect in the same time in
Launcher_network presenter.
Scope
Pane
Control
Area
There are features in NW presenter, and Not available in NNMMS.
Scoping pane
Tabular View
Scroll bar in content area
Features in ovw and not in NW presenter:
Map description dialog box
Sub map and map snapshots
For example:
When you add symbol it will be added in NW presenter.
Mange/unmanage symbol it will be reflected.
Sub map in ovw, nothing happened.
Delete submap in OVW, reflected.
Note:
To make launcher open other than the default map:
http://cn_nouran.cisco.com/OvCgi/jovw.exe?mapname=map1
Jovw.exe is NW
presenter
Ch:8
Check the network connectivity.
Check a node’s network configuration.
Check the amount of network activity.
Check for alarms.
1. Select a source node (click on the symbol).
2. Select a destination node (control-click on the symbol).
3. Invoke the Remote Ping dialog box from the Fault: Network
Connectivity: Remote Ping menu item.
Select Node
Fault Test IP/TCP/SNMP
Ovw Fault Network Connectivity Poll Node
Shows the shortest path between any two nodes
Extremely useful for troubleshooting
It has Graph and table tab.
Status Poll
Trace Route
Capability Poll (Windows only)
Event Viewer (Windows only, ovw only)
Diagnostics (Windows only, ovw only)
Network Activity
System utilization such as CPU Load, Disk Space, or the
Windows
Performance Monitor
Network Polling Statistics
Ch:15
Netmon Discovers network nodes.
Ovcapsd Checks for DMI and web capabilities (Windows only)
Ovtopmd Maintains the topology and object database.
ovstart starts ovspmd.
ovspmd starts netmon.
netmon queries the NNM management station’s SNMP agent for
configuration information, which includes:
IP Address
Subnet mask
Default Route
ARP Cache
For each new IP address found in the ARP Cache or Default
Route from the previous step, ping it to make sure it is alive,
make an SNMP query to determine the SNMP version supported,
then use SNMP to retrieve the configuration information noted in
step 3
Tell netmon to discover more by managing nodes.
Edit Manage Object
Loaclhosts command
Cmd loadhosts –v –m –p 255.255.255.0 -c 10.1.1.1
-v verify
-m subnetmask
-p ping host
-c start by 1.1.1.1 tell next 99 IP
Cmd loadhosts –m 255.255.255.0
1.1.1.1 koko
Ovsuf file: file containing background process, stratup config.
Its location “C:\Program Files\HP OpenView\conf”
It is a notepad file, read-only file.
To modify LRF : Local Registration file:
Ovstop process
Backup netmon file
Edit netmon
Ovdelobj netmon.lrf delete netmon entry from ovsuf
Ovaddobj netmon.lrf add netmon entry from ovsuf
Ovstart netmon or
Ovtopfix –l -i
Giving netmon a seed file to speed up initial discovery.
1. Cmd Ovstop netmon
2. Create a seed file, give MS the router and gateway, should be
stored in “C:\Program Files\HP OpenView\conf\seed”
3. Modify LRF “netmon.lrf” edit the file –s
{pathOVs_YES_START:ovtopmd,pmd,ovwdb:-P -s
c\:/seed:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:15:PAUSE}
4. Cmd cd C:\Program Files\HP OpenView\lrf
5. Ovdelobj netmon.lrf
6. Ovaddobj netmon.lrf
7. Optional Redo Initial Discovery
8. Restart netmon cmd ovstart netmon
Stop NNM
Cmd ovstop –c
Remove folder content, “HP OpenView\databases\eventdb” and
“HP OpenView\databases\openview”.
Start NNM
Cmd ovstart –c
Viewing Alarms
Exploring and Using MIB Data
Ch: 10
Ch: 22
Trap : A specific message that is sent by an SNMP agent to UDP
port 162 (the default) of the NNM management station is called a
trap, or snmptrap. These messages always originate from outside
the NNM process structure. They are received by ovtrapd for
processing into NNM.
Event : An internal message format resulting from a trap which
has NNM header information added to it, or a message that
occurs between two NNM processes. It indicates an incident of
interest, regardless of the source of the incident.
Alarm: After an event has been received, processing of the event
occurs. The result of the processing is an alarm. Not all events
result in alarms, but every alarm is the result of one or more
vents.
When an incident does occur, the involved NNM process or SNMP
agent generates and sends an event to NNM’s pmd process.
Events sent by SNMP agents are called SNMP traps.
NNM services can request information from outside the
management station. For example, netmon polls the network for
discovery of objects.
Services can send events to each other. For example, the pmd
service sends alarms to the ovalarmsrv process to display the
alarms in the alarms browser.
If the event comes from outside the management station, it is
received by ovtrapd.
ovtrapd sends the event on to the postmaster, pmd.
pmd sends all events, whether from ovtrapd or another process,
through the Event Correlation System (ECS), where the events
are processed.
Some of the events may be sent to processes that have
subscribed to them. Other events may be correlated. Sometimes
a new event, or alarm, is generated.
ovalarmsrv subscribes to all alarm events.
For example, netmon polls a device to see if it is up and running.
When the device returns an event that says it is up, ovalarmsrv
does not get the event. However, if the device does not respond,
then an alarm results saying the device is unreachable. This
alarm is sent to ovalarmsrv and appears in the alarms browser.
The ECS system correlates some events.
For example, netmon continues to poll the device that is not
responding. Each time there is no response, an event occurs.
After the first event, ECS correlates the events. In the alarms
browser, you only see the first event.
Correlation of events can be turned on or off.
Action Alarm Details
Action Show Correlated Alarms
Select node Alarm
ECS provides correlations for use with NNM which produce one
of the following actions:
Pass Through - The event passes through ECS with no change.
Suppression - The event is suppressed within ECS. This event is
not broadcasted to the NNM process.
Associated or correlated - The event is correlated with another
event. A parent child relationship is set up with the events.
New event - A new event is generated as a result of the original
event.
To change the Alarm Browser size;
ovalarmsrv:ovalarmsrv:
OVs_YES_START:pmd:700:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:120:PAUSE
By default: 3500 events
BSE: Binary Event Store
Log event. By default, incoming events and correlated alarms are
logged to the Binary Event Store. The maximum size of the binary
event store can be changed by modifying pmd.lrf. To increase the
size of the binary event store from the default of 16 MB to 32MB:
Edit pmd.lrf and add the option shown in the example below:
pmd:pmd:
OVs_YES_START_::SOV_EVENT;b32:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:15:PAUSE:
cd OV_LRF (on UNIX) or cd %OV_LRF% (on Windows)
ovaddobj pmd.lrf
ovstop pmd
ovstart -c
Ch:13
Ch:14
Describe the purpose and structure of a MIB.
Distinguish between MIB objects and
instances.
Browse a node’s MIB from the GUI, web
interfaces, or command line.
Graph a MIB object’s value as it changes.
Load additional MIBs for management.
Name. Uniquely defines the MIB object at the current level in the
MIB hierarchy.
ACCESS:
read-only. The value of the object may be retrieved (for example,
snmpget) but not changed.
read/write. The value of the object may be both retrieved and
changed (for example, snmpset).
•Symbolic Representation — used by people
•Numeric Representation — used by computers
Ovw tools SNMP MIB Browser
Launcher Object View IT Resource SNMP MIB
Browser
SNMPGET
Retrieve a single MIB object value (SNMPv1).
SNMPWALK
Make multiple requests to retrieve all MIB object
values under a certain branch of the MIB hierarchy
(SNMPv1).
SNMPSET
Set the value of a single MIB object (SNMPv1).
MIB Browser:
.iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.at.atTable.atEntry.atPhysicalAddress
.iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.ip.ipDefaultTTL
.iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.system.sysName
Cmd snmpget node_name .iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib2.system.sysName
MIB_object_ID: .iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib2.interfaces.ifTable.ifEntry
MIB Instance: 1
Cmd snmpwalk target_node .1.3.6.1.2.1.1
Cmd snmpget target_Node .1.3.6.1.2.1.1
Options Load and Unload MIBs
1. Download MIBs from ftp://ftp.cisco.com/pub/mibs
2. Prerequisites MIB:
CISCO−SMI−V1SMI.my
SNMPv2−TC−V1SMI.my
CISCO−CONFIG−COPY−MIB−V1SMI.my
CISCO−FLASH−MIB.my
3. @ MS: cmd snmpset −v 1 −c private <device name>
ccCopyProtocol.<random number> integer 1
ccCopySourceFileType.<Random number> integer 4
ccCopyDestFileType.<Random number> integer 1
ccCopyServerAddress.<Random number> ipaddress "<server ip
address>" ccCopyFileName. <Random number> octetstring "<file
name>" ccCopyEntryRowStatus.<Random number> integer 4
-v: version
-c : community Name
Integer 1 : TFTP protocol
Integer 4 : Running-Config
4. Install TFTP server
snmpset -v 1 -c cisco 172.19.1.215
ccCopyProtocol.12 integer 1
ccCopySourceFileType.12 integer 4
ccCopyDestFileType.12 integer 1
ccCopyServerAddress.12 ipaddress
"172.19.1.212" ccCopyFileName.12
octetstring "backup"
ccCopyEntryRowStatus.12 integer 4