Cochlear Implant Presentation
advertisement
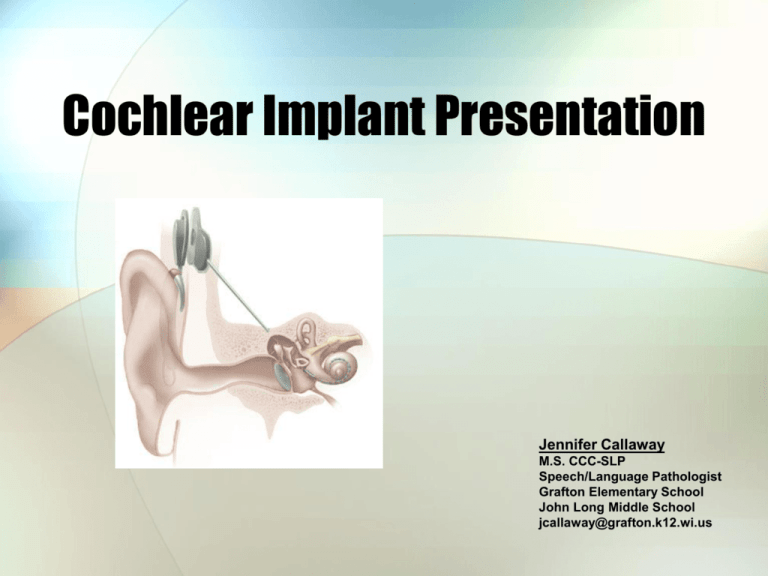
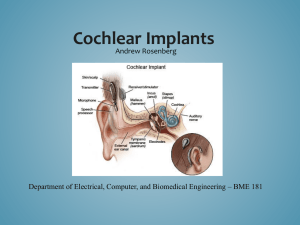
Cochlear Implant Presentation Jennifer Callaway M.S. CCC-SLP Speech/Language Pathologist Grafton Elementary School John Long Middle School jcallaway@grafton.k12.wi.us What is a Cochlear Implant? • A small, complex electronic device • Provides a sense of sound to a person who is profoundly deaf or severely hard of hearing • Implant is surgically placed under the skin behind the ear • An implant has four basic parts: • Microphone • Speech processor • Transmitter and receiver/stimulator • Electrodes Structures of the Ear and the Cochlear Implant •Normal Ear •Middle ear: •Tympanic membrane •Ossicular chain (Malleus, Incus, Stapes) •Inner ear: •Cochlea •Vestibular Nerve •Cochlear Implant •Receiver-stimulator portion of implant is surgically placed beneath the skin •Small opening made into the cochlea and implant electrode is threaded in Who receives Cochlear Implants? • Both children and adults can be candidates for implants. • Approximately 59,000 people worldwide have received implants. (According to the Food and Drug Administration 2002 data) • In the United States: • 13,000 adults have cochlear implants • • 10,000 children have received them What is the cost? About $30,000 to $55,000 The Surgical Procedure • Performed under general anesthesia • Operation takes approximately three hours • Patients generally able to go home the same day of surgery • Patient not able to hear automatically • ‘Hook Up’ Procedure occurs about 1 month post-implant • Takes some time for the brain to get used to the stimulation from the implant • Involves a rehabilitation program Cochlear Implants vs. Hearing Aids • A cochlear implant is very different from a hearing aid. • Hearing aids amplify sound. • Cochlear implants compensate for damaged or non-working parts of the inner ear. • Enable people to detect very soft speech and environmental sounds • Hearing through an implant may sound different from normal hearing Types of Hearing Aids What a Cochlear Implant Can NOT do: • An implant does NOT restore or create normal hearing. • It cannot replicate the same sensitivity or speech understanding in all acoustic environments as a normal hearing person. • Rather, it can give useful auditory understanding of the environment and help the individual to understand speech. Limitations and Special Considerations • Physical Activities: • External portion must be removed during swimming • Voice does not carry well in large outdoor spaces • Poor acoustics in gyms • Sound bounces off walls • Background noise competes with speaker’s voice One Model: Nucleus Esprit 3G • Made by Cochlear • Easy-to-use controls and light weight - only 15 grams with batteries • Batteries: 3 high power zinc-air batteries •Battery life varies • Two programs for different listening environments • Built-in telecoil for access to phones and theaters • Wireless access to Microlink FM • Whisper Setting™ to bring soft sounds closer What does a Cochlear Implant sound like? • http://www.utdallas.edu/~loizou/cimplants/ • • Normal speech Speech via Cochlear Implant (8 channel) Troubleshooting PROBLEM SOLUTION Intermittent buzzing sound * Look for sources of electromagnetic interference including: a. Radio/TV transmission towers b. Security systems c. Some digital cellular phones No sound * Switch processor off for a few seconds and then turn back on again. * Check mode setting * Change all three HIGH POWER 675 batteries and clean battery contacts * Plug in the auxiliary microphone * Check coil using signal check Static * Plug in the auxiliary microphone Muffled or distorted sound * Remove any materials which may be covering the headpiece * Plug in the auxiliary microphone * Change all three batteries with HIGH POWER 675 batteries No sound after getting wet * Leave in Dri-Aid pack overnight * Call your implant center Intermittent sound * Change all three batteries with HIGH POWER 675 batteries * Plug in auxiliary microphone * Check coil using signal check Any Questions? jcallaway@grafton.k12.wi.us References and Images Used • • • • • • • • • • • • • www.thelisteningcenter.com/ www.utdallas.edu/~loizou/cimplants/ www.hei.org/research/depts/aip/audiodemos.htm www.cochlear.com/ www.cochlearimplant.com/ www.phys.unsw.edu.au/ ~jw/Fearnetal.html www.bcig.org/images/news.gif www.childrensspecialists.com/ body.cfm?id=762 www.lhsc.on.ca/ cochlear/hearing.htm www.american-hearing.org/ name/coganpatient.html http://apollo.med.unc.edu/ent/oto-hns/images/CI2.jpg www.chsc.org/images/hastyles_resize.jpg www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/hearing/images/ear_cochlear.asp Purpose of Presentation • Audience: educators, parents, students, professionals • Objective: Answer the following questions: • What is a cochlear implant? • Who benefits from a cochlear implant? • How do they work? • How are hearing aids and cochlear implants different? • What do I do when something goes wrong? • What are good communication techniques?