PHYS GS Exam (ENGL Version)
advertisement

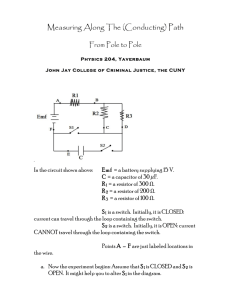
Take g = 10 m/s2 Choose the correct answer 1) For a system that is energetically isolated and within which there is friction: a. The mechanical energy is conserved b. The total energy is not conserved c. The variation of the mechanical energy is equal to the opposite of the variation of the internal energy of the system d. The variation of the mechanical energy is equal to the variation of the internal energy of the system 2) A ball is launched from the origin with an initial velocity 40 m/s and making an angle 60° with the horizontal. The maximum altitude of the ball is at a. 80 m b. 60 m c. 69 m d. 20 m 3) An elastic spring, of constant K, undergoes a variation∆𝑥 = 𝑥2 − 𝑥1 . The work done by the force of tension is equal to: a. b. c. d. 1 2 1 2 𝑘(𝑥12 - 𝑥22 ) 𝑘(𝑥2 − 𝑥1 )2 𝑘 (𝑥2 − 𝑥1 ) 1 2 𝑘(𝑥2 − 𝑥1 ) 4) A block of mass m = 2 kg is released from rest, from a distance d = 4 m, onto a massless spring with a force constant k = 100 N/m that is fixed along a frictionless incline of angle θ = 30°, as shown in the figure below. The maximum compression of the spring is: a. 1m b. 0.89m c. 0.1m d. None of the above 5) A tuck of mass 2300 kg, moves in a direction that is considered positive, with a speed of 20 m/s. The tuck enters into head-on collision with a car of mass 1200 kg and that is moving in a direction opposite to that of the truck with a speed of 40 m/s. After the collision, the truck and the car move at the same velocity: a. 2 m/s in the positive direction b. 5 m/s in the positive direction c. 26.86 m/s in the positive direction d. 0.57 m/s in the negative direction 6) A ballistic pendulum is a simple system for measuring the speed of a bullet. A bullet, of mass m = 10 g, makes a completely inelastic collision with a block of wood of mass 4 kg which is suspended by two ropes each of length 1m. After the impact, the bullet becomes embedded in the wood and the system swings to a maximum angle of 36°. The speed of the bullet just before collision is: a. 774 m/s b. 1613 m/s c. 1.93 m/s d. None of the above 7) In a non-collinear and elastic collision between two balls a. The linear momentum of the system at the instant of collision is not conserved b. The kinetic energy of the system is always conserved c. The mechanical energy of the system is always conserved d. The linear momentum and the kinetic energy of the system are conserved just before and after the collision. 8) A 10 g bullet moving directly upward at 1000 m/s strikes and passes through the center of mass of a 5 kg block initially at rest. The bullet emerges from the block moving directly upward at 400 m/s. The maximum height reached by the block is equal to a. 0.073 m b. 0.73 m c. 7.3 m d. 73 m 9) The mechanical energy of an oscillator that is performing a simple harmonic motion and of natural pulsation 𝜔0 and elongation 𝑥 is written in the form: a. 𝑥 ′′ + 𝜔02 𝑥 = 0 1 b. 𝑥 ′2 + ω2 𝑥 2 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 2 c. 𝑥 + d. 𝑥 ′′ + 1 0 𝑥 ′2 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 ω20 𝜔02 𝑥 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 10) As the friction increases, the pseudo-period T of the oscillator a. increases b. decreases c. remains constant d. None of the above 11) In a simple harmonic motion of amplitude 𝑋𝑚 , the k.E is equal to the E.P.E at the position(s) 𝑋 a. 𝑥 = ± 2𝑚 𝑋𝑚 b. 𝑥=± c. d. 𝑥 = ± 𝑋𝑚 𝑥=0 √2 12) The period of the energy in a simple harmonic motion is equal to a. Twice the period of the elongation for an oscillator b. The same value as that of the elongation for an oscillator c. Half the period of the elongation for an oscillator d. None of the above 13) For a simple harmonic oscillator and given that at t = 0, the initial position𝑥0 = −4 𝑐𝑚 and the initial ⃗ 0 = 0.281𝑖 , the solution is 𝑥 = 𝑋𝑚 cos(𝜔0 𝑡 + 𝜑), then velocity is 𝑉 a. 𝑋𝑚 = 4 cm and 𝜑 = -2.3 rd b. 𝑋𝑚 = 6 cm and 𝜑 = -2.3 rd c. 𝑋𝑚 = -6 cm and 𝜑 = -2.3 rd d. 𝑋𝑚 = - 4 cm and 𝜑 = -2.3 rd 14) As the friction in the forced oscillations decreases, the frequency at which the resonance occurs a. Decreases b. Increases c. Remains constant d. None of the above 15) The extremity of an oscillator, with spring constant K = 80 N/m, is connected to a vibrator of adjustable frequency f and for each frequency f a recording is performed. Using the adjacent table that shows the amplitude 𝑋𝑚 relative to each f, the value of m is a. 2 kg f (Hz) 1.5 2 2.5 2.8 3 3.2 3.3 3.6 4 4.5 b. 0.2 kg c. 1 kg 𝑋𝑚 (m) 0.4 0.6 1 1.5 2.1 2.3 2 1.5 1 0.7 d. 0.5 kg 16) A 500-loop circular wire coil with radius 4 cm is placed between the poles of a large electromagnet. The magnetic field is uniform and makes an angle 60° with the plane of the coil; it decreases at the rate of 0.2 T/s. The magnitude of the induced emf is: a. 0.435 V b. 0.251 V c. 4.35 V d. 2.51 V 17) A circular loop of wire of area 20 cm2 and resistance R = 0.39 is in a region of a magnetic field B = 0.38 t3 .The magnetic field is directed perpendicularly into the plane of the loop. At t = 0, B = 0. The absolute value of the electric current in the loop at the instant when B = 1.33T is equal to: a. 0.135 A b. 1.35 A c. 0.0135 A d. None of the above 18) When an open coil circuit rotates with a uniform circular motion in front of a uniform magnetic field, it acts as a generator that produces a. An alternating sinusoidal current b. A constant current c. A constant voltage d. An alternating sinusoidal voltage 19) A 0.25-m-long bar moves on parallel rails that are connected through a resistor R = 6. Neglect all friction forces. The circuit is placed in a uniform magnetic field B = 1.2 T that is directed into the plane of the figure. At an instant when the induced current in the circuit is counterclockwise and equal to 1.75 A, the bar moves with a constant velocity that is directed: a. To the right with a value 35 m/s b. To the left with a value 35 m/s c. To the right with a value 2.9 m/s d. To the left with a value 2.9 m/s 20) In the preceding exercise, the bar is subjected to a Laplace’s force acting a. To the right with a value 1.9 N b. To the left with a value 0.525 N c. To the left with a value 1.9 N d. To the right with a value 0.525 N 21) The inductance of a solenoid with cross-sectional area A = 5 cm2 and length 20 cm, wound with 100 turns wire on a nonmagnetic core is equal to a. 10 H b. 20 H c. 10 H d. 40 H 22) At the instant when a circuit including a coil is switched off, the coil behaves as a: a. Generator b. Receiver c. Resistor d. Capacitor 23) Consider a circuit containing a generator G(E = 10V, r = 1) connected in series with a conductor of resistor R = 8 and resistive coil of inductance L = 0.5 H and internal resistance r’ = 1 . When the steady state is reached, the steady current is equal to: a. 1.05 A b. 1 A c. 0.95 A d. 1.11 A 24) In a non-ideal transformer, the transformation ratio m is equal to: a. b. c. d. 𝑁2 𝑁1 𝑁1 𝑁2 𝐼2 𝐼1 𝑉1 𝑉2 25) Consider the following circuit where the switch K is in the position 1, the channel Y1 displays UAM and the channel Y2 displays UBM = UR. When the bottoms INV and ADD are pushed, the voltage displayed on the screen of the oscilloscope will be: a. That across the resistor UBM b. That across the capacitor UAB c. That across the generator E d. None of the above 26) In the preceding circuit, consider the two situations: First when the switch k is in the position (1) and the second when it is in the position (2). The ratio between the time constants in both situations is: a. b. 𝜏2 𝜏1 𝜏2 𝜏1 = 1 2 = 2 c. 𝜏1 = 𝜏2 d. None of the above 𝑡 27) In the R-C circuit and during the charging mode of a capacitor, the voltage uc = E( 1 - 𝑒 − ⁄𝜏 ), the voltage across the resistor R is equal to the voltage across the capacitor at the instant a. t = b. t = 5 c. t = ln2 d. t = 2 ln 28) In an R-L-C series circuit, the two waveforms shown on the screen of the oscilloscope represent two voltages across two electric loads, the most probable that: a. (a) across the resistor and (b) across the generator b. (b) across the resistor and (a) across the generator c. (a) across the resistor and (b) across the capacitor d. (b) across the resistor and (a) across the coil 29) In the preceding exercise, the effective current passing through the R-L-C series circuit where the resistor R = 200 and the internal resistance of the coil r = 168 value of the effective current in the circuit is: a. 0.032 A b. 0.0023 A c. 0.045 A d. 0.057 A 30) In an R-L-C series circuit where the voltage across the generator leads the voltage across the capacitor 𝜋 by an angle (phase difference) 𝜑 = 2 𝑟𝑑. In this case, the circuit is considered to be a. Resonating b. Capacitive c. Inductive d. None of the above