The First Muslims - Mater Academy Lakes High School
advertisement

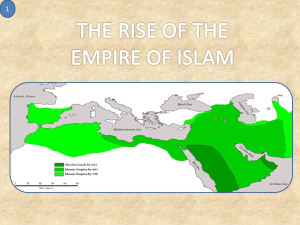
The First Muslims How can religion influence the development of an empire? How might religious beliefs affect society, culture, and politics? The Arabs Western Asia has witnessed some of the most powerful civilizations in history, beginning with the Sumerians and continuing with the Assyrians, the Babylonians, the Persians, and the brief conquests of Alexander the Great. • In the seventh century we see another group of people, the Arabs. • arose in the Arabian Peninsula and spread their influence throughout Western Asia and beyond. • They lived in the Arabian Peninsula (desert - lacking in rivers and lakes.) • The Arabs were nomads who moved constantly to find water and food for their animals. Survival in such a harsh environment was not easy. • the Arabs organized into tribes to help one another. • Each tribe was ruled by a sheikh (SHAYK) who was chosen from one of the leading families by a council of elders. • each tribe was independent, all the tribes were loosely connected to one another. • When settled, they lived as farmers and sheepherders on the rain-fed areas of the Arabian Peninsula. • After the camel was domesticated in the first millennium B.C., the Arabs populated more of the desert. • expanded the caravan trade into these regions. • Towns developed along the routes as the Arabs became major carriers of goods between the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean, where the Silk Road ended. Religion - Life of Muhhammad Early Arabs were polytheistic. • recognized a supreme god named Allah, but they also believed in other tribal gods. • Allah was symbolized by a sacred stone, and each tribe had its own stone. • All tribes, however, worshiped a massive black meteorite, the Black Stone, which had been placed in a central shrine called the Kaaba (KAW • buh). • This shrine is in the city of Makkah (Mecca), which is located in the Arabian Peninsula • The Arabian Peninsula took on a new importance when political unrest in Mesopotamia and Egypt made the usual trade routes in Southwest Asia too dangerous to travel. • A safer route through Makkah flourished. • Towns along thing route benefited from economic Prosperity. The Life of Muhammad Born in Makkah to a merchant family, he was orphaned at five. • grew up to become a caravan manager and married a rich widow named Khadija. • Muhammad became troubled by the growing gap between the generosity of most Makkans and the greediness of the wealthy elite and began to visit the hills to meditate and relfect. • • • • During one of these visits, Muslims believe, Muhammad received revelations from God. According to Islamic teachings, the messages were given by the angel Gabriel. Gabriel told Muhammad to recite what he heard. Muhammad had a knowledge of Jewish and Christian thought and came to believe that Allah had already revealed himself through Moses and Jesus—and thus through the Jewish and Christian traditions. • He believed, however, that the final revelations of Allah were now being given to him. Quran - the holy book of Islam. (Muhammad’s written down revelations.) • The word Islam means "peace through submission to the will of Allah." • Quran contains the ethical guidelines and laws by which the followers of Allah are to live. • Those who practice the religion of Islam are called Muslims. • According to Islam, there is only one God, Allah, and Muhammad is God's prophet. Muhammad returned home after receiving the revelations and reflected on his experience. • His wife urged him to follow Gabriel’s message, and she became the first convert to Islam. • Muhammad then set out to convince the people of Makkah of the truth of the revelations. • The wealthy feared that his attacks on corrupt society would upset the established social and political order. • After three years of preaching, he had only 30 followers. Question – How did this differ from Jesus and Christianity? Muhammad became discouraged by the persecution of his followers, as well as by the Makkans’ failure to accept his message. I • n 622 he and some of his closest supporters left Makkah and moved north to the rival city of Yathrib, later renamed Madinah (Medina; "city of the prophet"). • journey of Muhammad and his followers to Madinah is known as the Hijrah (HIH • jruh). • The year the journey occurred became year 1 in the official calendar of Islam, still in use today. Muhammad soon began to win support from people there as well as from Arabs in the desert • he formed the first community of practicing Muslims. • Muslims saw no separation between political and religious authority. (No separation of church and state.) • Submission to the will of Allah meant submission to his prophet, Muhammad. • Muhammad became both a religious and a political leader. • His political and military skills enabled him to put together a reliable military force to defend himself and his followers. Question: How does this differ from Jesus and Christianity? In 630 Muhammad returned to Makkah with 10,000 men. • The city quickly surrendered, and most of the townspeople converted to Islam • Two years after his return to Makkah, just as Islam was spreading through the Arabian Peninsula, Muhammad died. • All Muslims are strongly encouraged to make a pilgrimage to Makkah, known as the hajj (HAJ), if possible. Teachings of Muhammad / Beliefs of Islam Like Christianity – • Islam is a monotheistic religion. • Allah is the all-powerful being who created the universe and everything in it. • Islam emphasizes salvation and offers the hope of an afterlife. • Those who desire to achieve life after death must subject themselves to Allah’s will. Unlike Christianity• Islam does not believe that its first preacher was divine. • Muhammad is considered a prophet, but he was also a man like other men. • Muslims believe that because humans rejected Allah’s earlier messengers, Allah sent his final revelation through Muhammad. • Quran. • The Quran consists of 114 chapters and is the sacred book of Islam. It is also a guidebook for ethics and a code of law combined. 5 Pillars of Islam 1. Belief – Muslims believe that there is no deity but the one God, and Muhammad is his messenger 2. Prayer - perform prescribed prayers 5 times a day facing Mecca. 3. Charity - give part of their wealth to the poor and (Zakaat) tax 4. Fasting - During Ramadan, Muslims refrain from food and drink from dawn to sunset 5. Pilgrimage - believers are expected to make a pilgrimage to Makkah at least once in their lifetime shari'ah (shuh • REE • uh). a law code drawn up by Muslim scholars after Muhammad’s death provided believers with a set of practical laws to regulate their daily lives based on scholars’ interpretations of the Quran and the example set by Muhammad in his life. regulates all aspects of Muslim life including family life, business practice, government, and moral conduct. • The shari’ah does not separate religious matters from civil or political law. (again no separation of church and state.) • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Believers are expected to follow sound principles for behavior. In addition to the Five Pillars Muslims must practice honesty and justice in dealing with others. Muslims are forbidden to gamble Cannot borrow (no credit cards/loans) eat pork drink alcoholic beverages engage in dishonest behavior. Family life is based on marriage. (Marriage is typically arranged.) Women elect to wear the hijab