Diapositiva 1
advertisement

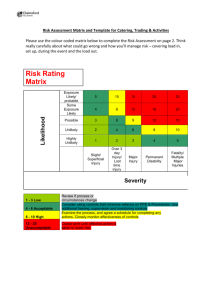
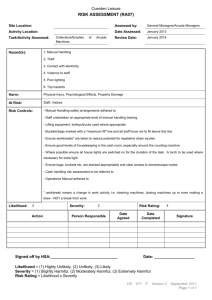
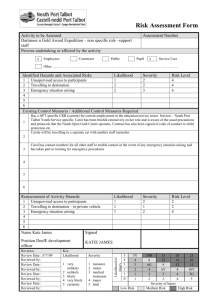
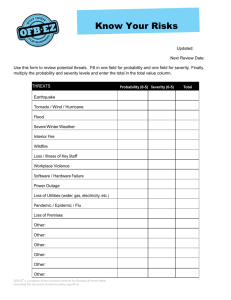
Service Quality in the Petroleum Industry Measuring Up Josh Ritchie Schlumberger Service Quality Compliance Manager – Drilling & Measurements Argentina, Bolivia, Chile Agenda • Measuring Up • Quality Improvement in the Service Industry – Attention to Quality – Management System – Risk Analysis Measuring Up – Tire Industry • Well known tire manufacturer produced 6,000,000 tires, 2,000 which failed and caused accidents. • 4.9 Sigma (99.977% efficient) versus 3.4 Sigma (99.36% efficient) Measuring Up : Medical Industry • 3.4 Sigma – 99.36% efficient • 5,000 incorrect surgical procedures per week in the U.S. • 200,000 incorrect drug prescriptions annually in the U.S. Measuring Up : Airlines • Heathrow Airport in London is the busiest airport in the world: 468,000 flights per year • Based on fatality rate from airline safety records, 1 fatality incurs every 5 years • 6.42 Sigma (99.99999997% efficient) versus 3.4 Sigma (99.36% efficient) How can we improve? • Defining and Measuring Quality • Focus on Quality – incorporating into the organization • Management Systems • Knowledge Management What is Quality? Wikipedia: • ISO 9000: "Degree to which a set of inherent characteristic fulfills requirements." • Six Sigma: "Number of defects per million opportunities." • Peter Drucker: "Quality in a product or service is not what the supplier puts in. It is what the customer gets out and is willing to pay for." Measuring Quality • Lost time / Operating time (efficiency) • Failures per pumping hour or per meter drilled (MTBF) • Net Pay / Gross Interval drilled • < 5 deg/100’ dogleg severity Power of Focus • Doubled in size since 2003 • Injury Rate held constant (companywide focus on Safety) • Increase in Serious Quality Incidents, directly proportional to company growth Focus on Quality • Raise importance of SQ to that of HSE • Culture change in organization – You would stop a job if Safety was compromised – Would you stop it if Quality was compromised? Quality Management System Commitment, Leadership and Accountability • The foundation of the Quality Management System (QHSEMS) is leadership, commitment and accountability from top management and its readiness to provide adequate resources for QHSE. • Particular attention is drawn to the importance of senior management providing a visible expression of commitment. • Failure to do so will undermine the credibility of Quality policy and objectives. Policies and Objectives • Dictate limits and requirements. • Define the restraints under which business is conducted. • Give the personnel clear and precise communication about principle issues. • Provide a certain level of control over identified risk. Organization and Resources • Organization • Resources: – Information Management – Personnel (Training and Competency) – Standards • Sets of rules for implementing policies that define the requirements and minimum acceptable criteria – Guidelines (companion documents to standards) • Provide additional technical or procedural information to ensure compliance with standards Risk Management • Hazard Analysis and Risk Control (HARC) – New Activities and Services – Existing Activities where the rate of occurrence of undesired events is abnormally high – Management of Change – Existing Activities with new exposures – Infrequent / irregular activities HARC A simple, one-page form that: • Guides employees at any level through the HARC Process • Classifies Quality Hazards • Facilitates implementation of prevention and mitigation measures to reduce risk HARC Work flow Identify all hazards associated with planned activities Assess Likelihood of each undesired event Assess Potential Severity of each undesired event Place analysis on the Risk Matrix. Is it acceptable? No Yes Document in HARC form, agree review cycle, proceed Risk reduction with improved Prevention Risk reduction with improved Mitigation HARC: Likelihood and Severity • Likelihood Very Low Low Incidents not Incidents known to have occurring less occurred than once per year • Severity – – – – – Multi-Catastrophic Catastrophic Major Serious Light Medium High Very High Incidents occurring once or more per year Incidents occurring once or more per month Incidents occurring once or more per week C M S L N HARC: The Risk Matrix • Risk Matrix: A twodimensional matrix used to quantify Risk Level by plotting Likelihood versus Severity. • Potential Risk: Risk Level (as defined on the Risk Matrix) before the implementation of Risk Control measures. • Residual Risk: Risk Level (as defined on the Risk Matrix) after the implementation of Risk Control measures. HARC • Mitigation and Prevention measures are put in place to reduce the likelihood and severity PREVENTION LIKELIHOOD LIKELIHOOD MITIGATION SEVERITY SEVERITY Audits and Reviews • How well do you conform to your Standards? • Performed annual by each location • HQ Audit every 3 years – Personnel from various locations • Output are Remedial Work Plans put into place to ensure changes are made where nonconformance lies: ongoing cycle of improvement. Management System - Recap Plan Do Check Feedbac k Conclusions • The Petroleum Industry has much room for improvement with respect to Quality – our current performance would cause 13,565 deaths annually in the airline business • Define Quality with your Service Providers • Power of Focus • Management Systems – Computer code – everyone working in the same fashion • Risk Control for Quality