Public Finance and Public Policy
advertisement

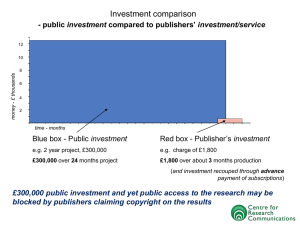
Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan CopyrightGruber © 2010Third Worth Edition Publishers Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 1 of 24 1.1 The Four Questions of Public Finance Why Study Public Finance? 1.2 Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World 1.3 Why Study Public Finance Now? Policy Debates over Social Security, Health Care, and Education 1.4 Conclusion PREPARED BY FERNANDO QUIJANO AND SHELLY TEFFT Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 2 of 24 1.1 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? The Four Questions of Public Finance public finance The study of the role of the government in the economy. four questions of public finance When should the government intervene in the economy? How might the government intervene? What is the effect of those interventions on economic outcomes? Why do governments choose to intervene in the way that they do? Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 3 of 24 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? 1.1 The Four Questions of Public Finance When Should the Government Intervene in the Economy? Market Failures market failure Problem that causes the market economy to deliver an outcome that does not maximize efficiency. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 4 of 24 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? 1.1 The Four Questions of Public Finance APPLICATION The Measles Epidemic of 1989–1991 After the measles vaccine was introduced in 1963, measles cases had become relatively rare in the U.S. by the 1980s. Over the period from 1989 to 1991, however, there was a huge resurgence in measles. It is clear that this outbreak resulted from very low immunization rates among disadvantaged inner-city youths: These unimmunized children were imposing a negative externality on other children who had received their immunizations but for whom immunization may have worn off. The federal government responded to this health crisis in the early 1990s: The government publicly encouraged parents to get their children immunized. The government also paid for the vaccines for low-income families. The result was impressive. Immunization rates, which had never been above 70% before the epidemic, rose to 90% by 1995. Government intervention clearly reduced this negative externality. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 5 of 24 1.1 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? The Four Questions of Public Finance When Should the Government Intervene in the Economy? Redistribution redistribution The shifting of resources from some groups in society to others. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 6 of 24 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? 1.1 The Four Questions of Public Finance How Might the Government Intervene? Tax or Subsidize Private Sale or Purchase One way that the government can try to address failures in the private market is to use the price mechanism, whereby government policy is used to change the price of a good in one of two ways: 1. Through taxes, which raise the price for private sales or purchases of goods that are overproduced, or 2. Through subsidies, which lower the price for private sales or purchases of goods that are underproduced. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 7 of 24 1.1 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? The Four Questions of Public Finance How Might the Government Intervene? Restrict or Mandate Private Sale or Purchase The government can directly restrict private sale or purchase of goods that are overproduced, or mandate private purchase of goods that are underproduced and force individuals to buy that good. Public Provision The government can provide the good directly, in order to potentially attain the level of consumption that maximizes social welfare. Public Financing of Private Provision Governments may want to influence the level of consumption but may not want to directly involve themselves in the provision of a good. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 8 of 24 1.1 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? The Four Questions of Public Finance What Are the Effects of Alternative Interventions? Direct Effects direct effects The effects of government interventions that would be predicted if individuals did not change their behavior in response to the interventions. Indirect Effects indirect effects The effects of government interventions that arise only because individuals change their behavior in response to the interventions. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 9 of 24 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? 1.1 The Four Questions of Public Finance APPLICATION The Congressional Budget Office: Government Scorekeepers The methods and results derived from empirical economics are central to the development of public policy at all levels of government. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) provides Congress with the objective, timely, nonpartisan analyses needed for economic and budget decisions. The CBO increasingly plays a critical role as a “scorekeeper” for government policy debates. Legislative spending proposals that are to become law must first have their costs estimated by the analysts at the CBO. It is not an overstatement to say that the economists who work at the CBO frequently hold the fate of a legislative proposal in their hands. The large price tag that the CBO assigned to the Clinton administration’s plan to reform health care in the United States in 1994 is often cited as a key factor in the defeat of that proposal. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 10 of 24 1.1 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? The Four Questions of Public Finance Why Do Governments Do What They Do? political economy The theory of how the political process produces decisions that affect individuals and the economy. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 11 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World The Size and Growth of Government Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 12 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World The Size and Growth of Government Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 13 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Decentralization A key feature of governments is the degree of centralization across local and national government units—that is, the extent to which spending is concentrated at higher (federal) levels or lower (state and local) levels. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 14 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Spending, Taxes, Deficits, and Debts Federal Revenues and Expenditures, Surplus or Deficit, and Debt, 1930–2008 • For most of the twentieth century, except for the World War II period, federal government tax receipts have kept pace with expenditures. But expenditures have exceeded receipts by several percentage points of GDP on average since the 1970s. The resulting federal government debt is now at about 40% of GDP. Source: Office of Management and Budget (2008), Tables 1.2 and 7.1. (Debt figures for 1930–1939 come from the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Bureau of the Public Debt.) Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 15 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Spending, Taxes, Deficits, and Debts Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 16 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Spending, Taxes, Deficits, and Debts Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 17 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Distribution of Spending The Distribution of Federal and State Expenditures, 1960 and 2007 • This figure shows the changing composition of federal and state spending over time, as a share of total spending. (a) For the federal government, defense spending has fallen and Social Security and health spending have risen. (b) For the states, the distribution has been more constant, with a small decline in education and welfare spending and a rise in health spending. Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, NIPA Table 3.16. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 18 of 24 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? 1.2 Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Distribution of Spending public goods Goods for which the investment of any one individual benefits everyone in a larger group. social insurance programs Government provision of insurance against adverse events to address failures in the private insurance market. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 19 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Distribution of Revenue Sources The Distribution of Federal and State Revenues, 1960 and 2008 • This figure shows the changing composition of federal and state revenue sources over time, as a share of total revenues. (a) At the federal level, there has been a large reduction in corporate and excise tax revenues and a rise in payroll tax revenues. (b) For the states, there has been a decline in property taxes and a rise in income taxes and federal grants. Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, NIPA Tables 3.2 and 3.3. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 20 of 24 1.2 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance? Facts on Government in the United States and around the World Regulatory Role of the Government Another critical role the government plays in all nations is that of regulating economic and social activities: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the labeling and safety of nearly all food products and bottled water, tests cosmetics to ensure their safety, and approves drugs and medical devices to be sold to the public. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is charged with regulating the workplace safety of the 135 million Americans employed at 8.9 million job sites. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulates interstate and international communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is charged with minimizing dangerous pollutants in the air, water, and food supplies. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 21 of 24 1.3 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance Now? Policy Debates over Social Security, Health Care, and Education Social Security, health care, and education are each the subject of debate, with both the “liberal” and “conservative” positions holding differing views in their approach to these major policy issues. Social Security Social Security is the single largest government expenditure program. The financing structure of this program is basically that today’s young workers pay the retirement benefits of today’s old. Health Care There are currently 45 million Americans without any health insurance, about 18% of the non-elderly U.S. population. Projections suggest that health care will consume almost half of our GDP within the next century. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 22 of 24 1.3 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Why Study Public Finance Now? Policy Debates over Social Security, Health Care, and Education Education There is an enormous dissatisfaction with our current educational system, highlighted by the dismal performance of U.S. students on international tests. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 23 of 24 1.4 CHAPTER 1 ■ WHY STUDY PUBLIC ECONOMICS? Conclusion It is clear from the facts presented here that the government plays a central role in the lives of all Americans. It is also clear that there is ongoing disagreement about whether that role should expand, stay the same, or contract. The facts and arguments raised in this chapter provide a backdrop for thinking about the set of public finance issues that we explore in the remainder of this book. Public Finance and Public Policy Jonathan Gruber Third Edition Copyright © 2010 Worth Publishers 24 of 24